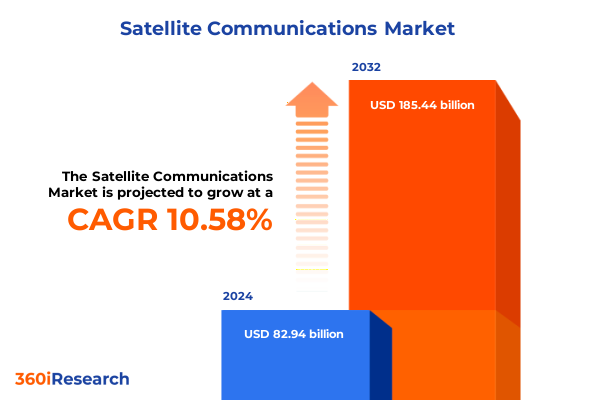
The Satellite Communications Market size was estimated at USD 82.94 billion in 2024 and expected to reach USD 91.16 billion in 2025, at a CAGR of 10.58% to reach USD 185.44 billion by 2032.
Executive summary introduction to a rapidly transforming satellite communications ecosystem shaped by convergence, orbits, and service innovation
Satellite communications is undergoing a profound transformation as space, telecommunications, cloud, and data‑driven technologies rapidly converge. What was once a domain dominated by a small number of large geostationary platforms has evolved into a complex ecosystem of low Earth and medium Earth constellations, high‑throughput payloads, sophisticated ground station equipment, and service‑centric business models. This changing environment is redefining how governments, defence organizations, commercial enterprises, maritime operators, transport providers, and space science institutions design, deploy, and consume connectivity.
At the heart of this evolution lies a clear shift from hardware‑centric thinking to integrated solutions that combine equipment such as amplifiers, antennas, receivers, transmitters, and very small aperture terminals with managed broadcasting, fixed satellite, mobile satellite, and transaction services. As satellite imagery and synthetic aperture radar feed into cloud platforms and analytics pipelines, satellite communications is increasingly seen not only as a connectivity layer but as a critical enabler of real‑time intelligence and automation across industries.
This executive summary provides a structured view of how these forces are reshaping the satellite communications landscape. It highlights the most important technological and commercial inflection points, examines the implications of orbit selection and frequency band strategies, and explores how evolving end‑user requirements are influencing market channels from direct sales and distributors to e‑commerce and retail. In doing so, it aims to equip senior decision‑makers with the context required to set priorities, align investments, and position their organizations for long‑term resilience.
As the sector moves into a new phase characterized by proliferating constellations, direct‑to‑device concepts, and deeper integration with terrestrial 5G networks, understanding the interplay between policy, tariffs, supply chains, and innovation has never been more critical. The following sections delve into the most consequential shifts, regional nuances, and strategic considerations shaping satellite communications today.
Transformative shifts in satellite communications driven by orbital diversification, advanced payloads, service models, and network convergence
The satellite communications landscape is being reshaped by a series of transformative shifts that span orbits, technologies, and service models. One of the most visible changes is the move from reliance on a relatively small number of geostationary platforms to a hybrid environment that combines geostationary orbit with proliferating low Earth and medium Earth constellations, and, to a lesser extent, high Earth orbits for specialized missions. Low Earth systems promise lower latency and global coverage, while geostationary assets continue to deliver reliable, wide‑area broadcasting and backbone capacity. This orbital diversification is driving new thinking in network design, capacity planning, and regulatory coordination.
Complementing these orbital shifts is a rapid acceleration in payload and ground segment capabilities. High‑throughput satellites equipped with advanced transponders are paired with agile ground station equipment and very small aperture terminal solutions that can dynamically allocate bandwidth, prioritize traffic, and support complex service‑level agreements. At the same time, synthetic aperture radar and high‑resolution satellite imagery are increasingly integrated into cloud‑native workflows, enabling continuous monitoring for sectors such as agriculture, energy, maritime surveillance, and disaster management.
