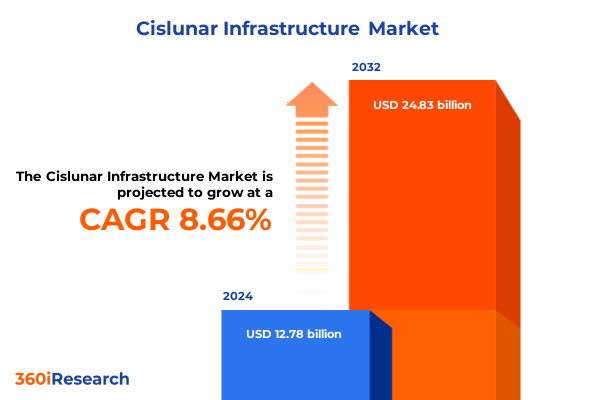
The Cislunar Infrastructure Market size was estimated at USD 13.84 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 14.99 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 8.71% to reach USD 24.83 billion by 2032.
Establishing the Imperative Strategic Framework and Unveiling the Emerging Dynamics of Cislunar Infrastructure for Next Generation Space Operations
The concept of cislunar infrastructure encompasses all the systems, platforms, and networks enabling sustainable operations between Earth and the Moon. Historically, human activity beyond low Earth orbit has been episodic and mission-driven, yet emerging government and commercial endeavors are catalyzing a paradigm shift toward persistent presence. The establishment of habitable stations in lunar orbit and on the surface, the deployment of in-space transportation vehicles, and the creation of propellant depots collectively form an interconnected framework that can support a diverse array of scientific, commercial, and defense missions.
Driven by ambitious initiatives such as the Artemis program and a growing appetite for lunar resource utilization, this infrastructure holds the promise of extending humanity’s reach into deep space. Governments are forging strategic partnerships with established aerospace corporations and innovative startups to develop modular systems that reduce mission risk and accelerate deployment. Meanwhile, advancements in electric propulsion, 3D-printed habitats, and autonomous robotics are converging to make cislunar operations more cost-effective and resilient.
This executive summary presents a comprehensive overview of the current state of cislunar infrastructure. It examines transformative shifts shaping the landscape, analyzes the cumulative impact of United States tariff policies in 2025, offers key segmentation and regional insights, profiles leading industry players, and provides actionable recommendations for decision-makers. By synthesizing these elements, this summary sets the stage for a deeper exploration of opportunities and challenges poised to define the next era of space exploration and commercialization.
Mapping the Disruptive Transformations in Technological, Regulatory, and Commercial Paradigms Redefining the Cislunar Infrastructure Ecosystem
The cislunar ecosystem is undergoing rapid transformation as technological breakthroughs intersect with evolving policy frameworks and commercial imperatives. On the technological front, the maturation of electric propulsion systems has enabled spacecraft to undertake extended missions between Earth orbit and lunar destinations more efficiently than ever before. Simultaneously, autonomous rendezvous and docking capabilities are being refined to support the assembly of modular space stations and in-orbit refueling depots, laying the groundwork for sustainable lunar logistics.
Regulatory landscapes are also shifting to accommodate novel commercial entrants and cross-border collaborations. The Artemis Accords have established principles for resource extraction and safe operations, fostering an environment of transparency and risk mitigation among participating nations. Moreover, national space agencies are streamlining licensing processes to incentivize private investment in lunar landers, habitats, and communications networks.
Commercial business models are converging on an integrated service approach that blends transportation, logistics, data relay, and power generation. Strategic partnerships between mission integrators, component suppliers, and end users are enabling vertically integrated value chains. Concurrently, geopolitical competition for lunar leadership is driving accelerated timelines, as emerging spacefaring nations seek to secure critical positions in cislunar supply chains. Together, these disruptive transformations are redefining how stakeholders conceive of and invest in infrastructure beyond Earth’s orbit.
