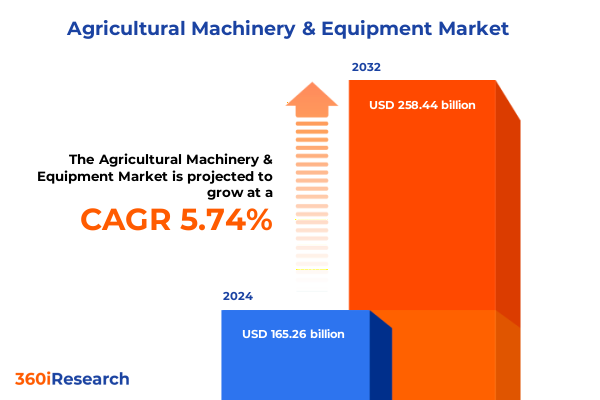
The Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market size was estimated at USD 165.26 billion in 2024 and expected to reach USD 174.41 billion in 2025, at a CAGR of 5.74% to reach USD 258.44 billion by 2032.
A concise orientation to the agricultural machinery and equipment landscape that connects trade policy, input economics, and technology imperatives for decision makers
The agricultural machinery and equipment sector is at an inflection point where structural shifts in trade policy, input economics, and technology adoption are reshaping competitive advantage. This introduction frames the primary forces that market leaders must navigate: a re‑intensified tariff regime that alters the cost of key metal inputs and imported subassemblies, accelerating electrification and automation trends that change product architectures, and evolving end‑user behaviors that favor flexible ownership and precision services over one‑time capital purchases. Taken together, these dynamics make product design, supplier footprint, and distribution strategy as critical as traditional product performance metrics.
Readers will find in the following sections an integrated view that links policy changes to manufacturing economics and customer demand patterns. The narrative establishes why near‑term tactical choices-sourcing decisions, pricing adjustments, and inventory management-must be balanced with medium‑term strategic moves such as localizing high‑content components, re‑platforming modular systems for electrification, and developing financing and service offerings that preserve utilization and residual value for both commercial and smallholder farm customers. The goal is to prepare leaders with a pragmatic orientation: how to stabilize operations now while repositioning for resilience and growth amid continued policy and market volatility.
How electrification, precision services, and geopolitical shifts are jointly reconfiguring product design, supply footprints, and commercial business models across the sector
The landscape for agricultural machinery is being transformed by converging technological advances, evolving ownership models, and geopolitical policy shifts. Electrification of powertrains and the spread of precision ag and autonomy are no longer experimental; they are driving design changes that reduce dependency on conventional drivetrains while increasing reliance on high‑value electronics and specialized battery supply chains. At the same time, the industry is moving from a pure equipment sale model toward outcomes‑based offerings in which telematics, uptime guarantees, and flexible rental or lease arrangements become central to customer value propositions.
Geopolitical re‑alignment and trade policy are accelerating supplier diversification and on‑shoring conversations. Manufacturers that previously optimized for lowest landed cost are now re‑engineering bill‑of‑materials and logistics routes to reduce exposure to tariff shocks and export restrictions. This is creating a bifurcated pace of change: incumbents with deep dealer networks and capital to invest in retooling will pursue localized procurement and incremental electrification, whereas nimble new entrants will exploit modular architectures and cloud‑native service platforms to capture share in precision services and aftermarket upgrades. The operational implication is clear: product roadmaps must be re‑sequenced to prioritize components and subsystems most sensitive to tariff and supply risks, while commercial models must evolve to monetize recurring services and data‑driven agronomic outcomes. Transition costs and timing will vary by equipment type, with high‑steel content items such as larger tractors and harvesting machines facing different exposure than precision irrigation modules or sensor‑heavy implements.
Evaluating the cumulative commercial and operational consequences of expanded United States steel, aluminum, and trade measures on agricultural machinery value chains in 2025
Recent U.S. tariff policy changes have materially altered the input cost and trade calculus for agricultural machinery manufacturers, suppliers, and customers. The reinstatement and expansion of tariffs on steel and aluminum, together with broader tariff actions and the prospect of additional measures tied to critical minerals, are increasing the cost and uncertainty of metal‑intensive components and downstream assemblies. This has immediate consequences for manufacturers’ margin structures, procurement strategies, and pricing behavior, and repercussions for farmers who face higher acquisition costs and tighter equipment finance markets. The net effect is an environment in which incumbents must balance absorbing costs, raising prices, or pursuing more aggressive localization strategies.
