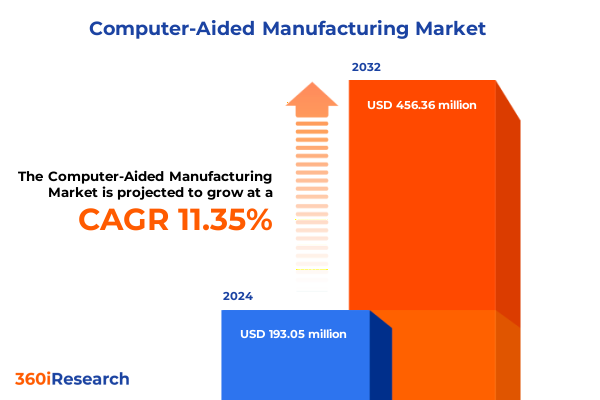
The Computer-Aided Manufacturing Market size was estimated at USD 193.05 million in 2024 and expected to reach USD 214.30 million in 2025, at a CAGR of 11.35% to reach USD 456.36 million by 2032.
A focused orientation that positions computer-aided manufacturing as the connective tissue between digital design and resilient industrial production across modern supply chains
This executive summary opens with a focused orientation that frames computer-aided manufacturing as a core enabler of industrial competitiveness and supply-chain resilience. The introduction situates CAM not merely as a collection of tools, but as the connective tissue between design intent and physical production, where software-driven toolpath planning, integrated simulation, and services such as implementation and support converge to accelerate throughput and reduce time-to-quality. As manufacturing ecosystems grow more distributed and digitally instrumented, CAM’s role extends beyond NC code generation to encompass interoperability with PLM, ERP, and factory automation stacks, enabling closed-loop feedback from the shop floor back to engineering.
Moving from capability to consequence, this section establishes the report’s scope: an examination of CAM components and services; deployment choices that shape agility; capability tiers from basic 2D operations to advanced multi-axis strategies; application contexts spanning subtractive and additive processes; organization-level adoption patterns; and the industry verticals where CAM is mission-critical. Taken together, this introduction clarifies that stakeholders must evaluate CAM investments not in isolation but as configurable systems that touch product quality, capital utilization, and supply-chain exposure. The framing prepares the reader for detailed analysis of structural shifts, policy-driven disruptions, segmentation-specific intelligence, and recommendations for leaders who must balance speed, precision, and resilience.
How rapid advances in automation, AI, hybrid manufacturing, and supply-chain reshoring are redistributing capabilities across the CAM ecosystem and reshaping adoption priorities
The landscape for computer-aided manufacturing is being reshaped by technological acceleration and strategic reconfiguration of global supply chains. Advances in automation and AI are compressing cycle times and lowering the barrier to programming complex multi-axis machining, thereby democratizing capabilities that were previously the preserve of high-end shops. Simultaneously, hybrid workflows that combine additive and subtractive operations are creating new process topologies that demand CAM systems able to orchestrate multimodal toolpaths and manage mixed-fixture operations. As a result, workflows that once required distinct CAD, CAM, and PLM silos are converging into more integrated platforms that emphasize data continuity and version control across the product lifecycle.
At the same time, operational priorities around resilience and nearshoring are elevating supply-chain visibility requirements and increasing demand for CAM deployments that support rapid requalification and vendor diversification. These forces are reinforced by capital investment trends in smart manufacturing: manufacturers are prioritizing sensors, factory automation hardware, and cloud-enabled analytics to unlock predictive maintenance and adaptive machining strategies, making CAM an active participant in the digital thread rather than a downstream, static planning tool. Taken together, these technological and strategic shifts are expanding the remit of CAM vendors and creating new windows for providers that can deliver secure, scalable, and tightly integrated solutions.
A concise analysis of how 2024–2025 U.S. tariff adjustments on steel, aluminum, and critical technology inputs reshaped sourcing costs and capital equipment decisions
Tariff policy and trade measures enacted in 2024 and 2025 have created an elevated policy backdrop that directly affects material inputs, capital equipment sourcing, and the economics of cross-border manufacturing. In particular, U.S. administration actions in 2025 increased tariff rates on imported steel and aluminum, raising the effective duty on those commodity inputs and derivative articles as part of a Section 232 adjustment that became effective in early June 2025; those changes altered cost structures for machine builders, tooling suppliers, and manufacturers that source metal-intensive components. The proclamation raising tariffs on steel and aluminum to higher ad valorem levels in June 2025 is a primary policy event that supply-chain and procurement functions must incorporate into near-term sourcing and inventory decisions.