On the equipment side, innovation in amplifiers, antennas, receivers, and transmitters is enabling more compact, energy‑efficient, and software‑defined architectures. Flat‑panel electronically steered antennas are expanding mobility use cases for aviation, maritime, and land‑based transport, while advanced receivers and transmitters are supporting higher‑order modulation schemes that enhance spectral efficiency across C, Ku, Ka, and L bands. These developments allow operators to extract more capacity from finite spectrum resources and tailor performance to specific applications.
Service models are undergoing equally significant change. Beyond traditional fixed satellite services and broadcasting services, there is a pronounced rise in mobile satellite services, managed services, and transaction‑based offerings that align pricing with usage. Enterprises increasingly demand end‑to‑end solutions that bundle capacity, ground equipment, cybersecurity, and application‑layer support, shifting value creation from pure bandwidth provision to outcome‑oriented service delivery. Managed services, in particular, are gaining traction among organizations that prefer predictable performance without overseeing network complexity.
Another major shift is the growing emphasis on integration with terrestrial networks, including 5G and emerging non‑terrestrial network standards. Satellite backhaul for remote cell sites, direct‑to‑device concepts using standard handsets, and hybrid architectures that blend satellite and terrestrial paths are blurring traditional boundaries. This convergence is prompting closer collaboration between satellite operators, mobile network operators, and cloud service providers, while also raising important questions around spectrum sharing, interference management, and service orchestration.
Finally, commercial and government end‑users are redefining expectations around resilience, security, and sustainability. Defence and government agencies seek assured communications with anti‑jam and anti‑interference capabilities, while commercial sectors such as maritime, transport, and space science require flexible, mission‑tailored connectivity. Environmental considerations are also gaining prominence, influencing satellite design, orbital debris mitigation strategies, and ground infrastructure energy efficiency. Together, these transformative shifts are propelling satellite communications into a more dynamic, interconnected, and service‑centric era.
Cumulative impact of evolving United States tariffs through 2025 on satellite communications supply chains, costs, and long‑term strategic choices
The cumulative impact of United States tariff policies through 2025 is emerging as a critical factor in the satellite communications ecosystem, particularly as supply chains become more global and complex. Tariffs applied to electronic components, semiconductors, specialty metals, and manufacturing equipment used in amplifiers, antennas, receivers, transmitters, and ground station equipment have contributed to rising input costs and increased volatility in lead times. For many stakeholders, these measures intersect with ongoing trade tensions involving key manufacturing hubs, shaping sourcing strategies and partnership decisions.
For satellite operators and equipment manufacturers, tariffs on imported components can translate into higher capital expenditure for both space and ground segments. Organizations relying on overseas suppliers for antennas, transponders, synthetic aperture radar payloads, and very small aperture terminals may face higher procurement costs or be compelled to reconfigure their supplier portfolios. In certain cases, companies are exploring nearshoring or onshoring options to mitigate tariff exposure, which in turn reshapes the geography of manufacturing and testing facilities.
Service providers that deliver broadcasting services, fixed satellite services, mobile satellite services, managed services, and transaction‑based offerings are also feeling the downstream effects. As equipment costs rise, there is pressure on pricing models and margins, especially in segments where competition from terrestrial alternatives constrains the ability to pass cost increases to customers. This is particularly evident in applications such as asset tracking, data backup and recovery, and voice communication where satellite competes or interworks with cellular and fiber‑based solutions.
Tariff uncertainty further complicates long‑term planning for constellation deployment across low Earth, medium Earth, high Earth, and geostationary orbits. Launch vehicles, satellite buses, and certain propulsion and power subsystems may be subject to trade measures that influence procurement strategies and alliance structures. While some organizations benefit from protective policies that favor domestic manufacturing and encourage research and development investment, others face higher barriers when integrating foreign‑sourced technologies into U.S.‑regulated systems.