Industry associations and equipment manufacturers have publicly cautioned that higher metal tariffs and the removal of prior exemptions will push input prices higher and compress equipment affordability for many operators. Independent analyses show that expanding tariff coverage to derivative and downstream products increases the value of goods subject to additional duties and raises the pressure on sectors that consume significant volumes of steel and aluminum. At the same time, trade friction can trigger retaliatory measures from trading partners, with export‑dependent agribusinesses and manufacturers exposed to demand shocks in key markets. Firms with high exposure to imported electronic subsystems also face separate risks from export controls and supply‑chain bottlenecks for specialized components. Adapting to this environment requires a multi‑pronged approach that includes re‑pricing strategies, near‑term hedging against raw‑material volatility, supplier diversification, and targeted reshoring where economic and scale conditions permit.
Segment‑level exposure and opportunity mapped by type, automation, power source, application, ownership, end user, and distribution dynamics for targeted strategy
Segmentation analysis reveals where exposure and opportunity are concentrated across types, automation levels, power sources, drive configurations, applications, ownership modalities, end users, and distribution channels. By type, heavy, metal‑intensive categories such as combine harvesters and large tractors exhibit the greatest sensitivity to tariffs on steel and aluminum, while irrigation systems and seeding implements, which integrate a higher proportion of plastics, polymers, and electronics, are more sensitive to shifts in electronics supply chains and semiconductor constraints. Within haying and forage machinery, balers and mowers face different margin dynamics because of differing steel gauge and component complexity. Tractors segmented by horsepower bands experience distinct replacement cycles and financing dynamics: compact and mid‑range power categories typically have shorter replacement intervals and stronger penetration of non‑traditional ownership models, whereas high‑horsepower units are capital‑intensive and therefore more exposed to cost inflation and changing tariff regimes.
Automation level reshapes product economics as well. Fully automatic and semi‑automatic machines carry higher embedded software and sensor content, increasing exposure to global electronics supply and to trade measures that affect electronic subsystems; conversely, manual units have lower electronic content but higher steel content per unit. Power source segmentation highlights a transition risk: diesel‑operated platforms remain dominant in many markets, but electric‑operated designs are accelerating, creating a shifting demand profile for batteries, rare earth magnets, and electrified drivetrains. Drive type segmentation matters for harvesting equipment, where four‑wheel drive and two‑wheel drive configurations have different cost structures and are sold into different field‑size and operator segments. Application segments-fertilizing and pest control, land development, post‑harvest operations, and threshing and harvesting-map to different aftermarket service intensities and dealer network requirements. Ownership type and end‑user segmentation show that leased equipment and finance‑backed purchases often permit higher technology adoption because of lower upfront cost barriers, and commercial farms more readily absorb advanced precision packages than smallholder farms, which prioritize affordability and simplicity. Distribution channel dynamics indicate that OEM channels are the locus for product launches and integrated service offerings, while aftermarket channels are essential for lifecycle services, retrofits, and second‑hand equipment flows.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Agricultural Machinery & Equipment market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Type
- Automation Level
- Power Source
- Drive Type
- Mobility
- Application
- End User
- Ownership Type
- Use Case
- Sales Channel
Regionalized strategies for manufacturing, sourcing, and commercialization across the Americas, Europe Middle East & Africa, and Asia‑Pacific to safeguard competitiveness
Regional dynamics create differentiated risk and opportunity profiles for manufacturers, suppliers, and dealers. In the Americas, integrated supply chains, a dense dealer network, and proximity to major steel and aluminum producers provide advantages for near‑shoring and fast response, but the same region is sensitive to reciprocal tariffs and commodity price volatility that can quickly erode domestic demand. Europe, the Middle East and Africa present a mosaic of regulatory standards and financing conditions where electrification and emissions rules are driving product upgrades, while varied access to capital for farmers creates uneven adoption of premium technologies. Asia‑Pacific is a mixed environment in which large, fast‑growing agricultural markets coexist with robust manufacturing clusters; here, alternative sourcing and regional supplier networks offer resilience but also intense competition and price pressure from regionally based OEMs and contract manufacturers.
