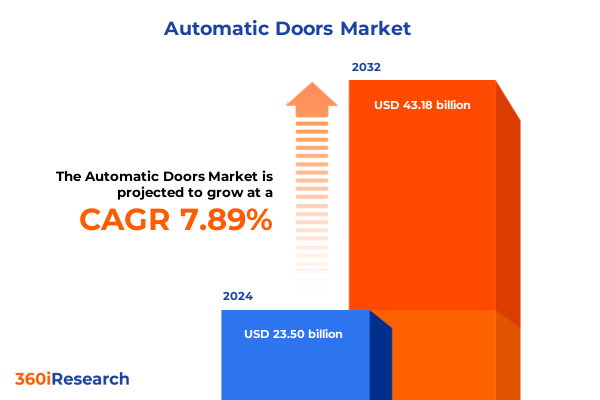
The Automatic Doors Market size was estimated at USD 25.22 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 27.12 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 7.98% to reach USD 43.18 billion by 2032.
A comprehensive introduction positioning the automatic doors industry amid evolving safety, digital integration, compliance, and procurement priorities
The automatic doors industry sits at an inflection point where traditional building access hardware converges with digital controls, stricter regulatory scrutiny, and evolving end-user expectations. This introduction frames the market through three interlocking prisms: functional performance and safety, integration with access and building management systems, and the procurement realities driven by materials and component supply chains. Rapid urbanization, heightened accessibility standards, and growing emphasis on touchless interfaces have raised the baseline expectations for product reliability, while rising attention to sustainability and life-cycle costs is shifting buyer evaluations from initial price to total cost of ownership.
As stakeholders seek continuity in operations and clarity on risk, the sector’s value chain-from raw material supply to final installation and aftermarket services-has become a central focus. Manufacturers and specifiers are increasingly required to demonstrate traceability of metal and electronic components, provide robust maintenance frameworks, and deliver systems that interoperate with broader security and facility management architectures. In consequence, design priorities emphasize modularity and serviceability alongside safety and compliance. This report’s introduction positions readers to understand why these non-price attributes now shape procurement decisions and how companies are adapting their product roadmaps and go-to-market strategies to align with institutional purchasers and high-rise commercial projects.
Transformative shifts shaping the automatic doors industry driven by intelligent systems, sustainability goals, bundled solutions, and trade policy pressures
The landscape that manufacturers, integrators, and specifiers operate in is undergoing transformative shifts driven by technological convergence, supply chain reconfiguration, and regulatory interventions. First, the march toward intelligent buildings has accelerated adoption of sensor-based and motion-driven operation mechanisms, embedding access control, energy management, and analytics capabilities at the door level. As a result, product architectures are moving from electro-mechanical assemblies toward software-enabled platforms that demand new competencies in firmware security, data integration, and remote diagnostics.
Second, sustainability and circular-economy principles are influencing material choices and manufacturing processes. Aluminum and stainless steel remain core structural materials because of strength and durability, yet composite and glass systems are being optimized for weight reduction and end-of-life recyclability. Consequently, procurement teams and architects now evaluate suppliers not only on mechanical performance but also on embodied carbon disclosures, repairability, and the availability of recycled content.
Third, buyer behavior is shifting toward bundled solutions that combine hardware, controls, installation, and aftermarket service under single commercial agreements. This trend favors manufacturers that can deliver consistent service footprints and predictable maintenance economics across regions. In tandem, channel dynamics are changing as installers and OEMs invest in training and digital tools to manage the growing complexity of networked door systems.
Finally, geopolitical and trade policy developments have altered sourcing calculus. Tariffs, country-of-origin rules, and investigative actions on strategic industrial inputs are forcing companies to rethink global footprints, nearshore production options, and inventory strategies. These changes have immediate procurement implications and longer-term consequences for design choices, particularly for doors that contain significant steel, aluminum, electronic actuators, or Chinese-sourced control modules. Taken together, these transformative shifts require cross-functional responses spanning product development, procurement, and commercial operations.
An in-depth analysis of how 2025 United States tariff expansions and exclusion changes are reshaping costs, compliance, and sourcing for automatic doors
Since early 2025 the United States has enacted a series of trade-policy adjustments that directly influence the cost structure and sourcing risk for products containing steel, aluminum, and certain Chinese-origin components. In February 2025, Presidential proclamations broadened the application of Section 232 duties and terminated many alternative arrangements and general exclusions, creating a framework where derivative products and downstream assemblies that incorporate steel or aluminum became subject to additional duties. This administrative routing required customs guidance to establish reporting mechanics for duties that are applied to the metal content of finished goods, complicating entry classification and increasing compliance workloads for importers. The proclamation and its implementing guidance clarified that downstream assemblies with embedded metal could be assessed duties based on their metal value rather than the finished-goods price, altering landed-cost calculations across complex assemblies.
