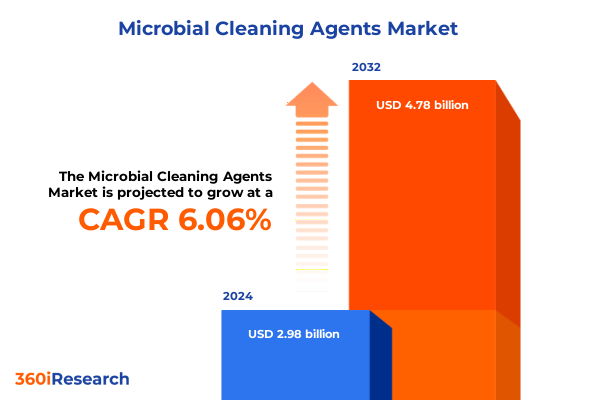
The Microbial Cleaning Agents Market size was estimated at USD 3.16 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 3.35 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 6.09% to reach USD 4.78 billion by 2032.
A concise industry introduction describing microbial cleaning agents, their biological mechanisms, and why they are becoming a distinct toolkit for modern cleaning challenges
Microbial cleaning agents are emerging from the intersection of microbiology, formulation chemistry, and sustainability-driven product design to become a distinct class of cleaning technology. These solutions leverage enzymes and living or inactivated microbes to break down soils, neutralize odours, and in some cases establish a surface microbiome that suppresses harmful biofilms over time. Unlike traditional, purely chemical formulations, microbial cleaning approaches emphasize targeted biochemical activity-amylases, proteases, lipases, and cellulases catalyse the decomposition of starches, proteins, lipids, and cellulose respectively-while probiotic or Bacillus-based blends can colonize surfaces transiently to reduce recontamination risk. The technology is now intersecting demand trends for safer indoor environments, lower-temperature laundry cycles, and formulations with improved biodegradability.
As a strategic framing, this introduction positions microbial cleaning agents not as a single product category but as a toolkit of biological mechanisms (enzymatic catalysis, competitive colonization, and biofilm disruption) that manufacturers and end users can deploy across household, commercial, and industrial contexts. The commercial conversation is shifting from whether biological cleaners can work to which combinations of microbes, enzymes, and delivery formats best fit a particular use case and regulatory environment. That shift makes early, evidence-based supplier and product decisions essential for procurement, R&D, and marketing teams aiming to capture first-mover advantages in a crowded sustainability narrative.
How sustainability, biotechnology advances, regulatory scrutiny, and evolving distribution channels are jointly reshaping the future of cleaning technologies
The landscape for cleaning technologies is undergoing several concurrent, transformative shifts that will determine supply, adoption, and product design over the next five years. First, sustainability and lifecycle thinking are forcing formulators to replace high-toxicity chemistries with biodegradable enzymes and biological actives that reduce wastewater impact and occupational hazards. This is being pursued by incumbent hygiene firms and agile biotech entrants alike, and it is prompting co‑development partnerships between ingredient specialists and cleaning brands.
Second, advances in industrial biotechnology-enzyme engineering, stabilized liquid enzyme formats, and precision strain selection for Bacillus and other benign genera-are increasing product performance while lowering costs of integration into both liquid and solid formats. These innovations make enzymatic stain removal, low-temperature efficacy, and prolonged odour control practical at scale. Third, regulatory attention and label‑claim scrutiny are intensifying: products that imply infection control or persistent antimicrobial action increasingly face pesticide or antimicrobial regulatory review in multiple jurisdictions, which shifts the burden onto manufacturers to validate claims scientifically and to engage with regulators early.
Finally, route-to-market dynamics are evolving. E‑commerce and subscription models accelerate adoption for household consumers, while contract procurement and hygiene service providers lead uptake in healthcare, hospitality, and industrial cleaning. Taken together, these trends create an environment where formulation science, regulatory planning, and channel strategy must be coordinated; companies that align R&D roadmaps with clear regulatory strategies and channel pilots will disproportionately capture growth opportunities.
