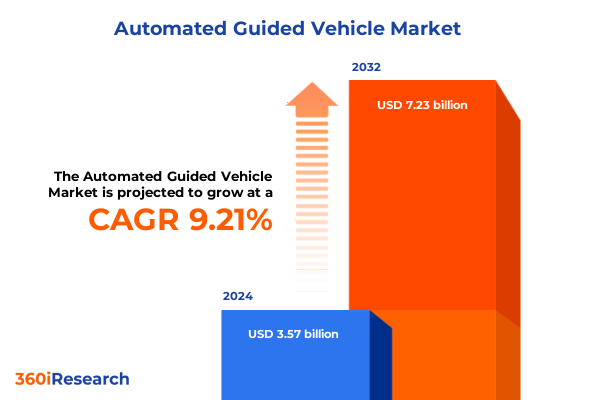
The Automated Guided Vehicle Market size was estimated at USD 3.57 billion in 2024 and expected to reach USD 3.88 billion in 2025, at a CAGR of 9.21% to reach USD 7.23 billion by 2032.
Automated guided vehicles move from niche automation tools to strategic levers redefining intralogistics, manufacturing, and omnichannel fulfillment worldwide
Automated guided vehicles have moved from being specialized equipment in a handful of advanced factories to becoming core infrastructure for modern intralogistics. These systems, operating on predefined or dynamically updated paths, now underpin material movement in warehouses, manufacturing plants, hospitals, and distribution centers that can no longer rely on abundant, low-cost labor. As organizations tighten service level commitments and shorten order cycles, the precision, repeatability, and safety of AGVs make them a central tool for maintaining reliability under pressure.
At the same time, AGVs increasingly coexist and interoperate with autonomous mobile robots, robotic picking systems, and highly automated storage solutions. This convergence reflects a broader shift toward intelligent, orchestrated material flow in which vehicles, conveyors, and people are coordinated in real time by software. In such environments, AGVs are no longer just mechanized carts; they are connected assets that feed data into warehouse management, manufacturing execution, and analytics platforms, giving leaders more granular control over inventory, capacity, and risk.
These developments are unfolding against a backdrop of acute labor shortages in logistics and manufacturing, ongoing supply chain volatility, and rapidly rising expectations from e-commerce and just-in-time production. Together, these forces are pushing organizations to evaluate AGVs not as experimental technology, but as a strategic lever to stabilize operations, improve safety outcomes, and support long-term competitiveness.
From fixed-path tuggers to intelligent fleets, AGVs evolve with AI, 5G, and safety standards to transform warehouse, factory, and hospital workflows
The automated guided vehicle landscape has undergone a fundamental transformation over the past few years, shifting from relatively simple, fixed-path systems to highly orchestrated fleets capable of adapting to dynamic environments. Where early deployments relied heavily on fixed magnetic tape or wired tracks, the market now features laser-based, optical, and increasingly vision-driven navigation that allows vehicles to respond to changing layouts, congestion, and safety constraints. This flexibility is critical as facilities are reconfigured more frequently to support new product lines, seasonal e-commerce peaks, and unpredictable supply conditions.
Equally transformative is the integration of AGVs with advanced software platforms and communications technologies. Fleet management and navigation software now incorporate machine learning to optimize routing, avoid traffic bottlenecks, and prioritize urgent moves, while leveraging 5G or high-reliability Wi-Fi for low-latency coordination. In leading facilities, AGVs interact not only with warehouse management and manufacturing execution systems but also with digital twins that simulate material flow, enabling operators to refine layouts and task assignments before physical changes are made.
Safety and regulatory expectations are evolving in parallel with these technical advances. Updated functional safety standards and more capable sensor suites are driving adoption of redundant laser scanners, three-dimensional vision, and sophisticated obstacle detection, allowing AGVs to share space safely with pedestrians, forklifts, and collaborative robots. As a result, AGVs are increasingly selected not only for productivity gains, but also as part of broader safety and ergonomics programs, particularly in facilities handling heavy loads, hazardous materials, or cold-chain logistics.
These shifts together are redefining the value proposition. Buyers are looking beyond simple payback calculations toward platforms that can scale from a handful of vehicles to facility-wide fleets, adjust to new workflows without major downtime, and integrate with broader automation ecosystems. Vendors that can deliver this combination of flexibility, intelligence, and safety are steadily pulling ahead in competitive evaluations.