Assessing the Cumulative Effects of United States Tariff Policies on Cislunar Infrastructure Supply Chains and Operational Viability in 2025
In 2025, cumulative United States tariff policies have introduced both challenges and incentives for cislunar infrastructure development. Broad-based Section 232 tariffs on steel and aluminum imports have elevated the cost structure for launch support hardware, affecting the manufacturing of aeroshells and structural components. At the same time, Section 301 tariffs targeting specific high-tech imports have increased pricing pressure on critical electric propulsion units and satellite communication subsystems.
These elevated import duties have compelled manufacturers to reexamine their supply chains, prompting a shift toward domestic sourcing agreements and the qualification of alternate suppliers from allied nations. To mitigate cost overruns, program managers are negotiating tariff exclusions for mission-critical hardware, leveraging defense and NASA waiver provisions. However, the timeframes associated with administrative relief processes have introduced schedule risks, potentially delaying planned deployment of logistics package elements and propellant tanker vehicles.
Conversely, the tariff landscape has catalyzed strategic investments in local production capabilities, driving greater vertical integration among component suppliers and prime contractors. This reorientation presents an opportunity to bolster resilience in the face of geopolitical uncertainty, ensuring that mission-critical subsystems for lunar landers and in-space transportation vehicles remain readily available. As cost and schedule pressures intensify, stakeholders must weigh the balance between short-term tariff impacts and long-term supply chain robustness.
Uncovering Critical Segmentation Insights Across Component, Technology, Module, Application, and End User Dimensions of Cislunar Infrastructure Markets
Insight into the cislunar infrastructure market emerges most clearly when viewed through a multidimensional segmentation lens. From a component perspective, the market comprises aeroshells, electric propulsion units, logistics packages, lunar landers, and propellant tanker or orbital transfer vehicle platforms. This component-level breakdown reveals where investment flows are concentrating, particularly in propulsion systems that extend mission range and in protective aeroshell designs for surface operations.
Examining the landscape by technology highlights three primary pillars: communication satellites that ensure data relay between lunar assets and ground control, in-space transportation vehicles that provide crew and cargo mobility, and space stations that serve as hubs for assembly, research, and refueling. Each technological domain advances at a distinct pace, with propulsion innovation often outpacing habitat and station development.
A module-centric view further clarifies the ecosystem, encompassing communication infrastructure, in-space services and logistics, power generation and storage solutions, space transportation and propulsion systems, and staging and operations platforms. By analyzing module-level dynamics, stakeholders can pinpoint the enabling capabilities required for a sustainable cislunar economy.
Considering applications, the market is driven by defense and security initiatives, mineral extraction endeavors, and scientific research objectives. Defense and security requirements emphasize space weapon systems and advanced surveillance technology, while mineral extraction focuses on regolith processing and resource mapping. Scientific research priorities range from astrobiology investigations to low gravity experiments, each demanding tailored infrastructure support.
Finally, end-user segmentation distinguishes government agencies, private enterprises, and research institutions, each with unique procurement cycles, risk tolerances, and mission profiles. When integrated, these segmentation dimensions provide a holistic understanding of where value is created and which market segments warrant targeted strategic attention.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Cislunar Infrastructure market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Component
- Technology
- Module
- Application
- End User
Analyzing Regional Dynamics and Strategic Drivers Across Americas, Europe Middle East Africa, and Asia Pacific for Cislunar Infrastructure Development
Regional dynamics play a pivotal role in shaping the future of cislunar infrastructure development. In the Americas, a combination of government-led exploration programs and commercially funded lunar missions is driving robust ecosystem growth. Established prime contractors are collaborating with agile startups to develop next-generation landers and orbital logistics hubs, supported by policy frameworks that incentivize commercial investment and public-private partnerships.
Across Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, strategic initiatives are aligning around the European Space Agency’s contributions to the lunar gateway and regional defense consortia that aim to secure critical communication and surveillance capabilities. Collaborative ventures between national space agencies and private firms are advancing modular power systems and in-orbit servicing platforms, reinforcing the region’s position as a key contributor to the global cislunar supply chain.