Practical implications of 2025 tariff modifications on ingredient sourcing, HTS classification, and supply chain risk management for biological cleaning formulations
Recent U.S. tariff policy developments have altered the calculus for international sourcing, supplier diversification, and cost management across ingredient-intensive categories, and cleaning ingredient manufacturers must interpret these changes through the lens of HTS classification and origin. Broadly speaking, Section 301 tariff actions and subsequent modifications announced in 2024 and implemented into 2025 raised additional duties on multiple product groups and created an environment where import costs and administrative compliance burdens increased for many chemical and industrial inputs. The tariff actions were implemented as HTS‑specific measures and included both permanent adjustments and a series of time‑limited exclusions for certain items; importers are therefore advised to treat tariff exposure as a function of HTS classification and country of origin rather than as a categorical industry‑wide levy.
For microbial cleaning agents specifically, the commercial impact is twofold. First, manufacturers that import finished enzyme preparations, formulated probiotic concentrates, or specialized carriers from countries targeted by tariffs may experience higher landed costs, longer procurement lead times, and intermittent exclusion windows that require active management. Second, auxiliary inputs-packaging materials, stabilizers, and certain surfactants-may also be affected by tariff changes, raising total supply chain cost even when the biological active is domestically sourced. To navigate this environment, supply chain managers should prioritize three activities: map critical inputs to their precise HTS subheading and recent USTR notices, pursue alternative sourcing or nearshoring where feasible, and document exclusion eligibility proactively. These steps reduce the chance that sudden duty changes will compress margins or force reactive price increases for commercial and household customers.
Detailed segmentation insights connecting enzyme and microbial types to product forms, application requirements, end‑user behaviours, and channel economics
Segmentation analysis identifies the technical building blocks and commercial pathways that determine where microbial cleaning agents add the most value. From a raw‑material perspective, the market is studied across enzyme families and microbial genera including amylases for starch breakdown, proteases for protein soils, lipases for fatty residues, cellulases for fabric care, Pseudomonas for specialized biodegradation tasks, and Bacillus and Lactobacillus strains which are commonly used in probiotic or competitive colonization approaches. Each enzyme and microbial type brings distinct performance characteristics and handling requirements, and formulators design blends to address multi‑soil scenarios.
Product form matters: liquid formats permit immediate activity and are increasingly used where rapid application and continuous activity are required, whereas solid formats-including powders and tablets-offer supply chain advantages in transport efficiency and shelf stability; both forms remain strategically important for different channels and end‑use cases. Application segmentation clarifies the most common functional requirements: degreasing demands aggressive lipid‑targeting actives and surfactant compatibility, laundry detergent applications prioritize enzyme stability across pH and temperature ranges, odour control emphasizes sustained biodegradation of volatile compounds and neutralization rather than masking, and stain removal calls for targeted catalytic activity against specific soil chemistries. End‑user segmentation highlights divergent buyer requirements: commercial sectors such as educational institutions, healthcare facilities, and hospitality chains evaluate products across cleaning and remediation use cases and prioritize efficacy, safety, and cost of labour; households typically prioritize ease of use, fragrance profile, and perceived safety for pets and children; industrial buyers focus on process integration, equipment compatibility, and regulatory compliance for remediation tasks. Sales channels also influence product specification and packaging; offline retail-specialty stores and supermarkets & hypermarkets-drives consumer-facing packaging and sensory cues, while online stores enable subscription and refill models that change packaging economics and product lifetime considerations.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Microbial Cleaning Agents market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Source
- Product Form
- Application
- End-User
- Sales Channel
How geographic markets differ in regulation, procurement priorities, ingredient availability, and the pace of adoption for biological cleaning technologies
Regional dynamics shape technology adoption, regulatory obligations, and commercial priorities for microbial cleaning agents. In the Americas, demand patterns reflect a mature consumer market that values demonstrable performance, clear green claims, and convenience. North American buyers have shown strong interest in enzyme-enabled low‑temperature solutions and in probiotic approaches that reduce reliance on harsh disinfectants, but manufacturers must negotiate a detailed regulatory landscape where label claims implying persistent antimicrobial action can trigger additional oversight.