Moreover, tariffs interact with export controls, security reviews, and spectrum policy to create a multifaceted regulatory environment. Defence and government end‑users, who often prioritize sovereign capability and secure supply chains, may welcome measures that stimulate domestic industry, even if they introduce near‑term cost pressures. Conversely, commercial and maritime operators seeking cost‑efficient global connectivity can find themselves navigating a more fragmented supplier landscape and uneven pricing across regions.
By 2025, the overall effect of these tariff measures is not purely inflationary; it is also strategic. Companies that proactively adjust their sourcing, diversify suppliers, negotiate long‑term contracts, and invest in modular designs that can accommodate component substitutions are better positioned to manage regulatory shifts. In contrast, organizations that treat tariffs as short‑lived anomalies may face equipment bottlenecks, delayed projects, and reduced flexibility in orbit selection, frequency band deployment, and application development.
In this environment, effective risk management requires cross‑functional collaboration between procurement, engineering, legal, and corporate strategy teams. The interplay between tariffs and other policy instruments underscores the importance of scenario planning, sensitivity analysis, and careful evaluation of where to allocate manufacturing capacity, research resources, and strategic partnerships along the satellite communications value chain.
Key segmentation insights reveal how components, orbits, technologies, bands, applications, end‑users, and channels shape satcom strategy
The satellite communications market exhibits pronounced differentiation along several key segmentation dimensions, each of which has distinct strategic implications. From a component perspective, the balance between equipment and services defines how value is created and captured. Equipment such as amplifiers, antennas, receivers, and transmitters remains fundamental to network build‑out, yet the momentum is clearly shifting toward service‑oriented models. Broadcasting services, fixed satellite services, mobile satellite services, managed services, and transaction services collectively form a layered service stack in which recurring revenue, performance guarantees, and application‑specific offerings play an increasingly central role.
Orbit type is another critical lens for understanding market dynamics. Geostationary orbit continues to underpin wide‑area broadcasting and backbone connectivity, offering predictable coverage and established regulatory frameworks. Low Earth orbit is driving innovation in low‑latency broadband and global coverage, particularly for mobility and remote enterprise sites, while medium Earth orbit is carving out niches in navigation, high‑reliability communications, and specialized enterprise networks. High Earth orbit, though less widely deployed, supports scientific missions and niche communications applications, rounding out a multi‑orbit environment in which hybrid architectures become more attractive.
Technology segmentation highlights the breadth of capabilities converging within satellite communications. Ground station equipment now incorporates software‑defined radios, virtualized network functions, and intelligent gateway orchestration, while SATCOM equipment at the user edge is becoming more compact and versatile. Satellite imagery and synthetic aperture radar support a growing array of data‑centric services, from environmental monitoring to security and logistics optimization. Transponders and very small aperture terminals remain essential building blocks for connectivity, but their roles are increasingly embedded within integrated solutions that tie together hardware, software, and cloud‑based analytics.
Frequency band choices across C, Ku, Ka, and L bands significantly influence system performance, cost structures, and regulatory considerations. C band offers robustness and is well‑suited for certain broadcasting and critical infrastructure use cases, whereas Ku and Ka bands enable higher data throughput and are often favored for broadband connectivity and backhaul. L band, with its resilience and penetration characteristics, is particularly important for mobile satellite services, including maritime, aviation safety, and land‑based mission‑critical communications. Strategic operators are designing portfolios that leverage multiple bands to balance coverage, capacity, and resilience across user segments.
Application‑level segmentation reveals how satellite communications is embedded into business and mission workflows. Asset tracking and monitoring rely on global, low‑power connectivity that can follow cargo, vehicles, and remote infrastructure. Broadcasting remains a core application, though it is increasingly complemented by on‑demand and IP‑based media distribution. Data backup and recovery harness satellite as a resilience layer to protect against terrestrial network failures. Voice communication, whether enabled by satellite phones or VoIP services delivered over satellite links, continues to support safety‑of‑life communications, remote workforce operations, and emergency response.