Cumulative impact of evolving United States tariffs through 2025 reshapes AGV supply chains, cost structures, and localization strategies across industries
The cumulative impact of United States trade policy through 2025 is increasingly visible across the automated guided vehicle value chain, which depends heavily on globally sourced components. Earlier rounds of tariffs on Chinese machinery and electromechanical products raised the landed cost of key inputs such as motors, sensors, controllers, and precision metal assemblies. In 2025, new national security investigations under Section 232 were launched into imports of robotics and industrial machinery, creating the possibility of additional duties layered on top of existing measures and signaling heightened scrutiny of foreign-origin automation equipment.
For AGV manufacturers and integrators, these developments have had a dual effect. On one hand, higher tariffs on components and subassemblies sourced from China and other manufacturing hubs have compressed margins and increased project pricing, particularly for small and mid-sized buyers that are sensitive to capital expenditure. Analysis of similar categories such as construction and industrial robots suggests that tariffs can raise the cost of key robotic components by double-digit percentages, which in turn delays or scales back some automation programs. On the other hand, these same policies are accelerating broader supply chain restructuring as companies adopt “China+1” strategies, diversify sourcing across Southeast Asia and Mexico, and in some cases reshore production closer to the U.S. market, all of which tend to increase the relative attractiveness of automation to offset higher labor and facility costs.
By 2025, the net result is a more complex decision environment rather than a simple drag on AGV adoption. Large manufacturers and logistics providers with strong balance sheets often respond by doubling down on automation as they localize production and seek to protect margins in higher-cost labor markets. They pressure suppliers to qualify non-tariffed sources of actuators, electric motors, and sensors, and they negotiate multi-year agreements that stabilize pricing in exchange for volume commitments. Smaller organizations, however, face a harder trade-off: the same tariffs that encourage reshoring and local investment also increase the up-front cost of AGV systems, stretching payback horizons and making financing structures and as-a-service models more important.
Going forward, tariff policy is likely to remain fluid, but the trajectory is clear. Automation, including AGVs, is increasingly framed as both an economic and strategic asset, intertwined with national security considerations around supply chain resilience and technological dependence. Industry leaders must therefore embed trade-policy scenarios into their capital planning, evaluating not only headline tariff rates but also secondary effects on component availability, lead times, and vendor risk concentration.
Segmentation insights reveal how components, vehicle types, navigation modes, and end-user demands align AGV capabilities with precise operational pain points
Viewed through the lens of components, the AGV ecosystem is increasingly defined by the interplay between sophisticated hardware, robust services, and intelligent software. Hardware remains foundational, with actuators, controllers, sensors, and electric motors determining not only payload capacity and acceleration profiles but also energy efficiency and safety performance. Suppliers are integrating more diagnostic capabilities directly into these devices, enabling predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring. At the same time, services surrounding design, installation, and lifecycle support are expanding as buyers seek partners who can manage complex integrations with existing conveyors, storage systems, and IT infrastructure. Software has moved from a supporting role to a primary differentiator, with fleet management platforms and navigation software responsible for routing optimization, traffic control, and data capture across heterogeneous fleets.
Vehicle type segmentation underscores how AGVs are tailored to distinct material handling patterns. Cart-based vehicles are widely used for light to medium loads and are valued for their maneuverability in tight aisles and hospital corridors. Forklift-style AGVs mirror the capabilities of conventional lift trucks, automating pallet movement in high-bay warehouses, cold storage, and manufacturing docks. Hybrid vehicles and towing configurations support heavier or mixed loads, such as train-like movements of components feeding assembly operations, while unit load vehicles and assembly line vehicles are engineered for precise, repetitive transfers between production steps. This diversity allows end users to match vehicle architecture to workflow characteristics instead of forcing processes to conform to a single platform.
Navigation technology is another critical axis of differentiation as buyers weigh cost, flexibility, and robustness. Laser guidance systems remain popular for their accuracy and relative ease of layout change, particularly in environments with frequent slotting or rack reconfiguration. Magnetic tape or wire-based guidance, along with wired navigation, continues to serve applications where path stability and simplicity are more important than layout agility, such as predictable shuttle runs between fixed points. Optical navigation and GPS-based approaches are gaining traction where semi-structured or outdoor environments must be accommodated, or where facilities want to reduce floor and infrastructure modifications. As sensing and processing capabilities improve, combinations of these methods are increasingly used to deliver layered redundancy and smoother navigation in congested spaces.