Europe, Middle East & Africa presents a mix of strict chemical and packaging regulations-particularly in the European Union-alongside advanced commercial pilots for synbiotic and probiotic cleaners in institutional settings. Regulatory emphasis on biodegradability and restrictions on certain persistent chemicals drives formulators toward biological alternatives more rapidly in many European markets. The Asia‑Pacific region is heterogeneous: parts of the region move quickly on household demand for novel formats and fragrances, while advanced industrial adopters in select markets are integrating enzymes for food‑processing and wastewater remediation. Across regions, adoption speed correlates with regulatory clarity, availability of local enzyme and strain supply, and procurement preferences in institutional procurement, but every region shows growing interest in formulations that reconcile safety, efficacy, and sustainability.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Microbial Cleaning Agents market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Corporate strategies and partnership dynamics showing how ingredient innovators and system providers are co‑creating enzyme and probiotic cleaning solutions
Company strategies in this segment reflect two parallel plays: ingredient innovation and platform commercialization. Leading enzyme and bioscience suppliers are expanding liquid enzyme offerings and novel strain portfolios to make biological actives easier to integrate into household and industrial formulations; these moves lower technical barrier to entry for brand owners and accelerate piloting. At the same time, major hygiene and cleaning system providers are partnering with biotech firms to bring synbiotic, probiotic, and enzyme‑enhanced product lines to market and to pilot performance in high‑risk institutional settings.
This dynamic has produced a competitive architecture where specialty biotechnology firms and enzyme houses supply high‑value actives, and system providers and brand owners take responsibility for formulation, regulatory positioning, and global rollouts. The most commercially notable activity in 2024–2025 includes launches of probiotic/synbiotic product ranges by global household and institutional brands, and expansions of liquid enzyme portfolios from industrial ingredient suppliers seeking to capture growth in both liquid and concentrated formats. These strategic moves lower the adoption friction for downstream manufacturers and create new white‑label and co‑development opportunities for contract manufacturers and ingredient distributors.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Microbial Cleaning Agents market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- AB Enzymes GmbH
- Acuro Organics Limited
- Advanced Microbial Solutions, Inc.
- Alfanzyme Group
- American Biosystems, Inc
- Antozyme Biotech Pvt Ltd
- Apex International
- Aumenzymes
- Aumgene Biosciences
- BASF SE
- Creative Biogene
- Croda International PLC
- Elite Chemicals
- Enviroway Bioscience
- Envirozyme
- Infinita Biotech Private Limited
- International Flavors & Fragrances Inc.
- Kerry Group PLC
- Novonesis A/S
- Om Bio Sciences
- Qingdao Vland Biotech Inc.
- Scientific and Technical Limited
- TEX BIOSCIENCES PVT LTD
- The Procter & Gamble Company
- Ultreze Enzymes
Actionable recommendations for R&D, regulatory planning, sourcing resilience, and channel pilots to accelerate commercial adoption and minimize operational risk
Industry leaders should adopt an integrated, action‑oriented playbook that links formulation science, regulatory strategy, and supply chain resilience. At the formulation level, prioritize enzyme and microbial blends that solve specific, documented end‑user pain points-evidence of sustained odour reduction for hospitality settings, textile‑care benefits for premium laundry, or biofilm control in healthcare contexts-so marketing claims are rooted in measurable performance. Concurrently, embed regulatory review and label‑claim planning into product roadmaps early; products that imply disinfectant or persistent antimicrobial action risk classification under pesticide or antimicrobial rules, so engage toxicologists and regulatory counsel at the proof‑of‑concept stage to avoid costly relabeling or delayed market access.
From a sourcing perspective, map critical inputs to HTS codes and monitor tariff notices closely; maintain at least two validated suppliers for enzyme concentrates or microbial strains, and evaluate nearshoring or regional manufacturing partnerships to reduce tariff volatility and freight risk. For go‑to‑market execution, pilot across a mix of channels: specialty retail and supermarkets for consumer trial and sensory positioning, subscription online models for refill and sustainability propositions, and direct contracts with cleaning service providers to scale institutional adoption. Finally, invest in third‑party validation-peer‑reviewed studies or independent laboratory testing-to substantiate claims and to build trust with procurement functions in healthcare and hospitality, where risk aversion and compliance pressures are highest.