End‑user segmentation underscores the diversity of demand drivers. Commercial enterprises seek scalable, cost‑effective connectivity to enable digital transformation, while defence organizations prioritize secure, resilient communications with advanced encryption and anti‑jamming capabilities. Government users often focus on public safety, disaster response, and national infrastructure monitoring. Maritime operators require reliable coverage across sea lanes, ports, and offshore assets, whereas the space science community depends on satellite links for mission telemetry, deep space communication, and data downlink. Transport providers across aviation, rail, and road increasingly view satellite connectivity as a differentiator for both operational efficiency and passenger experience.
Finally, market channel segmentation reveals how solutions reach end‑users. Direct sales allow providers to build deep relationships with strategic accounts and complex projects, while distributors extend reach into specialized verticals and regional markets. E‑commerce is emerging as an important route for standardized terminals, subscription packages, and smaller contracts, reflecting growing commoditization in certain segments. Retail channels, particularly in developing markets, play a role in broadening access to satellite phones and entry‑level connectivity solutions. Understanding the interplay among these channels helps suppliers optimize coverage, pricing, and customer engagement strategies across the full spectrum of satellite communications offerings.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Satellite Communications market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Component Type
- Orbit Type
- Technology
- Frequency Band
- Application
- End-User
- Market Channel
Regional insights across the Americas, EMEA, and Asia‑Pacific highlight distinct regulatory, demand, and innovation patterns in satellite communications
Regional dynamics exert a powerful influence on how satellite communications technologies are adopted, regulated, and monetized. In the Americas, a combination of advanced infrastructure, strong demand from defence and government users, and a vibrant commercial ecosystem drives continual innovation. The United States plays a central role in constellation deployment, launch services, and ground segment development, while Canada and Latin American countries increasingly leverage satellite for rural broadband, disaster resilience, and enterprise connectivity in hard‑to‑reach locations. Regulatory environments across the region are generally supportive of spectrum allocation for both fixed and mobile satellite services, although coordination with terrestrial 5G deployments requires ongoing dialogue.
The Americas also see significant uptake in applications such as asset tracking, maritime and aviation connectivity, data backup and recovery, and broadcasting. Oil and gas, mining, agriculture, and logistics operators rely on satellite coverage to maintain operations in remote areas, while public safety agencies utilize satellite phones and managed services to ensure communications continuity. Market channels often blend direct sales for large defence and government contracts with distributor networks and e‑commerce platforms that support small and medium‑sized enterprises seeking ground station equipment, SATCOM terminals, and service subscriptions.
Across Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, satellite communications trends are shaped by a mix of mature and emerging markets. In Western Europe, there is a strong emphasis on integrating satellite with terrestrial broadband and 5G networks, including initiatives aimed at secure government communications and resilient infrastructure. The Middle East showcases extensive investment in broadcasting, mobility, and government programmes that rely on geostationary and high‑throughput systems, while parts of Africa continue to depend on satellite as a primary means of internet access and connectivity for education, healthcare, and financial inclusion.
In this broad region, regulatory frameworks can vary considerably, with some countries advancing progressive satellite licensing regimes and others maintaining more restrictive policies. Frequency band usage in C, Ku, Ka, and L bands reflects diverse priorities, from broadcasting and media hubs in the Middle East to enterprise and community connectivity projects across Africa. Market channels range from large integrators that handle complex defence and government projects to local distributors and retail outlets that make satellite phones and entry‑level services available to remote populations.
Asia‑Pacific presents another distinctive set of dynamics, driven by rapid economic growth, extensive coastlines, and significant investments in space programmes. Countries across the region are expanding their roles as satellite manufacturers, launch service providers, and operators of constellations in low Earth, medium Earth, and geostationary orbits. Satellite communications underpins maritime trade, aviation corridors, disaster management, and connectivity for remote islands and mountainous regions. As governments prioritize digital transformation and resilience, satellite imagery and synthetic aperture radar are being integrated into national security, environmental monitoring, and infrastructure planning initiatives.
