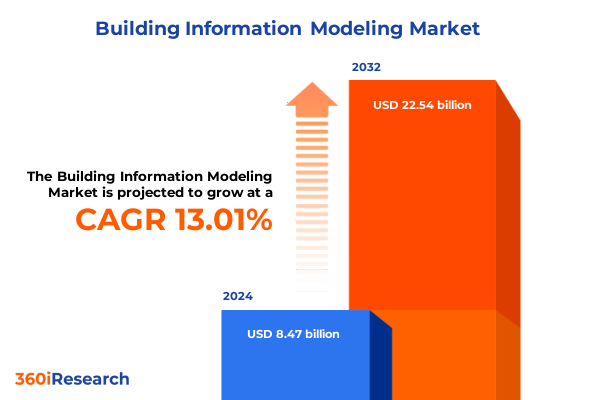
The Building Information Modeling Market size was estimated at USD 9.53 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 10.74 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 13.08% to reach USD 22.54 billion by 2032.
An executive introduction positioning Building Information Modeling as the strategic integrator of design, construction, and operations to unlock measurable improvements in project delivery
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has transitioned from a specialized design tool to an integrative backbone for modern project delivery, connecting disciplines across design, construction, and facilities management. This introduction frames BIM as a strategic enabler that reduces friction between stakeholders, supports digital workflows, and elevates data-driven decision-making throughout the asset lifecycle. By focusing on interoperability, process alignment, and governance, organizations can harness BIM to improve coordination, reduce rework, and enhance operational handover.
Throughout this summary, readers will find analysis grounded in observed industry practices, recent technology advancements, and stakeholder behavior. The objective here is to orient business leaders, technical architects, and procurement teams to the forces influencing adoption and to the practical levers available for capturing value. Emphasis is placed on integration strategies that span component selection, deployment choices, and project typologies, while also acknowledging the organizational and cultural work required to embed BIM as a repeatable capability rather than a one-off initiative.
A forward-looking analysis of the technological, regulatory, and delivery model shifts that are reshaping how Building Information Modeling is implemented across project lifecycles
The landscape for Building Information Modeling is undergoing transformative shifts driven by technological maturation, evolving delivery models, and heightened expectations for sustainability and digital continuity. Advances in cloud-native collaboration platforms and model-based data exchanges are redefining how teams coordinate across geographies, enabling near real-time model synchronization and shared data environments that reduce information latency and integration overhead. At the same time, improved APIs and open data standards are lowering barriers to interoperability, allowing specialized tools to plug into broader digital workflows and extend BIM’s reach into disciplines such as cost management and construction sequencing.
Concurrently, the industry is seeing a progressive move from isolated project-based BIM use toward enterprise-level implementations that encompass facility lifecycle management. This shift places a premium on governance, master data definitions, and role-based access to ensure model fidelity and trust. Sustainability mandates and regulatory expectations are also catalyzing the adoption of model-based analyses for energy performance and compliance reporting, nudging stakeholders to integrate performance data earlier in design processes. Taken together, these trends are reshaping procurement models, partnership structures, and the competencies required of both clients and delivery teams.
An assessment of how evolving United States tariff policies in 2025 could influence procurement, hardware availability, and service delivery dynamics for Building Information Modeling ecosystems
Tariff changes and trade policy adjustments can create ripple effects across the BIM ecosystem by influencing the cost and availability of hardware, software licensing models, and cross-border services. For organizations operating in complex supply chains, changes in tariffs necessitate reevaluation of procurement strategies for servers, workstations, and specialized sensors that support model creation and digital capture. Similarly, vendors that rely on hardware-dependent offerings or maintain regionally distributed support networks may adjust pricing, licensing terms, or service delivery footprints in response to altered trade conditions.
In addition, tariffs that affect imported engineering equipment or prefabricated building elements can alter project timelines and encourage greater reliance on local suppliers and modular construction approaches, which in turn elevates the importance of BIM-driven prefabrication workflows and digital twin readiness. For service providers, shifts in cross-border cost structures may prompt greater emphasis on remote delivery, automation, and standardized implementation packages that minimize the impact of logistics and hardware dependencies. Ultimately, tariff dynamics reinforce the need for organizations to diversify supplier relationships, stress-test procurement assumptions, and incorporate trade-sensitivity analyses into BIM program planning.
A comprehensive segmentation-driven perspective that clarifies how component choices, deployment modes, project scales, application uses, and end-user roles shape BIM adoption and value realization
Insights derived from component-level segmentation illuminate divergent priorities between software-centric and service-centric engagements. When focusing on the software component, considerations include platform interoperability, licensing flexibility, and analytic capabilities that support applications such as architectural design, structural design, and energy performance analysis. Conversely, the service component reflects demand for consulting and advisory expertise to define BIM strategy, implementation and system integration services to operationalize workflows, support and maintenance to ensure model integrity over time, and training and certification to uplift practitioner capabilities across project teams.