Payload capacity segmentation further refines solution choice. Vehicles engineered for less than 100 kg support tasks such as kitting, small-parts replenishment, and movement of totes or trays in manufacturing and e-commerce fulfillment. Systems rated between 100 kg and 500 kg are common in general warehousing, light manufacturing, and hospital logistics, where loads include cases, medical supplies, or subassemblies. Heavy-duty platforms designed for more than 500 kg are deployed around bulky or high-value items such as engines, body-in-white structures, or palletized beverages, often in conjunction with specialized load-handling frames or lift mechanisms.
Applications provide another window into AGV strategy. Transportation within and between zones, loading and unloading at docks or production cells, assembly line feeding, packaging support, and storage and retrieval all place different demands on acceleration, stopping accuracy, and interface design. For example, AGVs used in storage and retrieval must coordinate tightly with racking, conveyors, and warehouse control software, while those supporting packaging often need to synchronize with high-speed machinery and quality inspection systems. As organizations move toward lights-out or low-touch operations, they increasingly configure AGVs to span multiple application categories rather than operate as single-purpose assets.
End-user segmentation reveals just how broadly AGVs now penetrate industry. Food and beverage producers rely on hygienically designed vehicles to move ingredients and finished goods through temperature-controlled environments while respecting strict sanitation rules. Healthcare providers use AGVs to transport linens, meals, pharmaceuticals, and waste through dedicated corridors and elevators, improving infection control and freeing staff for direct patient care. Logistics and warehousing remain the most visible adopters, with AGVs orchestrating pallet movements and replenishment in large-scale distribution centers. Manufacturing users deploy AGVs to support just-in-time delivery of components to assembly lines, while retailers and e-commerce specialists harness them to sustain rapid order fulfillment and omnichannel services. Electronics and semiconductor facilities, often operating in cleanroom conditions, use highly specialized AGVs to handle delicate, high-value wafers and components.
Finally, distribution channels in this market reflect the balance between complex engineering requirements and the growing comfort with digital procurement. Offline channels remain essential for large-scale deployments that demand in-depth consulting, site surveys, and custom engineering. However, online channels are gaining importance as standardized vehicle platforms, software subscriptions, and modular accessories become easier to specify and order via digital configurators. This is encouraging a new generation of buyers, including mid-sized enterprises, to evaluate AGVs through pilot projects and incremental expansions rather than single, monolithic automation programs.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Automated Guided Vehicle market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Component
- Vehicle Type
- Navigation Technology
- Payload Capacity
- Application
- End-User
- Distribution Channel
Regional perspectives across the Americas, Europe, Middle East, Africa, and Asia-Pacific highlight distinct AGV adoption pathways and investment priorities
Regional dynamics shape both the pace and character of AGV adoption. In the Americas, the United States and Canada anchor a landscape defined by persistent labor shortages in warehousing and manufacturing, rising wage levels, and the need to support rapidly expanding e-commerce networks. North American operators are investing in AGVs to stabilize throughput as they reshore or nearshore production and distribution capacity, often consolidating fragmented facilities into larger, more automated hubs. Mexico’s role as a manufacturing and logistics platform is also expanding, with AGVs supporting cross-border automotive, electronics, and consumer-goods supply chains. Across the region, regulatory emphasis on worker safety and ergonomic risk reduction further strengthens the rationale for automating repetitive, high-risk material handling tasks.
In Europe, Middle East, and Africa, the picture is more heterogeneous but equally instructive. Mature industrial economies in Western and Northern Europe, such as Germany and the Nordics, have long histories of automation and are now layering AGVs onto sophisticated warehouse management and production systems in automotive, machinery, and food processing sectors. The Middle East, led by Gulf states, is emerging as a logistics and air cargo hub that increasingly depends on highly automated warehouses and free-zone facilities to differentiate on speed and reliability. Parts of Africa are at earlier stages of AGV adoption, with deployments clustered in export-focused manufacturing, mining-related logistics, and select port operations where automation can address infrastructure bottlenecks. Throughout this larger region, sustainability regulation and energy-cost volatility are reinforcing interest in energy-efficient AGVs and optimized intralogistics layouts.