In parallel, the Office of the U.S. Trade Representative completed statutory reviews of Section 301 actions that led to increased duties on selected technology-related inputs, including higher rates applied to certain wafers, polysilicon, and tungsten products effective at the start of 2025; those measures have direct implications for CAM-dependent segments of the manufacturing base that rely on semiconductor equipment, specialized tooling, and photovoltaic-grade materials. To manage near-term exposure, manufacturers and OEMs have been monitoring USTR exclusion lists and shorter-term extensions, as USTR announced time-limited extensions of certain product exclusions in mid-2025 to provide temporary reprieve for selected entries. These policy adjustments have increased the importance of tariff classification accuracy, alternative sourcing evaluation, and scenario-based cost modeling when procuring machine tools, cutting inserts, and specialty metals.
The combined effect is not only higher landed costs in affected product categories but also an incentive to re-evaluate where higher-value, metal-intensive operations are staged. For many manufacturers this has meant accelerated qualification of domestic or allied suppliers, increased emphasis on material yield and nesting efficiency in CAM programming, and a reevaluation of capital equipment total cost of ownership that incorporates revised duty profiles and potential retaliatory measures. Given the dynamic nature of tariff policy, procurement teams should maintain continuous monitoring of HTSUS classifications, USTR notices, and White House proclamations, and integrate tariff-sensitivity analysis into their capital and tooling investment decisions to reduce unanticipated margin erosion.
Clear segmentation intelligence showing how component, deployment, capability, application, organization size, and industry vertical distinctions determine CAM requirements and vendor strategies
Segmentation insights reveal where CAM investments will deliver the greatest operational leverage and where vendors must refine product and go-to-market strategies. When component segmentation is considered-distinguishing services and software, while recognizing that services encompass consulting, implementation, and support and maintenance and that software splits between integrated CAM suites and standalone CAM packages-buyers increasingly favor offers that combine predictable services with modular software licensing that supports both shop-floor continuity and engineering innovation. This hybrid preference reflects a need for implementation programs that reduce deployment risk while preserving upgrade flexibility.
Regarding deployment mode, distinctions between cloud-based and on-premise options matter because cloud deployments accelerate collaboration and remote simulation while on-premise installations continue to be required for highly regulated facilities or where data sovereignty and latency constraints dictate local control. Capability segmentation across 2D, 3D, and multi-axis tiers highlights how user requirements diverge: 2D remains essential for high-volume, well-defined tasks, 3D addresses more complex geometries and cavity work, and multi-axis capabilities unlock the most advanced part families used in aerospace and medical devices. Application-focused segmentation-spanning 3D printing, drilling, grinding, milling, and turning-shows that CAM solutions must support toolpath strategies for both additive and subtractive processes and manage transitions in hybrid cells. Organization-size segmentation differentiates adoption and procurement behaviors between large enterprises and small and medium enterprises, with larger firms prioritizing platform integration and governance while SMEs seek predictable total cost and rapid time-to-value. Finally, industry vertical segmentation across aerospace and defense, automotive, consumer goods, electronics, healthcare and medical devices, and industrial machinery demonstrates that CAM product roadmaps and services models must be vertically informed: aerospace and medical demand traceability and multi-axis precision, automotive emphasizes cycle-time optimization and scalability, electronics and consumer goods prioritize micro-machining and throughput, and industrial machinery focuses on robustness and lifecycle support. These segmentation lenses should guide product development, channel strategy, and pricing design so that vendor roadmaps align with the differentiated needs of manufacturing end-users.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Computer-Aided Manufacturing market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Component
- Deployment Mode
- Capability
- Complexity Tier
- Organization Size
- Application
- Industry Vertical
How regional demand patterns across the Americas, Europe Middle East & Africa, and Asia-Pacific create differentiated adoption paths, risks, and go-to-market models for CAM providers
Regional dynamics are shaping demand patterns, competitive intensity, and risk exposures across the CAM landscape. In the Americas, buyers are placing premium value on supply-chain resilience, nearshoring, and the ability to requalify suppliers quickly; these priorities are accelerating demand for solutions that support rapid reprogramming, material nesting efficiency, and local supplier integration. The Americas region also shows a preference for services-led deployments that reduce internal implementation burden and provide rapid support for scale-up of automated machining cells.