In Asia‑Pacific, competition and collaboration coexist, with domestic and international players offering ground station equipment, SATCOM solutions, and managed services tailored to local conditions. Spectrum policy is evolving to accommodate both traditional fixed satellite services and emerging mobile satellite services and direct‑to‑device concepts. Market channels reflect a mix of direct relationships with large telecom operators and broadcasters, distributor networks serving enterprise and government segments, and growing use of e‑commerce platforms to reach smaller organizations and consumers. Collectively, these regional nuances highlight the need for tailored strategies that reflect local regulatory landscapes, application priorities, and partnership ecosystems.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Satellite Communications market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Key company insights highlight how operators, manufacturers, and service providers compete through innovation, integration, and ecosystem alliances
The competitive landscape in satellite communications is characterized by a diverse mix of satellite operators, equipment manufacturers, ground segment specialists, service providers, and emerging data‑driven platforms. Established operators with fleets in geostationary orbit continue to invest in high‑throughput payloads and flexible digital architectures, while newer entrants focus on low Earth and medium Earth constellations that offer low‑latency broadband and global coverage. This multi‑orbit environment encourages differentiated positioning, with some companies emphasizing global reach and capacity, others prioritizing resilience and security, and still others targeting niche applications such as maritime, aviation, remote enterprise, or earth observation.
On the equipment front, manufacturers of amplifiers, antennas, receivers, transmitters, and very small aperture terminals are competing to deliver more compact, energy‑efficient, and software‑defined solutions. Advances in flat‑panel antenna technology and intelligent modems enable seamless handoff between beams, satellites, and even constellations, which is particularly valuable for mobility segments. Ground station equipment providers, meanwhile, are increasingly integrating virtualized network functions, cloud connectivity, and automation into their offerings, allowing operators to scale capacity dynamically and manage services more efficiently.
Service providers that package broadcasting services, fixed satellite services, mobile satellite services, managed services, and transaction‑based offerings are differentiating through customer experience, vertical specialization, and integration capabilities. Some focus on turnkey solutions for sectors such as defence, government, maritime, and transport, bundling connectivity with cybersecurity, application management, and regulatory compliance support. Others target commercial enterprises with self‑service portals, usage‑based billing, and APIs that facilitate integration with existing IT and operational technology systems.
Companies specializing in satellite imagery and synthetic aperture radar are expanding their influence by moving up the value chain into analytics, decision support, and data fusion with other sensors. This evolution is particularly relevant for customers in space science, agriculture, environmental monitoring, and security, who increasingly seek actionable insights rather than raw data. Partnerships with cloud providers and analytics firms are becoming a core element of competitive strategy, enabling faster delivery of insights and more scalable business models.
Market channels further shape competitive dynamics. Direct sales organizations build deep relationships with large defence and government buyers, broadcasters, and global enterprises, often engaging in long procurement cycles and complex system integration projects. Distributors and value‑added resellers extend reach into regional markets and specialized niches, while e‑commerce platforms make standardized terminals, satellite phones, and subscription packages more accessible to smaller organizations and individuals. Retail presence remains important in certain markets where in‑person demonstration and support are critical to adoption.
Amid this intense competition, successful companies are those that combine technological innovation with operational excellence and strong ecosystem partnerships. They invest in modular architectures that support future upgrades, maintain robust supply chains that can withstand regulatory and tariff disruptions, and cultivate long‑term relationships with customers through transparent service‑level commitments. As the industry evolves, the ability to collaborate across traditional boundaries-linking satellite networks with terrestrial telecom providers, cloud platforms, and application developers-will increasingly define competitive advantage.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Satellite Communications market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- Airbus SE
- ASELSAN A.Ş.
- AST & Science, LLC
- AVL List GmbH
- Campbell Scientific, Inc.