Deployment mode segmentation highlights trade-offs between cloud-based and on-premise choices, and within cloud-based options the distinctions between hybrid cloud, private cloud, and public cloud architectures matter for data sovereignty, latency, and cost predictability. Project size segmentation indicates that large projects often require robust governance frameworks and integrated model management, medium projects benefit from templated processes and scalable services, and small projects prioritize simplicity and rapid time-to-value. Application-focused segmentation underscores the range of BIM use cases from collaboration, clash detection, and visualization to construction management, cost estimation and quantity take-off, facility and asset management, MEP engineering, project scheduling and planning, and structural design, each demanding tailored workflows, data schemas, and stakeholder alignment. End user segmentation identifies distinct competency and procurement patterns among architects, civil and structural engineers, contractors, facility managers, and surveyors and BIM coordinators, with each role exerting different influence on tool selection, modeling standards, and validation practices.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Building Information Modeling market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Component
- Project Size
- Level Type
- Pricing Model
- Application
- End User
- Project Type
- Deployment Mode
A nuanced regional analysis revealing how geographic regulatory environments, talent pools, and procurement practices impact the implementation and scaling of BIM initiatives across global markets
Regional dynamics are shaping BIM adoption patterns in distinct ways, with geographic context influencing regulatory drivers, talent availability, and preferred delivery models. In the Americas, project portfolios often emphasize large infrastructure and commercial developments, driving attention toward enterprise collaboration platforms, robust integration with construction management systems, and solutions that support prefabrication and modular workflows. In Europe, the Middle East & Africa, regulatory frameworks and sustainability mandates have accelerated uptake of model-based energy and compliance analysis, while diverse market maturity levels across the region create opportunities for standardized training and certification programs. The Asia-Pacific region exhibits rapid digitization of construction processes and a strong emphasis on cloud-enabled collaboration to coordinate dense project pipelines and cross-border supply chains.
Across these regions, differences in procurement practices, data residency requirements, and existing IT infrastructure create variation in preferred deployment modes and partnership models. Transitioning from project-centric pilots to organization-wide BIM programs requires sensitivity to local contracting practices, labour models, and the availability of skilled practitioners, all of which vary significantly between the Americas, Europe, Middle East & Africa, and Asia-Pacific. Strategic implementations therefore balance global best practices with localized execution plans to ensure sustainable capability building and measurable improvements in project outcomes.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Building Information Modeling market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
A strategic overview of competitive positioning in the Building Information Modeling ecosystem emphasizing interoperability, domain specialization, and service-enabled delivery models
Competitive dynamics within the BIM ecosystem are driven by a mix of platform providers, specialist tool vendors, engineering consultancies, and system integrators that together form a complex supply landscape. Leading platform providers compete on interoperability, extensibility, and developer ecosystems that allow third-party applications to connect seamlessly to centralized model repositories. Specialist vendors differentiate through domain-specific capabilities such as advanced clash detection, MEP detailing, or high-fidelity structural analysis, often embedding automation and rule-based validation to reduce manual coordination tasks.
Service-oriented players are defining propositions around rapid implementation frameworks, managed model services, and certified training pathways that lower the barrier to adoption for clients with limited internal expertise. Partnerships between software vendors and systems integrators are increasingly important to deliver turnkey solutions that combine toolsets with predefined workflows and governance templates. For decision-makers, supplier selection should be informed by the provider’s ability to demonstrate successful integrations, long-term support commitments, and a roadmap that aligns with enterprise architecture and sustainability objectives. Emphasis should be placed on vendors that support open data standards, offer flexible commercial models, and have proven experience across comparable project typologies and regional contexts.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Building Information Modeling market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- 4M S.A.
- Accruent, LLC
- ArCADiasoft Chudzik sp.j.
- Asite Solutions Limited
- Autodesk, Inc.
- AVEVA Group PLC
- Bentley Systems, Incorporated
- Computer Methods International Corp.
- CYPE Ingenieros, S.A.
- Dassault Systèmes SE
- Graphisoft SE
- Hexagon AB
- ICON-BIM
- International Business Machines Corporation
- Kahua, Inc.
- MagiCAD Group Oy
- NavVis GmbH
- Nemetschek SE
- Newforma, Inc. by Ethos Capital LP
- Oracle Corporation
- Procore Technologies, Inc.
- Revizto, SA
- Schneider Electric SE
- Siemens AG
- Tejjy Inc
- Trimble Inc.