Across Europe, the Middle East & Africa, the EMR region emphasizes regulatory compliance, energy efficiency, and sustainability in procurement decisions, driving interest in CAM features that optimize material usage and toolpaths for energy reduction. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific remains the most diverse and capacity-rich market, combining high-volume contract manufacturers with advanced aerospace and electronics clusters that require multi-axis precision and hybrid additive-subtractive capabilities. Differences among these regions in labor cost, supplier networks, and policy drivers create distinct commercial models for vendors: subscription and cloud-native models can scale quickly in APAC, whereas partnership and localized support networks remain critical in the Americas and EMR to address compliance and installed-base modernization.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Computer-Aided Manufacturing market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Why vendors with integrated software suites, repeatable services playbooks, localized support, and demonstrated cybersecurity controls lead the competitive field in CAM solutions
Competitive dynamics in the CAM market center on the ability to deliver integrated software capabilities, robust services ecosystems, and secure deployment options. Leading suppliers differentiate through depth of multi-axis capabilities, strength in hybrid additive-subtractive workflows, and the maturity of their simulation, verification, and post-processing toolsets. Beyond core software, competitive advantage increasingly depends on the quality of implementation programs, including parameterized templates, digital-twin configuration, and ongoing support and maintenance contracts that reduce downtime and accelerate ROI.
Service partners and system integrators play a decisive role in converting feature-rich software into production-ready solutions. Firms that combine experienced consulting with repeatable implementation playbooks and localized spare-parts logistics achieve higher retention in larger accounts. For vendors targeting small and medium enterprises, simplified licensing, pay-for-use deployment options, and stronger out-of-the-box machining libraries lower the adoption barrier. Cybersecurity and IP protection have also become differentiators: customers evaluate how vendors secure CAM data, manage access to post-processed code, and support segregated environments for proprietary designs. Those vendors who articulate a clear value proposition across the lifecycle-from initial setup through ongoing optimizations-are positioned to capture the growing share of CAM-driven modernization programs.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Computer-Aided Manufacturing market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- 3d Systems, Inc.
- Autodesk, Inc.
- Bentley Systems, Incorporated
- Bobcad-Cam, Inc.
- Cascade Parent Limited
- CNC Software, LLC
- Dassault Systèmes SE
- GRZ Software LLC
- HCL Technologies Limited
- Hexagon AB
- Hypertherm, Inc.
- Makera Technology (Hong Kong) Company Limited
- MecSoft Corporation
- NTT DATA Group Corporation
- OPEN MIND Technologies AG
- Palette CAD AG
- PTC Inc.
- Sandvik Group
- Schott Systeme GmbH
- Siemens AG
- SigmaNEST
- SmartCAMcnc
- SolidCAM Ltd.
- Synopsys Inc.
- Tebis Technische Informationssysteme AG
- TOPSOLID SAS
- Trimble Inc.
- Zwsoft Co., Ltd.
Actionable strategic moves for manufacturers and vendors to mitigate tariff risk, close skills gaps, and capture value from hybrid CAM and digital thread approaches
Leaders should prioritize a set of pragmatic actions to secure near-term resilience while positioning for long-term competitiveness. First, integrate tariff-sensitivity and sourcing scenarios into capital-equipment procurement and tooling budgets so that duty changes do not trigger margin erosion; this includes validating HTSUS classifications, modeling landed costs under alternative duty regimes, and pre-qualifying domestic or allied suppliers to shorten qualification lead times. Second, accelerate adoption of hybrid CAM capabilities that support additive-subtractive operations and multi-axis machining, and couple those investments with training and implementation services to close operator skill gaps and reduce cycle-time variability.
