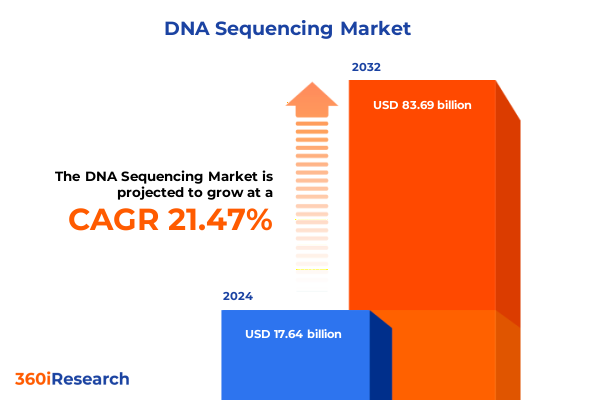
The DNA Sequencing Market size was estimated at USD 21.27 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 25.72 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 21.61% to reach USD 83.69 billion by 2032.
DNA sequencing enters a pivotal 2025 inflection point as performance soars, regulation recalibrates, and competitive dynamics reshape value chains
DNA sequencing stands at a pivotal moment in 2025. Performance has advanced at both ends of the throughput spectrum, while new chemistries and workflows are making previously specialized applications routine. At the same time, policy and trade developments are reshaping compliance obligations and supply chain calculus, demanding that leaders pair scientific ambition with operational discipline. In this environment, the question is no longer whether sequencing will permeate discovery, diagnostics, and applied markets-it is how organizations will compete on accuracy, speed, reliability, and total cost of ownership.
Technology trajectories reinforce this inflection point. High‑throughput short‑read systems have extended their lead in data quality and scalability, supported by iterative chemistry and software updates. Long‑read platforms, once reserved for specialized projects, now offer practical throughput for population‑scale structural variation and methylation analysis, while portable devices have improved accuracy and ecosystem readiness for field and real‑time use. Meanwhile, the competitive field has broadened with new entrants delivering alternative cost curves and partnering strategies that expand access through service providers and compatibility programs, and with incumbents re‑focusing core portfolios following portfolio realignment and divestitures. Notably, the separation of a prominent early cancer screening business has allowed a leading sequencer manufacturer to re‑center on platforms and workflows, underscoring a wider shift back to core sequencing value creation.
Policy and regulatory context is equally dynamic. The United States moved in 2024 to increase oversight of laboratory‑developed tests but, as of March 31, 2025, a federal court vacated the rule, resetting short‑term compliance expectations even as debates continue about the optimal oversight model. In Europe, transition timelines for in vitro diagnostic regulation have been extended under defined conditions to safeguard test availability while manufacturers complete conformity assessment, a change that shapes go‑to‑market plans for sequencing‑based assays. These developments, together with evolving export controls and tariff policy, make regulatory strategy and supply assurance central to sequencing execution in 2025.
Breakthrough chemistries, long‑read maturation, multi‑omics integration, and AI‑ready informatics collectively redefine the boundaries of sequencing workflows
Several forces are rewriting the practical limits of sequencing workflows. On the short‑read side, iterative chemistry and control‑software upgrades have lifted base‑quality distributions and improved run robustness, supporting higher throughput with fewer special‑case recipes. Benchtop systems have simultaneously pushed accuracy forward-some reporting Q50‑class datasets under defined conditions-while introducing on‑flow‑cell workflow simplifications that reduce hands‑on time and broaden compatibility with existing libraries. Together, these improvements are lowering barriers for labs seeking to expand from panels to exomes or to accelerate single‑cell and spatial omics pipelines without sacrificing precision.
Long‑read sequencing has matured into a scalable option for comprehensive genome and epigenome insight. Flagship platforms now deliver high‑fidelity reads at throughputs suitable for cohort studies, while newer short‑read instruments from the same vendors extend accuracy innovations into complementary applications. At the same time, nanopore‑based systems have advanced raw and duplex accuracies through chemistry and pore updates, enabling Q20+ single‑molecule performance with options to elevate to approximately Q30 through duplex strategies. These gains expand use cases from rapid infectious disease work to complex genome assembly and methylation profiling within unified workflows.