- Communications & Power Industries LLC
- Comtech Telecommunications Corp.
- EchoStar Corporation
- Eutelsat Communications SA
- General Dynamics Corporation
- Gilat Satellite Networks Ltd.
- Globalstar, Inc.
- Holkirk Communications Ltd.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Indra Sistemas, S.A.
- Intellian Technologies, Inc.
- Iridium Communications Inc.
- L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- Ligado Networks
- Maxar Solutions LLC
- Network Innovations Inc.
- Qualcomm Incorporated
- SES S.A.
- SKY Perfect JSAT Holdings Inc.
- Space42 PLC
- ST Engineering
- Telesat Corporation
- Thales Group
- The Marlink Group
- Viasat, Inc.
- Viking SatCom
Actionable recommendations for satellite communications leaders to strengthen portfolios, supply chains, partnerships, and go‑to‑market execution
Industry leaders operating in satellite communications can take several concrete steps to translate the trends outlined in this report into effective strategies. One priority is to reassess portfolio balance across equipment and services. Organizations that have historically focused on hardware such as amplifiers, antennas, receivers, transmitters, ground station equipment, and very small aperture terminals should explore deeper integration with managed services, mobile satellite services, broadcasting offerings, and transaction‑based models. This shift can create more resilient revenue streams and align value propositions with customer expectations for end‑to‑end solutions rather than standalone components.
In parallel, decision‑makers should revisit orbit and frequency band strategies in light of evolving application requirements. Combining geostationary, low Earth, medium Earth, and high Earth deployments can improve coverage, latency, and resilience, particularly when integrated into unified network management frameworks. Strategic use of C, Ku, Ka, and L bands enables tailored solutions for broadcasting, backhaul, asset tracking, mission‑critical voice communications, and data backup and recovery, helping to differentiate offerings in competitive markets and satisfy stringent service‑level commitments.
Supply chain resilience requires particular attention, given the cumulative impact of tariffs, export controls, and shifting regulatory priorities. Leaders should map dependencies across key components and subsystems, from satellite imagery payloads and synthetic aperture radar to transponders and user terminals, and identify opportunities to diversify suppliers, regionalize production, or adopt modular designs that allow for component substitution. Establishing longer‑term contracts with strategic suppliers and investing in inventory buffers for critical parts can further reduce exposure to disruptions.
Another actionable area is closer integration with terrestrial networks and digital platforms. Collaborating with mobile network operators, cloud providers, and application developers can unlock new use cases and revenue streams, especially in sectors such as transport, maritime, commercial enterprise, government, defence, and space science. By embedding satellite connectivity as a seamless extension of existing IT and operational technology infrastructures, providers can strengthen customer loyalty and decrease the perceived complexity of satellite adoption.
From a go‑to‑market perspective, optimizing market channels is essential. Direct sales teams should be equipped with deep vertical expertise to address complex defence, government, and large enterprise opportunities, while distributors can be empowered to penetrate regional and sectoral niches with tailored offerings. E‑commerce platforms can be leveraged for standardized SATCOM equipment, satellite phones, and subscription services, complemented by retail presence where hands‑on demonstration enhances trust and understanding. Aligning incentives across channels will help avoid conflict and ensure consistent customer experiences.
Finally, industry leaders should institutionalize strategic planning processes that incorporate scenario analysis around policy changes, spectrum allocation, and technological disruption. Regularly revisiting assumptions about demand in the Americas, Europe, the Middle East, Africa, and Asia‑Pacific, as well as monitoring advancements in direct‑to‑device technologies and non‑terrestrial network standards, will support more agile decision‑making. By combining robust internal governance with external partnerships and data‑driven insight, organizations can navigate uncertainty while positioning themselves to capture emerging opportunities in satellite communications.