A further policy escalation in mid-2025 raised the ad valorem rates applied under the Section 232 framework. Executive action increased the tariff rate on many covered steel and aluminum articles, which in turn elevated the tariff exposure on derivative articles that include metal components. Importantly, the expansion did not merely increase headline rates; it also expanded the range of HTS classifications and derivative categories subject to scrutiny, which places higher diligence burdens on manufacturers, distributors, and customs brokers. This broadened scope makes component-level cost allocation and contractual pass-through mechanisms more critical for commercial negotiations and bidding.
Concurrently, Section 301 actions relating to imports from the People’s Republic of China continued to evolve through the statutory review process. Certain high-risk component categories experienced rate increases at the start of 2025, and the Office of the U.S. Trade Representative issued extensions for some product exclusions to allow transition time for affected supply chains. The interaction between Section 301 and Section 232 regimes means that door assemblies with both Chinese-origin electronics and metal structure can be double-exposed to layered duties or to complex exclusion regimes with limited durations. Practically, this has driven manufacturers to re-evaluate bill-of-materials routing, qualify alternate sources for motors, sensors, and control boards, and document manufacturing processes to support potential “melted and poured” or “smelt and cast” exemptions where applicable.
The cumulative impact of these measures has been multifaceted. Near-term effects include higher landed costs for imports that contain significant metal content or Chinese-origin components, increased working capital tied to longer customs processing and classification reviews, and heavier administrative burdens for compliance documentation. Over the medium term, firms are responding by redesigning assemblies to reduce exposed metal content where possible, accelerating qualification of non-Chinese electronics suppliers, and intensifying localization or nearshoring where labor, capacity, and regulatory alignment permit. Because the duties are applied at the HTS and component-value level, companies that can transparently demonstrate domestic metal inputs or U.S.-based smelting and casting processes can materially reduce exposure. These operational responses are reshaping supplier contracts, procurement cadence, and capital allocation for manufacturing footprints.
Key segmentation insights revealing where product architecture, material selection, operation mechanism, installation type, and end-user demand create strategic vulnerabilities and opportunities
Understanding product, material, operational, installation, and end-user segmentation is essential to diagnosing where value and vulnerability coexist in the automatic doors ecosystem. When viewed by product type, folding doors, revolving doors, sliding doors, and swing doors present distinct engineering and supply-chain profiles: revolving doors, whether configured as four-leaf or three-leaf systems, typically combine significant metal frames, precision bearings, and integrated motor controls, making them highly sensitive to metal tariffs and component shortages; sliding doors, in their center-opening, four-panel, telescopic, or two-panel variants, mix aluminum rails, glass or composite panels, and electronic drives, creating trade-offs between structural performance and tariff exposure; folding doors are often used where space constraints and modular panels are required, and their componentization can facilitate supplier diversification; swing doors, in single- or double-leaf formats, remain the simplest mechanically but can include heavy-duty steel frames or stainless-steel hardware when specified for higher durability.
Material type further reframes sourcing and lifecycle costs: aluminum and stainless-steel systems excel in durability and corrosion resistance but can attract higher duty treatment when derivative rules apply to downstream assemblies; composite and wooden doors offer weight and aesthetic benefits but require different supplier ecosystems and introduce new fire and durability compliance requirements; glass doors bring architectural value and require robust framing and handling logistics. From an operations standpoint, the mechanism of operation-access control, mechanical, motion-based, push-button, or sensor-based-determines the proportion of value that sits in electromechanical and electronic subsystems. Sensor-based and access-control enabled doors depend on control boards, firmware, and networking modules that are often sourced through global electronics supply chains and therefore can be subject to separate trade measures or cybersecurity scrutiny.
Installation type divides opportunities between new-install projects and the replacement market. New installations allow for design optimization and specification-driven material choices, whereas replacement work, whether full replacement or partial retrofit, emphasizes compatibility with existing site conditions and speed of deployment. End-user segmentation into commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and residential buildings captures divergent performance priorities: commercial projects prioritize uptime, regulatory compliance, and integration with building management systems; industrial facilities emphasize ruggedness, ingress/egress throughput, and safety interlocks; residential applications prioritize aesthetics, quiet operation, and affordability. Accordingly, the most resilient commercial strategies marry product modularity with flexible procurement options so that supply-chain disruptions or tariff shocks can be managed without wholesale program delays.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Automatic Doors market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Product Type
- Material Type
- Operation Mechanism
- Installation Type
- End User
Regional insights explaining how tariff regimes, standards, and supply chain footprints differently influence automatic doors procurement and deployment across key global zones
Regional dynamics determine how tariff measures, supply chain resilience, and demand patterns intersect for door manufacturers and specifiers. In the Americas, procurement is affected directly by U.S. tariff actions and by supply-chain relocation trends that favor nearshoring. Buyers in North America increasingly demand validated domestic sourcing credentials for steel and aluminum content, and installers are investing in training to manage the more complex customs and compliance documentation that accompanies derivative duty regimes. As a result, commercial and industrial purchasers are favoring suppliers with demonstrable local manufacturing footprint or with clear mitigation plans for duty exposure.