The market is also experiencing an architectural shift in how sequencing capacity is accessed. New entrants emphasizing wafer‑scale architectures and alternative imaging modalities are building global networks of certified service providers, creating elastic access to high‑volume sequencing without immediate capital expenditure. Such networks have been complemented by partnerships with single‑cell leaders and large research consortia to generate data at unprecedented scale, reinforcing a trend toward decoupling sample generation, sequencing, and analytics across specialized partners. This modularity is changing procurement playbooks and strengthening the role of interoperability and data standards in competitive differentiation.
Finally, portfolio focus and ecosystem compatibility are reshaping competitive dynamics. After completing the separation of a high‑profile liquid biopsy business in mid‑2024, a major incumbent sharpened emphasis on core platforms and informatics, while other providers broadened compatibility programs to embrace single‑cell and spatial workflows. Litigation in spatial biology continued to influence product availability and roadmap decisions into 2025, leading to injunctions with carve‑outs to minimize disruption for existing instrument users. In aggregate, these shifts push the field toward open, standards‑driven interoperability, where chemistry, sample prep, and analysis tools must work seamlessly across vendors to unlock end‑to‑end productivity.
Cumulative 2025 impact of U.S. tariffs and export controls reshapes inputs, costs, and localization strategies across instruments, consumables, and data infrastructure
Trade and industrial policy changes now exert a meaningful, cumulative influence on the economics and risk profile of sequencing. On January 1, 2025, tariff increases announced in December 2024 took effect for specific inputs such as wafers and polysilicon, alongside measures on certain tungsten products. These follow a pattern of targeted increases across strategic sectors, including earlier actions affecting medical consumables and semiconductors, with staggered effective dates. For sequencing stakeholders, the implications cascade from semiconductor sourcing for instruments and compute infrastructure to metals and precision components embedded in flow cells and ancillary lab hardware.
Export controls add another layer. Since 2022, the United States has progressively tightened restrictions on advanced computing items and semiconductor manufacturing equipment destined for countries of concern, updating rules in October 2023, clarifying scope in April 2024, strengthening measures in December 2024, and further enhancing due‑diligence requirements in January 2025. For genomics, these actions can indirectly shape availability and lead times for GPUs and advanced memory used in basecalling, secondary analysis, and AI‑assisted interpretation, as well as influence cross‑border manufacturing plans for electronics and optics within sequencing instruments. Procurement, therefore, increasingly requires parallel strategies for hardware resilience, including multi‑vendor qualification, forward buys for critical compute, and regionalized data processing.
The operational bottom line in 2025 is a re‑balancing of landed costs and risk. While some suppliers have diversified production outside higher‑tariff or higher‑restriction corridors, many buyers continue to face price‑stability uncertainties for select consumables, sterile lab items, and electronics. Leaders are responding with dual‑source frameworks for core reagents, re‑negotiated service‑level agreements that prioritize spare‑parts availability, and closer collaboration with logistics partners to hedge against port delays and customs variability. The net effect is a shift from cost‑only optimization to a broader total‑resilience calculus, where inventory positioning, quality assurance across sites, and transparent bill‑of‑materials mapping become competitive capabilities rather than back‑office hygiene.
Segmentation insights reveal where offerings, technologies, samples, applications, and end users coalesce to drive adoption, differentiation, and workflow stickiness
Offerings continue to stratify around four anchors-consumables and reagents, instruments and platforms, services, and software-but the frontier is not at the category level; it lies in how these elements are orchestrated into end‑to‑end workflows. In consumables and reagents, sequencing kits remain the growth engine as chemistry refreshes translate quickly into measurable gains in data quality and throughput. Enzymes and buffers contribute to run consistency and turnaround time, while primers and probes are being tuned for higher‑plex panels and lower background, improving variant detection in challenging matrices. Within instruments and platforms, the center of gravity spans high‑throughput sequencers for population‑scale work, dedicated library preparation systems that compress hands‑on time, PCR machines that anchor upstream assay fidelity, and flow‑cell hardware whose microfluidics and materials science directly influence yield. Services have bifurcated into contract sequencing at scale and bioinformatics and data analysis offerings that act as force multipliers for lean teams; the best‑performing service models are increasingly bundled with technical support and maintenance, reducing downtime and smoothing the learning curve for new applications.