Asia-Pacific stands out as the most dynamic theater for industrial and logistics automation, and AGVs are integral to this momentum. China, in particular, has rapidly increased robot installations in manufacturing and logistics, supported by large-scale state-backed investment and industrial policies that promote domestic robotics suppliers. Japan and South Korea continue to pioneer high-reliability automation in automotive, electronics, and semiconductor supply chains, often using AGVs in tightly integrated cleanroom environments and high-mix production lines. Meanwhile, Southeast Asian economies such as Vietnam, Thailand, and Malaysia are attracting new factories and distribution centers as companies diversify beyond China, and AGV deployments are following these greenfield investments.
As tariff uncertainty and geopolitical risk reshape global value chains, the relative advantages of these regions are also evolving. Analytical work on highly automated “lighthouse” factories shows that China now hosts a large share of the world’s most advanced sites, but that North America and Europe offer leading capabilities in AI-enabled industrial software, digital twin technology, and high-value system integration. For AGV stakeholders, this means that component sourcing, manufacturing, and software development may increasingly be distributed across multiple continents, even as end-user deployments concentrate in logistics corridors that link Asia-Pacific production, European and Middle Eastern gateways, and American consumer markets.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Automated Guided Vehicle market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Strategic moves by leading AGV manufacturers and software innovators redefine competition through platforms, partnerships, and vertical-specific automation
Competition in the automated guided vehicle space is intensifying as established material-handling giants and specialized robotics firms race to deliver more capable, software-rich solutions. Global manufacturers such as Toyota Industries Corporation, Daifuku, and KION Group’s Dematic unit leverage extensive installed bases in forklifts, conveyors, and warehouse systems to embed AGVs into broader automation offerings. Their strategies emphasize end-to-end intralogistics platforms that combine vehicles, automated storage and retrieval systems, and control software, positioning AGVs as one component of a tightly integrated material-flow architecture rather than a standalone product.
Specialist players bring complementary strengths. Swisslog is advancing mobile robotics capabilities within its goods-to-person and shuttle solutions, including recent enhancements to its CarryPick system that improve performance for operations with frequently changing product mixes and packaging formats. JBT has built a strong position in heavy-duty AGVs for food and beverage, automotive, and general industrial users, focusing on robust engineering and high reliability in demanding environments. Seegrid and Balyo concentrate on intelligent navigation and the conversion of conventional lift trucks into autonomous vehicles, allowing facilities to retain familiar hardware while adding autonomy through sensor and software upgrades. These firms differentiate through perception algorithms, localization accuracy, and the ease with which fleets can be scaled or reconfigured.
Across the competitive landscape, partnerships have become a defining feature as companies seek to blend navigation software, vehicle platforms, and systems integration expertise. Collaborations between AGV manufacturers and control-software providers are enabling more modular solutions that can be adapted by regional integrators for specific industries, from cold-chain logistics to aerospace manufacturing. Hardware vendors are opening up vehicle control interfaces, while software companies develop standardized modules for traffic management, battery optimization, and analytics. This modularity not only accelerates time to market but also reduces switching costs for end users, who are increasingly wary of vendor lock-in.
Another clear trend among leading companies is the pivot toward services and recurring revenue models. Fleet monitoring, remote diagnostics, performance guarantees, and outcome-based contracts are gaining traction, particularly among large logistics providers and manufacturers that want predictable operating expenditures rather than large upfront investments. Vendors that can combine advanced vehicles, mature software platforms, and value-added services are better positioned to capture long-term customer relationships as AGV deployments scale from pilot projects to mission-critical infrastructure.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Automated Guided Vehicle market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- ABB Ltd.
- Aethon, Inc.
- Alstef Group SAS
- Balyo
- Clearpath Robotics by Rockwell Automation
- Daifuku Co., Ltd.
- E80 Group S.p.a.
- FORTNA Inc. by MHS Global
- Geekplus Technology Co., Ltd.
- Godrej and Boyce Mfg. Co. Ltd.
- Hitachi, Ltd.
- Hyster-Yale Materials Handling, Inc.
- inVia Robotics, Inc.
- JBT Marel Corporation
- Kion Group AG
- KMH Fleet Solutions
- Kompress India Pvt Ltd.
