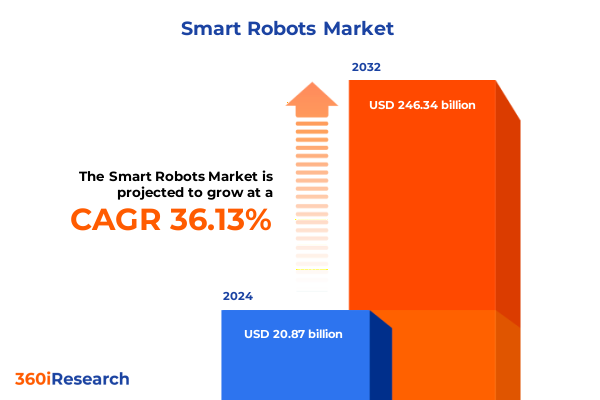
The Smart Robots Market size was estimated at USD 28.29 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 38.34 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 36.22% to reach USD 246.34 billion by 2032.
An authoritative framing of how advancing autonomy, AI integration, and cross‑industry adoption are redefining the role and value of smart robots
The robotics landscape is at a decisive inflection point where advancing autonomy, stronger AI integration, and shifting trade dynamics are reshaping how organizations conceive of automation. Adoption is no longer limited to traditional factory automation; intelligent robots are migrating into logistics networks, healthcare settings, inspection and maintenance tasks, and domestic environments. These changes are being driven by converging forces: more capable perception and control stacks, improved energy and actuator technologies, and software-first approaches that reduce the cost and time required to deploy complex behaviors.
Across multiple industries, operational leaders are re-evaluating processes that were once considered too variable or too human-centric for robotics. As robots gain the ability to learn from demonstrations, generalize across contexts, and operate safely alongside people, the value proposition shifts from pure cost-substitution to higher throughput, improved quality, and new service models. This introduction positions the remainder of the summary to examine how technological breakthroughs, trade policy shifts, and end-user segmentation collectively determine the near-term choices that vendors and adopters must make.
How software‑first intelligence, proliferating physical form factors, and outcome‑based commercial models are fundamentally reshaping robotics value chains
The landscape transformation driving smart robots today is anchored in a set of structural shifts that alter where and how value is created. First, intelligence is migrating from hardware to software: modular perception stacks, vision-language-action models, and foundation-model approaches are enabling robots to learn versatile skills from a combination of simulation, teleoperation data, and human demonstrations. This paradigm reduces bespoke engineering per task, shortening customization cycles and enabling more frequent field updates.
Second, form factors and deployment archetypes are diversifying. Cobots that safely share space with humans are maturing in factories and small-scale operations, while mobile manipulators and humanoid prototypes are expanding the remit of automation into warehousing and last‑mile operations. These variations are not mere product differences; they change the economics of integration and the roles of systems integrators, software providers, and third-party service operators.
Third, business models are evolving: consumption-based offerings, robotics-as-a-service, and outcome-linked commercial structures are lowering adoption barriers, particularly among small and medium enterprises. Financing and subscription models spread up‑front costs, shift risk profiles, and align vendor incentives to uptime and continuous improvement. Finally, ecosystem dynamics are shifting toward platform thinking. Companies that combine hardware, robust developer tooling, and scalable fleet orchestration stand to capture disproportionate value because customers increasingly prize seamless updates, fleet-level analytics, and predictable lifecycle management over point-product capabilities. These combined shifts demand fresh strategic thinking from product leaders, channel partners, and enterprise buyers alike.
Assessing the operational and strategic consequences of cumulative U.S. tariff measures through 2025 on robotics procurement, supply chain resilience, and innovation pathways
The accumulation of United States tariff actions through 2025 has introduced a new layer of operational and strategic complexity for robotics manufacturers and adopters. Policy moves aimed at reducing strategic dependencies and addressing national security concerns have translated into higher landed costs and longer procurement lead times for components that remain concentrated in foreign manufacturing hubs. These dynamics have forced supply chain managers to re-evaluate sourcing strategies, re-map supplier tiers, and accelerate contingency planning to preserve project timelines and margin structures.
In practice, the tariff environment has had two material effects. On hardware margins and procurement certainty it has increased price volatility for critical components such as sensors, actuators, and specialized control electronics, creating upward pressure on program costs and complicating capital approval for automation projects. On strategic sourcing it has catalyzed a reallocation of investment: some suppliers are electing near‑shore or regional manufacturing to avoid tariff exposure, while others are pursuing redesigns that replace tariff‑sensitive components with alternatives sourced from tariff‑excluded geographies. These twin responses are productive in the medium term-by diversifying risk-but they introduce near-term friction: qualification cycles lengthen, certification and quality assurance workloads climb, and integration partners face tighter margins.