Technology choices are now guided less by ideology and more by fitness to task. Short‑read next‑generation sequencing remains the default for many workflows where depth and accuracy at scale are paramount, benefitting from innovations such as sequencing‑by‑synthesis enhancements and alternative chemistries that expand system choice. Third‑generation long‑read approaches offer decisive advantages for structural variants, repeat expansions, and direct methylation calls, and are crossing into mainstream use as throughput and cost curves improve. Sanger sequencing, while no longer the workhorse for discovery, retains an important role for targeted confirmation and low‑complexity assays where simplicity and traceability are prized. Epigenetic sequencing is gaining strategic weight, with bisulfite‑based methods and chromatin immunoprecipitation workflows enabling methylome and protein‑DNA interaction maps that complement genomic variation data for a more complete biological narrative.
Sample diversity is reshaping laboratory design and quality systems. Human specimens span blood, saliva and buccal swab, urine, cell‑free DNA, tissue, and plasma, each with distinct pre‑analytical sensitivities and contamination risks that affect downstream library performance. Animal, plant, microbial, and environmental samples introduce additional variables, from lignified plant tissues to low‑biomass environmental swabs, and from microbial communities rich in bacteria, viruses, fungi, and archaea to agricultural samples requiring contamination control and reference genome strategies. The result is a premium on standardized intake, sample tracking, and protocol branching that preserves data quality across heterogeneous inputs.
Applications continue to broaden. Clinical diagnostics encompass oncology, infectious disease, rare and inherited disorder testing, reproductive health and prenatal assessments, and newborn screening-each with different evidence thresholds, turnaround imperatives, and reimbursement pathways. Research use remains expansive, with genomics and transcriptomics, functional genomics, and epigenetics research fueling instrument utilization. In biopharma, sequencing underpins drug discovery and development through biomarker discovery, companion diagnostic development, and target identification and validation, while agrigenomics centers on plant breeding and trait discovery and crop pathogen surveillance. Forensics and security maintain exacting requirements across human identification, criminal investigations, and disaster victim identification, and environmental and metagenomic studies continue to migrate from pilot to operational monitoring.
End‑user segments align with these patterns. Academic and research institutions-including government research institutes and university laboratories-serve as early adopters and method developers, bridging to translational use. Contract research organizations provide elastic capacity and cross‑platform expertise, while hospitals and diagnostic laboratories focus on clinically validated workflows and quality accreditation. Pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies integrate sequencing throughout R&D, clinical development, and post‑market studies, demanding interoperable data systems and predictable operating costs. Together, these segments illustrate why platform choice is no longer a single decision; it is an evolving portfolio strategy tuned to sample mix, application roadmaps, and evidence requirements.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the DNA Sequencing market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Offerings
- Technology Type
- Sample Type
- Application
- End User
Regional dynamics across the Americas, Europe–Middle East–Africa, and Asia‑Pacific reveal divergent regulatory tides, funding climates, and adoption pathways
In the Americas, the interplay of scientific scale, payer coverage maturation, and legal‑regulatory recalibration sets the pace. U.S. academic medical centers and consortium projects continue to push multi‑omic discovery, while clinical laboratories prioritize assay consolidation and turnaround‑time gains. The legal landscape shifted in 2025 when a federal court vacated the prior year’s rule expanding federal oversight of laboratory‑developed tests, resetting near‑term compliance expectations and easing transitional pressures for hospital labs even as professional bodies and policymakers debate longer‑term oversight models. Canada and Latin America sustain momentum via public‑private genomics initiatives and disease‑focused networks, with increasing demand for locally deployable workflows in infectious disease and oncology. Across the region, supply chain strategy remains front‑of‑mind due to tariffs and export controls that influence instrument components and compute, prompting dual‑sourcing and regionalized data processing.