Each region therefore requires a tailored commercial playbook. In the Americas, firms will prioritize dealer finance programs, strategic local content investments, and inventory strategies that mitigate tariff pass‑through. In EMEA, compliance, modular adaptation to emissions and safety standards, and partnerships with equipment rental and service providers become central. In Asia‑Pacific, supplier ecosystem management and competitive differentiation through low‑cost localized manufacturing or high‑value service bundles will determine success. Understanding these regional contrasts is critical to deciding where to localize production, which components to source regionally, and how to structure channel incentives to protect margins while maintaining market access.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Agricultural Machinery & Equipment market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
How scale, component control, dealer capabilities, and aftermarket specialization are defining competitive advantage in a higher‑cost and more regulated industry
The competitive landscape continues to be shaped by a mix of global OEMs, regional manufacturers, specialist component suppliers, and aftermarket specialists, each adjusting to a more volatile input and policy environment. Large OEMs with scale and diversified manufacturing footprints can exploit procurement leverage and move production between plants to mitigate tariff exposure, while mid‑tier and niche players face acute pressure on margins and may accelerate partnerships, joint ventures, or captive sourcing arrangements to survive. Component suppliers that provide high‑value electronics, powertrain modules, battery packs, and precision sensors will become strategic bottlenecks; firms that secure long‑term supply agreements or invest in allied manufacturing capacity will gain disproportionate advantage.
Dealership and distribution networks are also pivotal. Dealers that enhance their service capabilities, offer flexible financing, provide data‑driven maintenance programs, and manage used‑equipment flows will retain customer loyalty even if list prices rise. Independent aftermarket players that specialize in retrofits, conversion kits for electrification, and localized repair services can capture steady revenue streams as operators extend equipment life to defer capital outlays. Strategic alliances between OEMs and fintech providers to deliver embedded finance and residual‑value guarantees will be a critical differentiator for new equipment sales, particularly in markets where tariff‑driven price increases challenge affordability.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Agricultural Machinery & Equipment market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- AGCO Corporation
- Alamo Group Inc.
- Amazonen-Werke H. Dreyer GmbH & Company KG
- ARGO SpA
- Bucher Industries AG
- Caterpillar Inc.
- Changzhou Dongfeng Agricultural Machinery Group Co.,Ltd.
- China National Machinery Industry Corporation Ltd.
- CLAAS KGaA mbH
- CNH Industrial N.V.
- Daedong Corporation
- Deere & Company
- Delaval International AB
- Doosan Group
- Escorts Limited
- Excel Agriculture
- FMWORLD Agricultural Machinery
- Greaves Cotton Ltd.
- GRIMME Landmaschinenfabrik GmbH & Co. KG
- Hitachi Construction Machinery Co., Ltd.
- Iseki & Co., Ltd.
- JC Bamford Excavators Ltd.
- Kinze Manufacturing, Inc.
- KISANKRAFT LIMITED
- Kubota Corporation
- Kuhn SAS
- KZ Rostselmash LLC
- LEMKEN GmbH & Co. KG by Agrovission Company
- Lindsay Corporation
- Mahindra & Mahindra Limited
- Maschinenfabrik Bernard KRONE GmbH & Co.KG
- MASCHIO GASPARDO S.p.a.
- MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD.
- Netafim Limited
- PÖTTINGER Landtechnik GmbH
- Romi S.A.
- SDF Group
- Shivagrico Implements Ltd.
- Sonalika Group
- TAFE Motors and Tractors Limited
- Valmont Industries, Inc.
- Vermeer Corporation
- VST Tillers Tractors Limited
- Väderstad Group
- Weichai Lovol Intelligent Agricultural Technology CO., LTD
- Yanmar Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Zetor Tractors A.S.
- Zoomlion Agriculture Machinery Co., Ltd.
Practical near‑term triage and medium‑term strategic moves to protect margins, accelerate electrification, and convert product sales into recurring service value
Actionable recommendations for industry leaders begin with immediate triage and extend to structural repositioning. In the near term, firms must conduct bill‑of‑materials sensitivity analyses to identify the highest‑exposure components to steel, aluminum, and electronics tariffs and prioritize either short‑term hedging or supplier substitution for those items. Pricing strategies should be transparent and segmented by customer type and channel; where possible, protect dealer margins while using targeted finance offers to preserve placement rates. Operationally, build buffer inventories for critical subassemblies and secure multi‑source agreements to reduce single‑supplier and single‑market dependencies.
Medium‑term moves include selective localization of high‑content components where scale and regulatory incentives justify capital investment, and accelerating partnerships for battery, power‑electronics, and sensor supply to support electrification roadmaps. Revise product roadmaps to modularize platforms so that a common chassis can accept different power sources and automation stacks, thereby shortening development cycles and improving resilience to parts shortages. Commercially, expand lease and service‑based offerings to convert one‑time hardware revenue into recurring income, and enhance digital service capabilities to justify premium pricing. Finally, actively engage with policy makers and industry coalitions to shape exclusion processes, seek targeted relief for critical inputs, and ensure that trade remedy measures include practical carve‑outs for agriculture‑critical components. These combined actions will reduce near‑term shock while positioning firms to capture upside as markets stabilize.