Robust research methodology integrates value‑chain analysis, policy review, competitive assessment, and regional perspectives
The research underpinning this executive summary is built on a rigorous, multi‑layered methodology designed to capture the complexity of the satellite communications ecosystem. At its core is a structured analysis of the full value chain, spanning space segment assets in geostationary, low Earth, medium Earth, and high Earth orbits; ground segment components such as amplifiers, antennas, receivers, transmitters, ground station equipment, and very small aperture terminals; and the broad spectrum of services, including broadcasting services, fixed satellite services, mobile satellite services, managed services, and transaction‑based offerings. This holistic approach ensures that interdependencies across components, orbits, technologies, frequency bands, applications, end‑users, and market channels are fully reflected.
To inform qualitative insights, the study synthesizes information from a wide range of publicly available sources, company disclosures, regulatory filings, technical standards documents, and industry association publications. Particular attention is given to developments in satellite imagery, synthetic aperture radar, transponders, and emerging non‑terrestrial network frameworks, as well as to evolving policies related to spectrum allocation, export controls, and tariffs that affect satellite communications supply chains. By triangulating these inputs, the analysis aims to minimize bias and highlight both areas of consensus and points of divergence across stakeholders.
A significant emphasis is placed on understanding regional nuances across the Americas, Europe, the Middle East, Africa, and Asia‑Pacific. The research reviews how each region’s regulatory environment, economic structure, infrastructure development, and security priorities influence demand for applications such as asset tracking, broadcasting, data backup and recovery, and voice communications via satellite phones and VoIP services. This regional perspective is essential for interpreting how global trends manifest in local markets and for identifying where policy or investment shifts are likely to have the greatest impact.
In addition to secondary research, the methodology incorporates structured analysis of competitive strategies employed by satellite operators, equipment manufacturers, ground segment providers, and service integrators. This includes examination of product and service portfolios, partnership announcements, investment patterns, and go‑to‑market approaches across direct sales, distributors, e‑commerce, and retail channels. The objective is to capture how companies are responding to technological advances, regulatory changes, and evolving customer expectations.
Analytical frameworks are used to organize and interpret the data, including value chain mapping, technology readiness assessments, and risk analysis related to supply chains and regulatory shifts. Qualitative scenario exploration is applied to consider potential trajectories for multi‑orbit architectures, integration with terrestrial networks, and the influence of tariffs and other policy tools on sourcing and manufacturing decisions. While the study deliberately avoids making explicit market size or forecast statements in this summary, it does provide a robust foundation for understanding the structural forces that will shape strategic decisions in satellite communications.
Throughout, the research maintains a focus on transparency and traceability. Assumptions underlying key insights are clearly articulated, and alternative interpretations are considered where evidence is ambiguous or evolving. This disciplined methodological approach enables decision‑makers to apply the findings with confidence, adapting them to their specific organizational context, risk tolerance, and strategic objectives.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Satellite Communications market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Satellite Communications Market, by Component Type
- Satellite Communications Market, by Orbit Type
- Satellite Communications Market, by Technology
- Satellite Communications Market, by Frequency Band
- Satellite Communications Market, by Application
- Satellite Communications Market, by End-User
- Satellite Communications Market, by Market Channel
- Satellite Communications Market, by Region
- Satellite Communications Market, by Group
- Satellite Communications Market, by Country
- United States Satellite Communications Market
- China Satellite Communications Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 19]
- List of Tables [Total: 1749 ]
Conclusion underscores satellite communications as a cornerstone of resilient digital infrastructure amid technological and policy change
Satellite communications stands at a pivotal juncture, shaped by the convergence of multi‑orbit architectures, advanced payload and ground technologies, and increasingly sophisticated service models. The interplay between geostationary, low Earth, medium Earth, and high Earth orbits, combined with diverse frequency bands from C and Ku to Ka and L, is unlocking new possibilities for applications ranging from broadcasting and asset tracking to data backup, recovery, and mission‑critical voice communications. At the same time, broader forces such as tariff policies, export controls, and evolving spectrum regulations are exerting a profound influence on supply chains, investment decisions, and competitive positioning.