Across Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, market access hinges on navigating the evolving in vitro diagnostic regulatory framework. The European Union’s extension of certain IVDR transition timelines-under defined conditions and with interim obligations such as quality‑management system milestones and notified‑body engagement-helps stabilize availability while preserving safety objectives. For sequencing‑based assays, this clarity supports investment in conformity assessment and clinical evidence generation. Health‑system procurement, especially in Western Europe and the Nordics, continues to value data quality and interoperability, while parts of Central and Eastern Europe prioritize capital efficiency and service partnerships. In the Middle East, national genomics initiatives aim to localize capacity and workforce skills, and in parts of Africa, pathogen surveillance and newborn screening pilots are expanding, often through regional reference networks.
In Asia‑Pacific, demand is propelled by national programs in population health, agricultural resilience, and precision oncology, coupled with a vibrant private‑sector market. China remains a locus of platform innovation and manufacturing, with domestic providers and international players competing on chemistry, throughput, and price. Japan, South Korea, Singapore, and Australia emphasize quality and clinical translation, often pairing sequencing with strong bioinformatics and data‑governance frameworks. India’s expanding genomics ecosystem underscores the need for robust sample logistics and scalable cloud‑enabled analysis. Throughout the region, service‑provider networks and compatibility programs ease access to new platforms, and the maturation of nanopore and long‑read workflows is broadening field‑based and real‑time applications. Regional cybersecurity and data‑sovereignty regulations continue to influence how and where sequencing data are processed and stored.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the DNA Sequencing market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Competitive outlook highlights strategic pivots among platform leaders, emerging challengers, and ecosystem partners navigating litigation, partnerships, and scale
The competitive landscape blends renewal by incumbents with assertive advances from challengers and ecosystem partners. One leading manufacturer, after completing the 2024 separation of a liquid biopsy subsidiary, has refocused on platform performance, cost‑per‑genome, and software interoperability-supported by ongoing Nova‑class chemistry and software updates designed to enhance yield, Q‑scores, and usability. The company’s strategy underscores a broader industry pattern: concentrate on core sequencing value, surround it with robust informatics and partner‑ready workflows, and deepen clinical footholds where evidence and reimbursement align.
Long‑read and accuracy‑centric competitors have emphasized dual‑platform breadth. One provider’s high‑throughput long‑read system anchors structural variant and methylation applications at scale, while its short‑read instrument, commercialized in 2023 and subsequently integrated into major single‑cell compatibility programs, positions accuracy as a point of differentiation in oncology and minimal‑residual‑disease research. This two‑pronged portfolio seeks to meet customers across discovery and translational use, with chemistry and workflow updates aimed at lowering per‑sample costs and broadening applications coverage.
Nanopore‑based platforms have consolidated advances in pore design and chemistry. With R10.4.1 flow cells paired to Kit 14, users can achieve Q20+ single‑molecule data and elevate accuracy further using duplex basecalling, strengthening suitability for clinical‑adjacent and applied settings where turnaround and native‑molecule information-such as real‑time methylation-are valued. Ecosystem investments in kits and informatics continue to simplify workflows from sample prep through analysis, with tunable run conditions to balance accuracy and output.
Challenger short‑read providers are scaling through partnerships and service networks. One entrant leveraging wafer‑scale architecture has expanded its certified service‑provider footprint across the Americas, EMEA, and APAC, aligning with single‑cell leaders and large‑scale data initiatives to generate high‑volume, cost‑efficient datasets. Another benchtop specialist is advancing high‑accuracy chemistries and on‑flow‑cell enrichment workflows, making exome and targeted sequencing more accessible with reduced hands‑on time and elevated Q‑score distributions. These strategies collectively pressure incumbents not only on cost but on time‑to‑insight and workflow simplicity.