- KUKA AG
- Linde Material Handling GmbH
- Locus Robotics Corporation
- MasterMover, Inc.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
- NEURA Robotics GmbH
- Omron Corporation
- Robotic Automation P/L
- Seegrid Corporation
- SIASUN Robot & Automation CO.,Ltd
- SIEMPELKAMP Transport Systems GmbH
- System Logistics S.p.A.
- Teradyne Inc.
- TOSHIBA CORPORATION
- Toyota Material Handling, Inc.
- Vecna Robotics Inc.
- Yaskawa Electric Corporation
Actionable priorities for industry leaders to de-risk AGV investments, unlock productivity gains, and build resilient, human-centric automated operations
To capture the full value of automated guided vehicles under current competitive and regulatory conditions, industry leaders must treat AGV programs as cross-functional transformations rather than isolated capital projects. The starting point is a rigorous mapping of material flows, safety constraints, and labor challenges across warehouses, plants, or hospital networks. By quantifying bottlenecks, travel distances, and manual touchpoints, organizations can prioritize AGV use cases that will relieve the most acute pain while generating quick wins that build internal support for broader automation.
Technology choices should follow this operational analysis rather than precede it. Decision-makers should align vehicle types, navigation technologies, and payload capacities with the diversity of their workflows, ensuring that hardware specifications are not over- or under-engineered for actual tasks. Equally important is the selection of fleet management and navigation software that can support heterogeneous fleets and interface cleanly with existing warehouse management, manufacturing execution, and safety systems. Leaders should press vendors for clear roadmaps on interoperability, cybersecurity, and remote update capabilities, given that these factors will heavily influence lifecycle cost and risk.
Trade uncertainty and ongoing supply chain realignment require a more strategic perspective on sourcing and manufacturing footprints. Executives should stress-test AGV plans against multiple tariff and component-availability scenarios, exploring dual-sourcing options for critical hardware such as sensors and controllers and considering regional integration partners that can reduce cross-border complexity. Where possible, they should structure contracts to share risk with suppliers through service-level agreements that link performance and uptime to payment. At the same time, sustained investment in workforce development is essential: maintenance technicians, supervisors, and operators need targeted training so that AGVs augment rather than displace human capabilities, and so that facilities can recover quickly from disruptions without overreliance on external support.
Finally, leaders should build governance mechanisms that continuously measure AGV program outcomes against strategic objectives. This means tracking not just throughput and labor efficiency, but also safety incidents, energy consumption, resilience during demand spikes, and adaptability to product or layout changes. By institutionalizing such feedback loops and integrating them into capital planning and operations reviews, organizations can evolve from one-off AGV projects to a continuous-improvement model in which automation capabilities grow in lockstep with business ambitions.
Robust research methodology combining primary insights, secondary intelligence, and analytical rigor to decode the evolving automated guided vehicle landscape
The insights presented in this executive summary are grounded in a structured research methodology designed to balance breadth of coverage with depth of analysis. The approach begins with extensive secondary research across reputable sources, including robotics and automation industry associations, technology vendors, logistics and manufacturing trade publications, government statistics, and regulatory documentation. Particular attention is paid to developments in trade policy, labor markets, and industrial safety standards, given their outsized influence on AGV adoption and deployment patterns.
This secondary foundation is complemented by ongoing monitoring of product launches, partnership announcements, and case studies from leading AGV manufacturers and systems integrators. These sources illuminate how technologies such as laser and vision-based navigation, AI-enabled fleet management, and modular vehicle designs are being translated into real-world deployments. When triangulated with macroeconomic and supply chain data, they help distinguish between short-lived marketing narratives and structural shifts that are reshaping customer expectations and competitive dynamics.
Primary insights, where available, are derived from discussions and interviews with logistics managers, plant operators, automation engineers, and vendor representatives. These conversations provide nuanced perspectives on practical challenges such as integrating AGVs into legacy IT environments, navigating internal change-management hurdles, and managing the total cost of ownership over multi-year periods. They also clarify how end users perceive the impact of tariffs, labor shortages, and environmental, social, and governance commitments on their automation strategies.