Across the Americas, Europe, the Middle East, Africa, and Asia‑Pacific, satellite communications is emerging as a cornerstone of digital resilience and economic development. Commercial enterprises, defence and government agencies, maritime operators, space science organizations, and transport providers increasingly depend on satellite connectivity, imagery, and synthetic aperture radar to achieve strategic objectives. Market channels are diversifying, with direct sales, distributors, e‑commerce platforms, and retail outlets working in concert to reach a wide spectrum of users, from large international organizations to remote communities.
Against this backdrop, success for industry participants will hinge on the ability to align portfolios of equipment and services with evolving customer needs. Providers that integrate amplifiers, antennas, receivers, transmitters, ground station equipment, transponders, and very small aperture terminals into coherent solutions alongside managed services, mobile satellite services, and transaction‑based offerings will be best positioned to capture value. Likewise, organizations that proactively manage tariff and regulatory risks, build resilient supply chains, and collaborate across the satellite, terrestrial telecom, and cloud ecosystems will enjoy a durable competitive advantage.
Ultimately, the satellite communications sector is moving beyond its traditional role as a niche connectivity option for remote environments. It is becoming an essential part of mainstream digital infrastructure, underpinning everything from national security and disaster response to global commerce and environmental stewardship. By understanding the structural shifts, regional variations, and strategic levers highlighted in this executive summary, decision‑makers can chart a course that not only navigates current complexities but also anticipates the next wave of innovation and policy evolution.
The organizations that act decisively today-reassessing orbit and band strategies, enhancing service portfolios, strengthening partnerships, and institutionalizing informed risk management-will be the ones that define the next chapter of satellite communications. Those that delay may find themselves constrained by legacy architectures, fragile supply chains, and missed opportunities in a market that is becoming more central to global connectivity with each passing year.
Secure decisive satellite communications intelligence by engaging directly with Ketan Rohom to unlock the full value of this report
In a market defined by rapid technological change, intensifying competition, and evolving regulatory dynamics, timely access to rigorous intelligence separates industry leaders from followers. A comprehensive satellite communications study equips stakeholders with structured insight into component choices from amplifiers, antennas, receivers, and transmitters to complex service portfolios that span broadcasting services, fixed and mobile satellite connectivity, managed offerings, and transaction services. It also clarifies how orbit strategies across geostationary, high Earth, medium Earth, and low Earth constellations can be aligned with application needs such as broadcasting, asset tracking, data backup and recovery, and mission‑critical voice communication via satellite phones and VoIP services.
Beyond the technology itself, the report sheds light on how ground station equipment, SATCOM terminals, satellite imagery, synthetic aperture radar, transponders, and very small aperture terminal solutions are converging with C, Ku, Ka, and L band deployments to reshape commercial, government, defence, maritime, space science, and transport operations worldwide. Moreover, it explains how direct sales, distributors, e‑commerce, and retail channels each influence pricing power, customer intimacy, and speed of adoption, enabling executives to optimize go‑to‑market strategies.
To translate this intelligence into actionable strategy, readers are invited to connect with Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing. Ketan can guide you through the most relevant parts of the report for your organization’s priorities, clarify methodological choices, and help you structure license options that ensure decision‑makers across regions, business units, and functional teams can rely on a single, consistent evidence base. By engaging directly, you shorten the time from insight to execution and ensure that investments in satellite communications infrastructure, services, partnerships, and market development are grounded in objective, field‑tested research.
To purchase the full market research report or discuss tailored deliverables, contact Ketan Rohom and initiate a focused conversation on how this intelligence can support your near‑term decisions and long‑range planning. Acting now ensures that your organization does not merely respond to shifts in satellite communications but anticipates them, shaping a more resilient and competitive position in the years ahead.

- How big is the Satellite Communications Market?
- What is the Satellite Communications Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