Beyond direct cost effects, tariffs have also impacted the innovation pipeline. Startups and equipment manufacturers that previously relied on low-cost, globally sourced subassemblies face tougher break‑even thresholds, which can delay prototype-to-production ramps. At the same time, public incentives and industrial policy programs intended to strengthen domestic semiconductor and component production have accelerated some domestic capabilities, creating a countervailing momentum toward localized supply chains and strategic partnerships. Collectively, these forces are not eliminating international collaboration, but they are reconfiguring it: more phased regionalization, closer supplier relationships, and a higher premium on traceability and compliance.
A layered segmentation analysis linking robot types, applications, end‑users, components, autonomy levels, and distribution channels to practical product and go‑to‑market decisions
Segmentation clarifies where technical choices, go‑to‑market approaches, and value capture differ across the smart robots landscape. When the market is viewed by type, industrial-class systems such as articulated, cartesian, cylindrical, delta, and SCARA robots are optimized for high‑throughput, repetitive tasks that require precision, whereas service robots split between domestic devices like lawn mowers, vacuum cleaners, and window cleaners and professional units that focus on cleaning, inspection, logistics, and medical assistance. This diversity means product roadmaps and aftermarket strategies vary substantially: industrial robot programs emphasize cycle time, payload, and deterministic control, while service robots prioritize perception, human interaction, and regulatory compliance.
Looking at application, segmentation across assembly and handling, inspection and testing, packaging and palletizing, painting, and welding highlights how vertical knowledge shapes automation outcomes. Assembly and handling use cases further subdivide by sector such as automotive, electronics, food and beverage, metal fabrication, and pharmaceutical, each of which carries unique throughput, hygiene, and traceability requirements. Inspection and testing solutions frequently require tight integration with vision and analytics software, while welding variants-arc, laser, plasma, and spot-demand specific end‑effector designs and thermal management approaches.
End user segmentation across automotive, electronics and semiconductors, food and beverage, healthcare, and logistics underscores different procurement cycles and funding models. Healthcare adoption pathways reflect hospital, pharmacy, and R&D needs, where safety, regulatory validation, and clinical integration dominate; logistics divides between distribution and warehousing, where scale, interoperability, and fleet orchestration determine competitive advantage. Component segmentation-hardware, services, and software-reveals where margin pools are shifting; software and services increasingly drive recurring revenue and long-term customer relationships. Degree of autonomy-fully autonomous versus semi‑autonomous-matters for system validation and liability frameworks, with fully autonomous platforms facing higher certification burdens but offering larger operational upside. Finally, distribution channels through direct sales versus indirect routes such as channel partners, distributors, and e‑commerce alter adoption velocity: direct models suit complex, high‑value deployments while indirect channels accelerate democratized access through standardized packages and local support networks. This layered segmentation should inform product prioritization, partner selection, and service design.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Smart Robots market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Type
- Component
- Degree Of Autonomy
- Application
- End User
- Distribution Channel
How regional supply dynamics, regulatory priorities, and customer buying behaviors across the Americas, EMEA, and Asia‑Pacific should shape differentiated market strategies
Regional dynamics shape platform strategies, manufacturing footprints, and partnership models in ways that directly affect commercial returns. In the Americas, investment patterns are influenced by reshoring incentives, capital availability, and strong demand in automotive, aerospace, and logistics. Buyers in this region tend to favor integrated solutions with clear service pathways and local support networks, which favors vendors that can combine regional manufacturing or trusted distributor relationships with robust software ecosystems.
Europe, Middle East & Africa presents a mosaic of regulatory focus, energy transition goals, and advanced manufacturing pockets. European customers are often motivated by sustainability targets and product traceability, which raises the importance of energy efficiency, lifecycle analytics, and recyclable materials in procurement decisions. Regulations around safety, data privacy, and labor interaction also shape deployment choices, increasing the need for certified interoperability and demonstrable compliance.
Asia‑Pacific continues to lead in volume and rapid deployment, driven by large manufacturing hubs and rapid retail and logistics expansion. That region’s ecosystem offers deep component supply chains and strong integrator capabilities, which accelerates innovation cycles but also intensifies competition on price and speed. For multinational vendors, these regional differences suggest a hybrid approach: build shared core software and control IP while tailoring hardware configurations, service tiers, and channel models to the specific procurement and regulatory realities of each region.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Smart Robots market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
An assessment of competitive archetypes showing why incumbents, software‑first challengers, and integrated service models are dictating winner‑takes‑more dynamics
Competitive dynamics in the smart robots domain are characterized by a mixture of legacy industrial incumbents, specialized cobot vendors, software platform providers, and an expanding set of nimble, venture-backed entrants. Legacy manufacturers still command strong positions where deterministic performance and scale matter, drawing on deep OEM relationships and extensive service networks. Conversely, newer entrants and software-first players challenge on ease of use, speed of deployment, and developer ecosystems, often winning pilots that incumbents struggle to execute quickly.