Intellectual property and competition law continue to shape product availability, especially in spatial biology. In late 2024, a U.S. court granted a permanent injunction affecting a digital spatial profiler line-with carve‑outs to minimize disruption for installed users-following earlier jury findings of willful infringement. The legal context evolved further in 2024 when a major instrument company acquired selected assets from the affected firm, inheriting aspects of the litigation; subsequent court milestones in early 2025 sustained injunction dynamics pending appeal. For sequencing buyers, the takeaway is to scrutinize roadmaps and indemnification terms when adopting adjacent technologies that may be subject to active disputes.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the DNA Sequencing market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- 10x Genomics, Inc.
- Abbott Laboratories
- AbbVie Inc.
- Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- Azenta, Inc.
- Becton, Dickinson and Company
- BGI Genomics Co., Ltd.
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
- BioChain Institute Inc.
- Charles River Laboratories International, Inc.
- Danaher Corporation
- Eppendorf SE
- Eurofins Scientific SE
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- Genomics England
- Genscript Biotech Corporation
- Illumina, Inc.
- Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.
- Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings
- Macrogen Inc.
- Merck KGaA
- Myriad Genetics, Inc.
- Novartis AG
- Novogene Co, Ltd.
- Oxford Nanopore Technologies PLC
- Pacific Biosciences of California, Inc.
- PerkinElmer, Inc.
- QIAGEN N.V.
- Sartorius AG
- Shimadzu Corporation
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Twist Bioscience Corporation
Actionable priorities emphasize resilient sourcing, regulatory readiness, scalable data operations, and partnership models that accelerate translational impact
Prioritize resilient sourcing and lifecycle cost control. Map bill‑of‑materials exposure for instruments, flow cells, and library prep inputs to tariff and export‑control regimes, and qualify secondary suppliers where feasible. For compute, forecast GPU and memory needs for basecalling and secondary analysis, secure multi‑year agreements with approved providers, and evaluate hybrid architectures that balance on‑premise control with cloud elasticity in compliant regions. The objective is to stabilize run‑rate economics and protect turnaround time despite policy or logistics shocks.
Advance regulatory readiness with scenario planning. In the United States, build flexible compliance pathways that can accommodate shifts in oversight of laboratory‑developed tests, including documentation and adverse event reporting processes that can be activated without re‑architecting operations. In Europe, maintain disciplined progress toward IVDR conformity under the extended timelines, with clear milestones for quality‑management systems, notified‑body engagement, and technical documentation. Where applicable, align assay claims and evidence generation plans early to avoid rework.
Invest in data foundations that scale. Standardize pipelines for read processing, variant calling, and interpretation across instruments to reduce validation burden and facilitate cross‑study comparability. Implement data governance that addresses consent, retention, and cross‑border transfer constraints from the outset, and integrate auditability for both clinical and research use. As multi‑omics and spatial data become more common, plan for metadata schemas and storage strategies that preserve context and support downstream AI applications.
Lean into partnership models that compress time‑to‑value. Combine internal capacity with certified service providers to flex between peak demand and steady‑state operations. Favor platforms and chemistries with robust compatibility programs spanning single‑cell, spatial, and targeted‑enrichment workflows. Where appropriate, co‑develop application notes with vendors to lock in reproducibility and reduce onboarding time for new assays.
Align teams around measurable outcomes. Define operational key performance indicators-such as turnaround time, pass rate, and data‑quality thresholds-aligned to each application domain. Tie capital allocation to improvements in these metrics, and cultivate cross‑functional governance that unites lab operations, clinical affairs, bioinformatics, and compliance. This disciplined approach converts technological possibility into durable competitive advantage.
Methodological rigor underpins insights by integrating multi-source evidence, expert validation, and continuous monitoring of technology, policy, and adoption
This executive summary synthesizes insights from a structured research program that combined technology landscape scanning, regulatory analysis, ecosystem mapping, and expert consultation. On the technology front, we reviewed primary documentation and updates from platform providers and standards bodies to characterize chemistry advancements, performance trends, and workflow innovations. We complemented this with an appraisal of informatics developments, including basecalling improvements, secondary analysis acceleration, and quality‑assurance practices that measurably affect throughput and accuracy.