A transparent description of data sources, primary interviews, regulatory mapping, and analytical steps used to build the study’s evidence base and caveats
This research synthesizes primary interviews, public‑domain regulatory sources, scientific literature, and proprietary synthesis to ensure conclusions are evidence‑based and operationally relevant. Primary data collection included structured interviews with procurement and R&D leads across commercial cleaning services, manufacturers of household cleaning products, and ingredient suppliers; those conversations informed supplier risk matrices, channel adoption constraints, and priority product attributes. Secondary research drew on regulatory guidance from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and the Office of the U.S. Trade Representative for interpretation of pesticide/antimicrobial classification and tariff policy, respectively; peer‑reviewed studies and independent laboratory reports informed efficacy claims and selection of microbial strains and enzyme families.
Analytical steps included mapping ingredient inputs to HTS subheadings, constructing a regional regulatory matrix for claim permissibility, and stress‑testing supply chains under alternate tariff‑and‑exclusion scenarios. Where primary data were not obtainable, the study used triangulation from press releases, company technical notes, and peer‑reviewed literature to avoid single‑source bias. Limitations are flagged where regulatory pathways remain unsettled or where clinical evidence is still emerging; the full report contains the interview roster (anonymized) and the dataset used for segmentation analysis for clients who require replication or deeper custom modelling.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Microbial Cleaning Agents market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Microbial Cleaning Agents Market, by Source
- Microbial Cleaning Agents Market, by Product Form
- Microbial Cleaning Agents Market, by Application
- Microbial Cleaning Agents Market, by End-User
- Microbial Cleaning Agents Market, by Sales Channel
- Microbial Cleaning Agents Market, by Region
- Microbial Cleaning Agents Market, by Group
- Microbial Cleaning Agents Market, by Country
- United States Microbial Cleaning Agents Market
- China Microbial Cleaning Agents Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 17]
- List of Tables [Total: 2067 ]
Closing synthesis summarizing why microbial cleaning agents represent a practical, evidence‑based opportunity and what capabilities companies must develop to scale successfully
Biological cleaning technologies are no longer laboratory curiosities; they are an actionable class of solutions that respond to clear market priorities-efficacy, sustainability, and safer indoor environments. The accumulated evidence from scientific studies and recent commercial pilots shows that enzyme blends and Bacillus‑based products can deliver functional benefits for stain removal, odour control, and reduction of biofilm formation, provided formulations are matched to the use case and validated in situ. At the same time, regulatory classification and tariff exposure introduce practical constraints that require deliberate technical and commercial planning. Companies that coordinate R&D validation, regulatory engagement, and diversified sourcing will move from experimentation to scale most quickly.
In short, microbial cleaning agents offer differentiated value, but realizing that value requires disciplined product claims, robust third‑party validation, and proactive supply‑chain governance. Organizations that adopt these capabilities will be best positioned to convert scientific potential into repeatable commercial outcomes across household, commercial, and industrial segments.
Immediate next steps to convert insights into competitive advantage and request a tailored copy of the comprehensive microbial cleaning agents market report
For decision-makers ready to act, purchasing the full market research report is the fastest way to operationalize the insights in this executive summary. Reach out to Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing, to request the complete report package, explore bespoke add‑ons such as custom segmentation, primary interview transcripts, and tailored competitor benchmarking, or to schedule a briefing with the research team. The full study contains the detailed methodology, full dataset, HTS/ regulatory annexes, supplier matrices, and scenario analyses that support practical procurement, R&D, and go‑to‑market planning, and a direct conversation will help us match the deliverables to your strategic priorities. Please indicate your preferred timeline for delivery and any custom focuses (for example, a deeper examination of enzyme supply chains, regulatory pathways for probiotic claims, or white‑label manufacturing opportunities) so the sales team can prepare a targeted proposal and next steps.

- How big is the Microbial Cleaning Agents Market?
- What is the Microbial Cleaning Agents Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