Across Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, specifications are heavily influenced by regional standards for safety, fire, and accessibility, and by a strong emphasis on lifecycle environmental performance. Manufacturers serving these markets often balance higher-specification requirements with the need to optimize transcontinental logistics and to manage differing tariff and regulatory regimes across jurisdictions. For suppliers exporting into these geographies from the United States, the changing U.S. tariff landscape has a reciprocal effect: it changes input costs and can influence competitiveness abroad, making pricing strategies and contract structures more complex.
In the Asia-Pacific region, dense manufacturing ecosystems and well-developed electronics supply chains continue to provide competitive advantages, especially for sensor modules and motor controls. However, the interaction between regional trade policy, rising labor costs in some markets, and local content rules for major infrastructure projects is prompting tier-one manufacturers to diversify supplier bases and to evaluate regional manufacturing hubs. For multinational procurement teams, these regional differences mean that sourcing, compliance, and total delivery timelines must be orchestrated across multiple regulatory regimes, often necessitating more sophisticated demand planning and greater inventory buffers.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Automatic Doors market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Key company-level insights showing how platform leadership, supply-chain resiliency, and service scale are determining competitive advantage in automatic doors
Competitive dynamics in the automatic doors sector are increasingly shaped by three forms of differentiation: technical platform leadership, supply-chain resiliency, and service delivery scale. Companies that lead in platform capabilities-integrating secure access control, remote diagnostics, and standardized communication protocols-enjoy advantages in commercial building projects where interoperability with building management systems is a decisive procurement criterion. Those that invest in supply-chain resiliency, whether through vertical integration of metal fabrication, qualification of alternate electronics suppliers, or nearshoring of critical components, reduce their vulnerability to tariff volatility and customs classification risk.
Service delivery remains a potent competitive moat. Firms that provide nationwide or multinational installation and maintenance networks convert initial equipment sales into recurring service revenue and strengthen customer retention. To capture this value, leading suppliers are expanding training programs for installer-partners, deploying digital field-service platforms, and offering contractual service-level agreements that guarantee uptime and response times. Strategic partnerships are also evident: OEMs are collaborating with controls vendors and systems integrators to deliver end-to-end solutions that embed the door as part of a larger building-security proposition. Taken together, these dynamics favor integrated suppliers that can present a single commercial interface for hardware, controls, installation, and maintenance while managing regulatory and tariff-driven risks within their sourcing strategies.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Automatic Doors market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- Allegion PLC
- Alumitech Window and Door Solutions
- Assa Abloy AB
- Avanti Systems
- Deutschtec GmbH
- Dormakaba International Holding AG
- DSS Automatic Doors by FAAC Group
- Formula Automatic Door Co., Inc.
- Foshan Huadi Metal Produce Co., Ltd.
- GEZE GmbH
- GRUPSA GLOBAL, SL
- GU Automatic GmbH
- Haida Door Control Co., Ltd.
- Hangzhou Safedoor Automation & Hardware Co., Ltd.
- KBB Automatic Door Group
- MANUSA GEST, S.L.
- Matz-Erreka, S. Coop.
- Maxwell Automatic Doors Co, LLC
- Nabtesco Corporation
- Osent Automatic Door Group
- Overhead Door Corporation
- Panasonic Corporation
- PORTALP FRANCE SAS
- RGPRO Automatic Door Systems
- Rite-Hite Holding Corporation
- Royal Boon Edam International B.V.
- Sanwa Holdings Corporation
- Sanway Technology
- Shenzhen Hongfa Automatic Door Co., Ltd.
- Tormax by LANDERT Group AG
Actionable recommendations for industry leaders to redesign products, diversify suppliers, automate compliance, and monetize services to mitigate tariff-driven disruption
Industry leaders should adopt a differentiated, multi-layered response to manage tariff exposure, preserve margin, and maintain delivery predictability. First, prioritize bill-of-materials redesign to minimize tariff-sensitive content without compromising structural integrity or safety. Where metal content cannot be reduced, pursue certification and documentation that supports exemptions tied to smelted-and-poured or smelted-and-cast criteria, and contractually allocate tariff risk in supplier agreements to create clear commercial incentives for localization.