A pragmatic mixed‑methods research approach combining primary interviews, policy analysis, and component bill‑of‑materials decomposition to validate strategic insights
Research methodology for this analysis combined a multi‑disciplinary approach that integrates primary interviews, policy analysis, component‑level bill‑of‑materials review, and secondary industry sources. Primary inputs included structured interviews with senior procurement and R&D leaders at equipment manufacturers, dealer group executives, and senior aftermarket service providers to validate exposure pathways and commercial responses. Policy and regulatory review relied on official proclamations, tariff schedules, and agency guidance to map the direct legal effects on input tariffs and trade flows. Component and cost exposure were assessed by decomposing representative machine bills of materials, estimating metal and electronics content, and benchmarking variant sourcing strategies.
Complementary secondary research included industry association statements, consulting analyses, and reputable news and trade reporting to triangulate trends such as dealer finance penetration, adoption curves for electrification, and the pace of automation. Scenario analysis was used to test combinations of tariff severity, retaliatory measures, and supply‑chain interruptions, with sensitivity checks to highlight the high‑leverage decisions that materially affect margins and time‑to‑market. Throughout, the methodology prioritized cross‑validation: claims derived from interviews were checked against public filings and official proclamations to ensure factual consistency and practical relevance for commercial decision makers.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Agricultural Machinery & Equipment market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market, by Type
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market, by Automation Level
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market, by Power Source
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market, by Drive Type
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market, by Mobility
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market, by Application
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market, by End User
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market, by Ownership Type
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market, by Use Case
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market, by Sales Channel
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market, by Region
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market, by Group
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market, by Country
- United States Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market
- China Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 22]
- List of Tables [Total: 2703 ]
Synthesis of strategic priorities that reconcile near‑term tariff shocks with long‑term technology and commercial imperatives for durable competitiveness
In conclusion, the agricultural machinery and equipment sector must navigate an era of compounded disruption where tariff policy, supply‑chain reconfiguration, and rapid technology adoption interact to reshape competitive dynamics. Tariff escalations and the removal of exemptions increase the cost of metal‑intensive manufacturing and create incentives to rethink sourcing footprints, while electrification and automation introduce new component dependencies and commercial pathways. The firms best positioned to succeed will be those that can rapidly reprice and re‑engineer product lines, secure diversified component supply, expand dealer and aftermarket capabilities, and convert hardware offerings into recurring service relationships that preserve customer economics.
Ultimately, the pathway to resilience is both operational and commercial. Tactical decisions-inventory buffers, hedging, and selective supplier substitutions-buy time, but strategic investments in modular design, localized high‑value manufacturing, and service ecosystems create durable advantage. Companies that act decisively to align procurement, product development, and go‑to‑market models with the new trade and technology realities will not only defend margins but can also capture share as competitors wrestle with transition costs and market uncertainty.
Access the comprehensive market report and engage a senior sales representative to translate tariff, supply chain, and segmentation insights into prioritized business actions
For executives ready to convert insight into impact, acquiring the full market research report will provide the detailed intelligence you need to act decisively. The report contains granular segmentation matrices, regional supply‑chain diagnostics, tariff sensitivity modeling, supplier and component maps, citeable regulatory texts, primary interview summaries, and stepwise implementation playbooks that translate strategy into operational choices.
Engaging with the report equips commercial leaders with the evidence base to prioritize sourcing changes, adjust dealer and aftermarket strategies, calibrate price and finance options, and defend margins through contract redesign and targeted localization efforts. Because the agricultural machinery ecosystem is capital‑intensive and highly integrated, access to component cost drivers, alternative supplier lists, and scenario-tested tariff passthrough assumptions materially shortens reaction time and reduces execution risk.
To purchase the research report and speak to a senior sales representative about enterprise licensing, customization, or a briefing tailored for executive and board reviews, reach out to Ketan Rohom (Associate Director, Sales & Marketing). He will coordinate the purchase, arrange a tailored walkthrough of the findings most relevant to your organization, and schedule a private briefing to align the report outputs with your commercial and operational priorities.

- How big is the Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market?
- What is the Agricultural Machinery & Equipment Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