Partnerships and open ecosystems are becoming decisive. Companies that provide flexible SDKs, simulation tools, and robust fleet management capabilities are creating defensible moats because enterprise customers prize the ability to integrate robotics into existing digital thread and operations technology stacks. Similarly, companies that bundle hardware with predictable service-level agreements and financing options are displacing single-sale models in segments where uptime equals revenue. Given these dynamics, competitive advantage increasingly attaches to end‑to‑end propositions: hardware that is easy to procure and maintain, software that scales across sites, and services that minimize integration risk.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Smart Robots market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- ABB Ltd
- DENSO WAVE INC.
- FANUC Corporation
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- KUKA Aktiengesellschaft
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Nachi-Fujikoshi Corp
- Nuro, Inc.
- OMRON Corporation
- Seiko Epson Corporation
- Skydio, Inc.
- Tesla, Inc.
- Yaskawa Electric Corporation
Practical, high‑impact strategic moves for product, supply chain, commercial model, and partner enablement that protect margins and accelerate adoption
Leaders who intend to secure market advantage must align investments across four pragmatic domains: product architecture, supply resilience, commercial models, and partnerships. On product architecture, prioritize modularity and upgradability so customers can incrementally add capabilities without full system replacement. This reduces churn and opens pathways for recurring revenue through software feature releases. In parallel, invest in explainable perception and safety frameworks to shorten validation cycles and accelerate approvals in safety‑sensitive environments.
For supply resilience, adopt a supplier portfolio strategy that combines local sourcing for strategic components with geographically diversified tiers for commoditized parts. Additionally, embed tariff and regulatory scenario planning into procurement cadence and product roadmaps so hardware choices remain robust to abrupt policy shifts. Commercially, broaden offer sets to include subscription and outcome-based contracts for customers that need flexibility, and create transparent total cost of ownership frameworks to make ROI conversations frictionless. Finally, cultivate an ecosystem of certified integrators and channel partners to scale installations while preserving quality; invest in partner enablement, standardized reference architectures, and co‑funded pilot programs to accelerate adoption. Together, these recommendations translate market intelligence into concrete actions that de‑risk scale and create durable revenue streams.
A concise explanation of the research approach combining practitioner interviews, technical reviews, scenario testing, and segmentation validation to produce actionable findings
The research synthesis behind this executive summary combines primary interviews with systems integrators, end‑user operations leaders, and component suppliers, together with a structured review of industry literature and technical disclosures. Insights emerged from comparative analysis of deployment case studies across manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare environments, backed by technology deep dives into perception stacks, actuation trends, and autonomy frameworks. Scenario testing was applied to tariff and supply chain permutations to examine plausible responses and timelines for manufacturers and adopters.
Methodologically, the approach prioritized triangulation: qualitative narratives from practitioners were cross‑checked against technical whitepapers and regulatory announcements to reduce single‑source bias. Segmentation matrices were validated through vendor product catalogs and integration partner portfolios to ensure that type, application, and channel distinctions reflected current commercial realities. Finally, recommendations were stress‑tested with CFO and operations stakeholder perspectives to ensure feasibility, budgetary realism, and alignment to adoption constraints.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Smart Robots market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Smart Robots Market, by Type
- Smart Robots Market, by Component
- Smart Robots Market, by Degree Of Autonomy
- Smart Robots Market, by Application
- Smart Robots Market, by End User
- Smart Robots Market, by Distribution Channel
- Smart Robots Market, by Region
- Smart Robots Market, by Group
- Smart Robots Market, by Country
- United States Smart Robots Market
- China Smart Robots Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 18]
- List of Tables [Total: 2544 ]
A concluding synthesis emphasizing the imperative to align product agility, supply resilience, and partner ecosystems to convert robotics potential into measurable operational advantage
In conclusion, the smart robots landscape presents a pivotal blend of accelerating technical capability and evolving commercial and policy risks. Advances in learning paradigms, modular software, and fleet orchestration make more ambitious automation feasible, while trade and regulatory shifts require deliberate supply and commercial strategies. Decision-makers who balance product agility with supply resilience, and who adopt flexible commercial frameworks, will be positioned to capture outsized value as deployments broaden across industries.
The path forward is not uniform; sectoral differences in compliance, throughput, and labor interaction demand tailored adoption plans. Nonetheless, the common imperative is clear: integrate robotics strategy with broader digital transformation programs, treat supply chain and tariff exposure as a strategic variable, and prioritize partner ecosystems that can reduce friction at scale. Doing so will convert technological opportunity into measurable operational advantage.
Secure immediate access to the comprehensive smart robots market report and tailored briefing options by contacting our Associate Director for expedited enterprise licensing
Acquire the full market research report through a single direct contact to secure executive briefings, bespoke data extracts, and priority engagement that will accelerate commercial decisions. The report purchase unlocks access to proprietary segmentation matrices, vendor scorecards, and regionally tailored implementation playbooks that translate market intelligence into executable plans for sales, operations, and product strategy. For a confidential discussion about licensing options, enterprise seats, or custom consulting add-ons, contact Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing, to arrange a tailored proposal and expedited delivery of the materials you need to operationalize findings and capture first-mover advantage.

- How big is the Smart Robots Market?
- What is the Smart Robots Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