- TÜV Rheinland AG
Actionable recommendations for executives to operationalize Building Information Modeling through governance, capability building, vendor strategy, and sustainability-aligned integration
Industry leaders should approach BIM investments with a pragmatic, phased strategy that aligns technology selection with organizational capability building and measurable outcomes. Start by defining a clear governance framework and data standards that articulate roles, responsibilities, and model quality expectations, then prioritize pilot programs that validate interoperability, data handover processes, and integration with scheduling, cost, and asset management systems. Investing in training and certification ensures that designers, engineers, and contractors share common modeling conventions and understand how BIM artifacts support downstream workflows.
Procurement strategies should favor modular vendor ecosystems that enable best-of-breed integrations while avoiding vendor lock-in, and leaders should require evidence of open standards support as part of vendor evaluations. To mitigate supply-chain disruption and tariff sensitivity, diversify hardware and prefabrication suppliers, and design workflows that allow for remote support and offsite fabrication. Finally, embed sustainability and performance analysis early in design processes to align with regulatory expectations and long-term operational efficiency goals. By sequencing these initiatives and tracking outcomes through defined KPIs tied to rework reduction, coordination time, and asset handover quality, organizations can scale BIM from isolated use cases to enterprise capabilities.
A transparent, practitioner-centered research methodology combining interviews, secondary standards review, and comparative case analysis to validate insights on BIM implementation and adoption
This research synthesis draws on a triangulated methodology combining primary interviews with practitioners across design, construction, and facilities disciplines, secondary literature review of technical standards and regulatory documents, and analysis of observable implementation patterns across diverse project typologies. Primary inputs focused on implementation experiences, procurement preferences, and operational challenges, while secondary sources provided context on technology capabilities, open data standards, and emerging best practices. The approach emphasized cross-validation of claims through multiple independent practitioner perspectives to ensure robustness and reduce reliance on any single viewpoint.
Analytical methods included comparative case analysis to surface replicable implementation patterns, thematic coding of interview transcripts to identify common pain points and success factors, and scenario analysis to explore the implications of trade and procurement disruptions on delivery models. The methodology prioritized transparency about data sources and assumptions and sought to contextualize findings within prevailing industry trends without relying on speculative projections. Where specific practices or vendor capabilities were cited, they were corroborated across multiple practitioner interviews and supporting technical documentation.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Building Information Modeling market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Building Information Modeling Market, by Component
- Building Information Modeling Market, by Project Size
- Building Information Modeling Market, by Level Type
- Building Information Modeling Market, by Pricing Model
- Building Information Modeling Market, by Application
- Building Information Modeling Market, by End User
- Building Information Modeling Market, by Project Type
- Building Information Modeling Market, by Deployment Mode
- Building Information Modeling Market, by Region
- Building Information Modeling Market, by Group
- Building Information Modeling Market, by Country
- United States Building Information Modeling Market
- China Building Information Modeling Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 20]
- List of Tables [Total: 3021 ]
A conclusive synthesis underscoring the organizational, technical, and procurement imperatives required to scale Building Information Modeling from pilot projects to enterprise capability
In conclusion, Building Information Modeling has evolved into a cornerstone of modern project delivery that connects design intent with construction execution and operational management. Realizing its full potential requires more than software adoption; it demands organizational commitment to standards, investment in human capital, and thoughtful procurement and deployment strategies that reflect project scale and regional dynamics. As interoperability improves and cloud-enabled collaboration becomes more prevalent, the strategic value of BIM will increasingly accrue to organizations that can align governance, vendor ecosystems, and performance objectives.
Leaders who adopt a phased, outcomes-driven approach-anchored by pilot validation, robust training programs, and diversified supplier strategies-will be best positioned to leverage BIM as a repeatable capability that enhances coordination, reduces waste, and supports lifecycle performance objectives. The path to enterprise-level BIM is iterative: early wins build momentum, and sustained attention to data quality and integration unlocks broader organizational benefits over time.
A clear and compelling call to action inviting decision makers to secure a tailored Building Information Modeling research briefing and purchase the full report from an experienced sales lead
If you are ready to translate these strategic insights into practical decisions, reach out to Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing, to obtain the full research report and tailored briefing that aligns with your organizational priorities.
A direct engagement will provide a structured briefing that highlights the sections most relevant to your role, including deployment considerations, component and application implications, regional nuances, and competitive positioning. The briefing can be customized to focus on areas such as procurement strategy, partner selection, implementation roadmaps, and risk mitigation to accelerate value capture from Building Information Modeling initiatives. This next step is designed to transform the intelligence in this summary into an actionable plan that supports executive decision-making and operational integration across project lifecycles.
Contacting Ketan will initiate an exploratory conversation to clarify your objectives, identify which supplemental materials and appendices will be most useful, and arrange a timeline for delivery and follow-up discussions. For organizations seeking vendor shortlists, pilot program scopes, or executive briefings for stakeholders, this engagement will deliver the tailored insights required to move from insight to implementation with confidence.

- How big is the Building Information Modeling Market?
- What is the Building Information Modeling Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