Second, accelerate qualification of alternative suppliers for electronics, motors, and sensor modules, with an emphasis on supplier redundancy across multiple jurisdictions. This reduces single-source risk and creates negotiating leverage while protecting against sudden exclusion expirations or rate increases. Third, expand nearshoring and regional distribution centers for finished goods and spare-part inventories to shorten lead times and lower customs-related processing vulnerability. Shorter transit cycles also reduce the capital tied up in in-transit inventory and provide greater flexibility for retrofit and replacement projects.
Fourth, invest in digital compliance and classification tools that automate HTS mapping, capture required manufacturing documentation, and produce audit-ready entry files for customs. Automation reduces the administrative burden and lowers the probability of classification errors that can trigger retrospective duties. Fifth, develop value-based service offerings that move commercial conversations away from unit price to total cost of ownership and guaranteed uptime. By packaging maintenance and remote diagnostics into contracts, suppliers can offset part of the tariff-driven margin pressure through recurring revenue streams and improve customer stickiness.
Finally, engage proactively with trade associations and government liaison channels to remain informed about exclusion processes and to influence classification guidance where feasible. Firms that combine technical redesign with operational and commercial hedges will be best positioned to protect margins and to capture the next wave of specification-led procurement opportunities.
A transparent research methodology combining interviews, policy analysis, component-level decomposition, and cross-validated supply-chain scenario mapping
The research approach underpinning this executive analysis is multi-method and purposefully cross-functional to capture engineering, commercial, and policy effects. Primary inputs included structured interviews with senior procurement, product, and service leaders within manufacturing and installation organizations, and with distribution partners active in key regions. These qualitative engagements informed an assessment of sourcing strategies, BOM sensitivity to metal and electronics content, and service-network economics. Secondary inputs comprised regulatory and customs guidance, published proclamations and federal notices governing tariff regimes, and legal analyses that clarify the mechanics of duties applied to derivative articles and content-based valuation.
Analytically, the study combined component-level bill-of-materials decomposition, scenario mapping for layered tariff regimes, and supply-chain resilience scoring to highlight where companies face concentrated exposure. Cross-validation was achieved by reconciling interview insights with public customs guidance and official government proclamations affecting steel, aluminum, and Chinese-origin component tariffs. Wherever possible, assertions about policy mechanics were tied directly to primary government sources to ensure accurate interpretation of classification rules and timing of implementation. The research intentionally excluded proprietary financial estimates and forecasting projections and focused instead on operational risk, sourcing options, and strategic responses that are robust across multiple tariff scenarios.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Automatic Doors market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Automatic Doors Market, by Product Type
- Automatic Doors Market, by Material Type
- Automatic Doors Market, by Operation Mechanism
- Automatic Doors Market, by Installation Type
- Automatic Doors Market, by End User
- Automatic Doors Market, by Region
- Automatic Doors Market, by Group
- Automatic Doors Market, by Country
- United States Automatic Doors Market
- China Automatic Doors Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 17]
- List of Tables [Total: 1590 ]
A forward-looking conclusion that synthesizes strategic imperatives and resilience pathways for the automatic doors industry in a changing policy and technology environment
In sum, the automatic doors sector must navigate a period of intensified policy scrutiny and shifting commercial expectations. The combined influence of intelligent building integration, sustainability mandates, and a more punitive trade environment places a premium on design adaptability, supplier diversification, and service-led commercial models. While tariffs and related compliance requirements increase the short-term complexity of procurement and add administrative cost, they also accelerate structural responses that can strengthen resilience: better documentation of material provenance, localized capacity for critical inputs, and business models that prioritize downstream services.
Looking ahead, companies that move decisively to align product architectures with low-tariff exposure, who adopt rigorous compliance tooling, and who embed aftermarket services into their value propositions will find themselves in a stronger position to win specification-led contracts and to maintain stable margins. The imperative is clear: treat tariff risk as a strategic driver of product and operations design rather than as a temporary cost shock, and orchestrate cross-functional programs that convert compliance requirements into competitive advantage.
Request an executive briefing and purchase access to the full automatic doors market research report through Ketan Rohom for tailored insights and enterprise licensing
For a definitive, enterprise-ready exploration of the competitive dynamics, tariff-driven risks, and tactical responses affecting the automatic doors industry, request the full market research report from Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing. The report delivers structured analysis, supplier and component risk matrices, scenario planning for tariff regimes, and implementation roadmaps tailored for procurement, supply chain, and product leadership teams. Engage directly with Ketan Rohom to arrange a customized briefing, access proprietary appendices, and secure enterprise licensing for stakeholder distribution.

- How big is the Automatic Doors Market?
- What is the Automatic Doors Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