In the Asia-Pacific region, established and emerging spacefaring nations are rapidly expanding their lunar ambitions. China’s Chang’e program continues to push surface exploration boundaries, while Japan’s SLIM lander and India’s Chandrayaan missions underscore a commitment to scientific discovery and resource assessment. Concurrently, private enterprises in the region are developing reusable launch systems, in-space propulsion technologies, and lunar communication networks, often in partnership with local government agencies.
These regional insights underscore the importance of geopolitical context, funding mechanisms, and collaborative models in determining where strategic investments will yield the greatest impact for cislunar infrastructure.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Cislunar Infrastructure market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Profiling Leading Industry Players and Strategic Alliances Driving Innovation and Competitive Positioning in the Cislunar Infrastructure Domain
A detailed view of the competitive landscape reveals a diverse mix of established aerospace giants and innovative newcomers vying for leadership in cislunar infrastructure. Large prime contractors are leveraging decades of experience in deep space systems to secure flagship programs involving lunar gateway habitats and propulsion modules. Meanwhile, emerging companies are carving out niches by developing specialized subsystems such as 3D-printed propellant tanks, advanced electric thrusters, and autonomous lander platforms optimized for small payloads.
Strategic alliances between these players are increasingly common, with joint ventures formed to share technical expertise, manufacturing capacity, and program risk. For example, partnerships that unify communication satellite integrators with in-space logistics providers create end-to-end solutions for persistent lunar operations. Equally, collaborations between defense-focused firms and commercial entrants are facilitating the rapid fielding of surveillance and navigation systems tailored to cislunar domains.
The competitive intensity is further heightened by the entry of technology companies from adjacent sectors, including terrestrial telecommunications and advanced materials manufacturing. Their participation brings fresh perspectives on digital twin modeling, optical communication networks, and lightweight composite structures. Collectively, these strategic moves are reshaping the competitive contours of the market, demanding that incumbents and new entrants alike adopt agile business models and foster cross-industry innovation.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Cislunar Infrastructure market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- Advanced Space, LLC
- Airbus SE
- ArianeGroup SAS
- Astrobotic Technology, Inc.
- Blue Origin Enterprises, L.P.
- China National Space Administration
- European Space Agency
- Firefly Aerospace Private Limited
- General Atomics
- GITAI USA Inc.
- Intuitive Machines, Inc.
- ispace,inc.
- Leidos Holdings, Inc.
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Maxar Technologies Holdings Inc.
- Momentus Inc.
- Moon Express Inc.
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- Quantum Space, LLC
- Rocket Lab USA, Inc.
- Roscosmos State Corporation
- Safran S.A.
- Sierra Nevada Corporation
- Space Exploration Technologies Corp.
- Telespazio S.p.A.
- Thales Group
- The Boeing Company
- Viasat Inc.
Presenting Actionable Strategic Recommendations to Guide Industry Leaders in Building Resilient, Collaborative, and Future Ready Cislunar Infrastructure Capabilities
To navigate the complexities of the cislunar infrastructure landscape, industry leaders must adopt a series of strategic imperatives. First, diversifying supply chains to incorporate multiple qualified suppliers and to localize critical manufacturing capabilities can mitigate the impact of future trade policy changes. Secondly, forging public-private partnerships with space agencies and defense organizations accelerates development timelines and reduces capital requirements through shared risk.
Moreover, prioritizing investment in electric propulsion and in-orbit refueling infrastructure will extend mission durations and reduce dependency on Earth-launched propellant. Embracing standardized interfaces and open architecture principles can lower integration costs and foster interoperability between modules from different providers. Additionally, embedding digital twin simulations in design and operations workflows enhances predictive maintenance and optimizes resource utilization.
Furthermore, engaging proactively with regulatory bodies to advocate for tariff relief on mission-critical hardware and to influence emerging cislunar governance frameworks will create a more predictable business environment. Finally, integrating sustainability and circular resource management principles-from regolith recycling to power storage reuse-will not only align with international norms but also ensure the long-term resilience of lunar infrastructure networks.