Analytically, the research process emphasizes cross-segmentation and scenario thinking rather than single-point forecasts. Component, vehicle type, navigation technology, payload, application, end-user, and regional lenses are examined in combination to understand where demand is likely to be most resilient or vulnerable under different economic and policy conditions. While quantitative models underpin many of the conclusions, the emphasis in this summary is on qualitative interpretation that helps decision-makers grasp underlying mechanisms and trade-offs without relying on specific market-size projections.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Automated Guided Vehicle market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Automated Guided Vehicle Market, by Component
- Automated Guided Vehicle Market, by Vehicle Type
- Automated Guided Vehicle Market, by Navigation Technology
- Automated Guided Vehicle Market, by Payload Capacity
- Automated Guided Vehicle Market, by Application
- Automated Guided Vehicle Market, by End-User
- Automated Guided Vehicle Market, by Distribution Channel
- Automated Guided Vehicle Market, by Region
- Automated Guided Vehicle Market, by Group
- Automated Guided Vehicle Market, by Country
- United States Automated Guided Vehicle Market
- China Automated Guided Vehicle Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 19]
- List of Tables [Total: 1590 ]
Conclusion underscores AGVs as a foundational pillar of next-generation industrial, logistics, and healthcare ecosystems amid global trade and labor shifts
Taken together, the patterns described in this executive summary underscore the centrality of automated guided vehicles to the next generation of industrial, logistics, and healthcare operations. AGVs are no longer experimental pilots confined to a few showcase facilities; they are maturing into dependable infrastructure that underpins day-to-day performance in environments where labor is tight, safety expectations are rising, and service levels leave little margin for error. Their evolution from fixed-path machines to intelligent, software-orchestrated fleets reflects a broader shift toward data-driven, continuously optimized material flow.
The influence of trade policy, and particularly the cumulative effect of United States tariffs through 2025, adds a layer of complexity that leaders cannot ignore. Higher costs and supply chain disruptions are real constraints, especially for smaller organizations, yet they coexist with strong incentives to localize production and invest in automation that can sustain competitiveness in higher-cost regions. In this context, AGVs become both a tactical tool to relieve immediate bottlenecks and a strategic asset that supports long-term resilience and flexibility in the face of geopolitical and economic uncertainty.
Segmentation by components, vehicle types, navigation technologies, payload classes, applications, and end-user industries reveals a market that is broad, diverse, and capable of highly tailored solutions. Regional perspectives across the Americas, Europe, the Middle East, Africa, and Asia-Pacific highlight that there is no single adoption curve; instead, each geography combines its own mix of labor economics, industrial structure, regulatory frameworks, and technology ecosystems. Similarly, the competitive landscape shows that both global conglomerates and focused specialists have important roles to play, with collaboration and modularity growing in importance as customers demand openness and interoperability.
For decision-makers, the implication is clear. AGVs sit at the intersection of operations, technology, trade policy, and workforce strategy. Those who approach them as part of an integrated transformation agenda-anchored in rigorous analysis, informed by evolving regional and policy dynamics, and executed through strong partnerships-will be best positioned to capture their full potential. Organizations that delay decisive action risk finding themselves locked into inflexible processes, exposed to compounding cost pressures, and unable to meet the expectations of increasingly demanding customers and regulators.
Leverage deep AGV insights by engaging with Ketan Rohom to unlock tailored decision support and secure your next strategic automation advantage
The insights outlined throughout this executive summary only scratch the surface of the strategic, technical, and regional dynamics shaping automated guided vehicle deployment. To translate these themes into clear priorities, quantified business cases, and competitive benchmarks tailored to your organization, direct engagement with a specialist is essential.
To move from high-level understanding to decisive action, connect with Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing, and initiate a discussion on acquiring the full automated guided vehicle market research report. In this conversation, you can outline your core geographies, target end-user segments, and technology focus areas so that the report package and any accompanying advisory sessions directly support your strategic and capital planning cycles.
By engaging with Ketan, decision-makers can secure comprehensive documentation of vendor landscapes, regulatory developments, and adoption patterns, as well as scenario-based guidance on navigating tariffs, labor constraints, and technology risk. This is an opportunity to equip your leadership team, investment committees, and operational stakeholders with an evidence-backed roadmap that links AGV strategy to measurable improvements in throughput, resilience, and safety.
Now is an inflection point for intralogistics and factory automation, and the organizations that act with the best information will shape the next decade of performance standards. Reach out to Ketan Rohom to obtain the report and unlock structured, decision-ready intelligence that aligns AGV initiatives with your broader vision for digital and operational transformation.

- How big is the Automated Guided Vehicle Market?
- What is the Automated Guided Vehicle Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