Third, adopt an architectural approach to data: unify CAM with PLM and factory execution systems to create a durable digital thread that supports simulation-driven design, tool-life analytics, and predictive maintenance. Fourth, evaluate deployment models across cloud-based and on-premise options against regulatory and latency constraints and choose a hybrid operating model that balances collaboration with control. Finally, vendors and buyers should build modular commercial terms that combine a base level of support and maintenance with optional premium services for onboarding, advanced simulation, and field optimization; this reduces procurement friction and aligns incentives for continuous performance improvement.
A transparent mixed-methods research design combining primary interviews, vendor briefings, shop-floor validation, policy review, and scenario-based tariff sensitivity analysis
The research underpinning this report used a mixed-methods approach that combines primary interviews, vendor demonstrations, and a structured review of policy pronouncements and published industry surveys. Primary research included structured interviews with manufacturing executives, CAM product leaders, and systems integrators, supplemented by in-depth vendor briefings and shop-floor site visits to validate capability claims and implementation practices. Secondary research synthesized official policy documents, trade announcements, and published surveys on smart manufacturing investments to triangulate trends and validate practitioner sentiment.
Analytical methods included scenario modeling to quantify tariff sensitivity across representative tool and material categories, capability-mapping to align software features with application requirements, and buyer persona analysis to distinguish procurement behavior by organization size and vertical. Extensive cross-validation was performed between primary insights and public policy sources to ensure that recommendations reflect the latest regulatory posture and operational constraints. The methodology emphasizes transparency: annexes provide the interview protocol, a description of the scenario assumptions, and an index of cited official documents and surveys used to support the analysis.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Computer-Aided Manufacturing market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Computer-Aided Manufacturing Market, by Component
- Computer-Aided Manufacturing Market, by Deployment Mode
- Computer-Aided Manufacturing Market, by Capability
- Computer-Aided Manufacturing Market, by Complexity Tier
- Computer-Aided Manufacturing Market, by Organization Size
- Computer-Aided Manufacturing Market, by Application
- Computer-Aided Manufacturing Market, by Industry Vertical
- Computer-Aided Manufacturing Market, by Region
- Computer-Aided Manufacturing Market, by Group
- Computer-Aided Manufacturing Market, by Country
- United States Computer-Aided Manufacturing Market
- China Computer-Aided Manufacturing Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 19]
- List of Tables [Total: 1590 ]
A decisive conclusion that CAM must be treated as a systems-level capability linking procurement, digital integration, and hybrid production to sustain competitiveness under shifting policy and technology conditions
In conclusion, computer-aided manufacturing sits at an inflection point where policy, technology, and supply-chain strategy intersect to reshape how parts are designed, programmed, and produced. The confluence of elevated tariff activity on critical metals and selected technology inputs, the maturing of hybrid additive-subtractive processes, and the accelerating adoption of smart-manufacturing enablers means that CAM decisions must be made with both operational precision and strategic foresight. Organizations that couple investments in multi-axis and hybrid CAM capabilities with disciplined procurement practices and digital-thread integration will be better positioned to protect margins, shorten lead times, and capitalize on opportunities created by regional resourcing shifts.
Ultimately, the most durable advantage will accrue to enterprises and vendors that treat CAM as a systems-level capability-one that requires coordinated changes across people, processes, and technology-rather than a point-solution. By embedding CAM into broader digital transformation initiatives, companies can not only sustain manufacturing performance under changing tariff regimes but also unlock new forms of design freedom and production agility that define next-generation competitiveness.
Directly engage with the Associate Director of Sales & Marketing to secure the comprehensive CAM market report and bespoke briefings tailored to your operational needs
To purchase the full market research report and receive a tailored briefing on how the latest supply chain and policy developments affect your operations and procurement strategy, please contact Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing. Ketan can arrange a customized demonstration of the report’s findings, provide licensing options, and coordinate bespoke advisory support for implementation and competitive benchmarking. Prospective buyers are encouraged to request the executive briefing packet and the annex containing full methodology, HTS-coded tariff tables, and supplier due-diligence templates. For buyers seeking immediate actionable intelligence, Ketan can prioritize delivery of the regulatory-impact appendix and a practitioner’s playbook that translates the report’s strategic implications into vendor selection criteria and deployment roadmaps

- How big is the Computer-Aided Manufacturing Market?
- What is the Computer-Aided Manufacturing Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