Detailing a Comprehensive Research Methodology Incorporating Primary and Secondary Intelligence for Robust Cislunar Infrastructure Insights and Validation
This research utilizes a multi-stage methodology to deliver comprehensive insights into the cislunar infrastructure market. The secondary research phase encompassed the review of governmental publications, regulatory filings, technical white papers, conference proceedings, and peer-reviewed journal articles to establish foundational context and to identify prevailing industry trends. Patent databases and supplier catalogs were also examined to map technological advancements and component availability.
In the primary research phase, in-depth interviews were conducted with decision-makers at space agencies, defense departments, leading aerospace manufacturers, startup executives, and academic researchers. These conversations provided firsthand perspectives on program roadmaps, procurement strategies, and emerging collaboration models. Insights were further enriched by site visits to key manufacturing facilities and mission control centers, enabling verification of capabilities and operational workflows.
Data triangulation methods were employed to reconcile information across multiple sources, ensuring consistency and reliability of findings. Quantitative inputs such as contract awards, launch manifests, and technology readiness levels were cross-checked against qualitative assessments from industry experts. This rigorous approach underpins the actionable intelligence and strategic recommendations presented herein, offering stakeholders a validated and nuanced understanding of the cislunar infrastructure landscape.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Cislunar Infrastructure market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Cislunar Infrastructure Market, by Component
- Cislunar Infrastructure Market, by Technology
- Cislunar Infrastructure Market, by Module
- Cislunar Infrastructure Market, by Application
- Cislunar Infrastructure Market, by End User
- Cislunar Infrastructure Market, by Region
- Cislunar Infrastructure Market, by Group
- Cislunar Infrastructure Market, by Country
- United States Cislunar Infrastructure Market
- China Cislunar Infrastructure Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 17]
- List of Tables [Total: 1431 ]
Synthesizing Key Findings and Strategic Implications to Outline the Path Forward in Accelerating Cislunar Infrastructure Advancements and Partnerships
In synthesizing the insights across transformational shifts, tariff impacts, segmentation, regional dynamics, and competitive positioning, a clear narrative emerges: cislunar infrastructure is transitioning from conceptual frameworks to operational realities. The convergence of advanced propulsion technologies, modular station architectures, and supportive policy initiatives signals a new era of sustained lunar presence.
Throughout this analysis, it becomes evident that resilience and adaptability will define success. Supply chain diversification in response to tariff pressures, collaborative public-private partnerships that pool technical and financial resources, and the embracement of open architecture standards collectively form the strategic pillars for future growth. Regional initiatives across the Americas, EMEA, and Asia-Pacific underscore the importance of geopolitical alignment and shared investment priorities in driving mission outcomes.
Looking ahead, the cislunar domain presents unparalleled opportunities for scientific discovery, commercial enterprise, and national security. By integrating the recommendations outlined in this summary-spanning supply chain optimization, technology investment, regulatory engagement, and sustainability-stakeholders can position themselves at the forefront of a rapidly evolving space economy. The path forward demands vision, coordination, and strategic agility to realize the promise of infrastructure that will support humanity’s next giant leap.
Inviting Stakeholder Engagement with Associate Director of Sales and Marketing for Access to In-Depth Cislunar Infrastructure Market Research Report
For organizations poised to navigate the rapidly evolving cislunar landscape, securing comprehensive and forward-looking intelligence is critical for informed decision-making. By partnering with Ketan Rohom, Associate Director of Sales & Marketing, you gain direct access to an in-depth market research report that synthesizes qualitative insights, strategic recommendations, and robust regional and segmentation analyses. This meticulously crafted report distills the disruptive shifts, supply chain considerations, and competitive dynamics shaping cislunar infrastructure development into actionable intelligence. Whether you are a government agency evaluating procurement strategies, a private enterprise seeking partnership opportunities, or a research institution forging new scientific frontiers, this market research report provides the clarity and depth required to chart a confident course beyond Earth’s orbit. Reach out to Ketan Rohom today to explore customized engagement options and to obtain the comprehensive data and expert analysis necessary to drive your cislunar initiatives forward

- How big is the Cislunar Infrastructure Market?
- What is the Cislunar Infrastructure Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