The regulatory and policy perspective draws on official notices, press releases, and guidance documents issued by competent authorities, as well as reputable coverage from wire services and professional associations. Particular attention was paid to the evolution of U.S. oversight for laboratory‑developed tests, European IVDR transition extensions and milestones, and changes to U.S. tariff and export‑control regimes with effective dates relevant to 2025 operations. This ensured that implications for compliance planning, procurement, and data governance were interpreted in the correct temporal context.
Ecosystem and competitive dynamics were assessed through triangulation of vendor communications, partnership announcements, litigation dockets and outcomes, and independent reporting. This lens enabled us to parse how incumbents and challengers are positioning portfolios, where compatibility and service networks are expanding access, and how legal outcomes in adjacent fields like spatial biology influence sequencing adoption strategies. Throughout, we prioritized cross‑validation of claims, caution around vendor‑specific performance figures, and avoidance of speculative market sizing.
Finally, we mapped the provided segmentation taxonomy onto observed buying behavior and workflow evolution. This included analyzing how offerings combine into cohesive solutions, how technology selection correlates with application needs, how sample diversity drives protocol design, and how end‑user segments translate requirements into purchasing and partnership decisions. The result is a coherent view that links technology realities, regulatory context, and operational constraints to the decisions leaders must make now.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our DNA Sequencing market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- DNA Sequencing Market, by Offerings
- DNA Sequencing Market, by Technology Type
- DNA Sequencing Market, by Sample Type
- DNA Sequencing Market, by Application
- DNA Sequencing Market, by End User
- DNA Sequencing Market, by Region
- DNA Sequencing Market, by Group
- DNA Sequencing Market, by Country
- United States DNA Sequencing Market
- China DNA Sequencing Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 17]
- List of Tables [Total: 3180 ]
The road ahead favors platforms and programs that unite accuracy, accessibility, and responsible data use to embed sequencing at the core of decision-making
DNA sequencing’s center of gravity is moving from isolated breakthroughs to system‑level execution. Chemistry and software improvements are compounding into tangible gains in data quality and run reliability; long‑read and nanopore platforms now stand beside short‑read stalwarts as complementary tools rather than niche alternatives; and challenger architectures are pushing affordability and access through service networks and compatibility with single‑cell and spatial workflows. These developments expand the addressable problem space across research, clinical, and applied markets, but they also elevate expectations for interoperability and operational excellence.
At the same time, regulation and trade remain powerful shapers of strategy. With the U.S. court decision vacating the 2024 LDT rule and the EU’s extended IVDR transitions, compliance roadmaps must be adaptable, evidence‑driven, and milestone‑based. U.S. tariff and export‑control trends introduce variability in instrument and compute inputs, nudging buyers toward dual‑source and regional processing models. Leaders who proactively manage these constraints will not only contain risk; they will gain speed-turning friction into a catalyst for stronger, more resilient operations.
Ultimately, advantage will accrue to organizations that match platform choice to precise application needs, invest in scalable and auditable data operations, and build partnerships that compress time‑to‑value. The science is moving quickly, but the differentiators in 2025 are clarity of strategy, discipline in execution, and the ability to translate technical gains into reliable, real‑world outcomes.
Secure decisive advantage now by engaging Ketan Rohom to tailor insights and acquire the full report for your next-phase sequencing strategy decisions
Now is the moment to convert insight into advantage. Engage with Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing, to acquire the complete market research report and unlock a deeper layer of analysis, vendor benchmarking, and use‑case exemplars tailored to your organization’s goals. Beyond the executive summary, the full report provides decision‑grade evidence to support capital planning, portfolio prioritization, and partnership strategy.
Whether your next move involves instrument fleet transitions, scaling clinical sequencing services, expanding bioinformatics and data governance, or navigating cross‑border procurement under evolving trade rules, a tailored briefing will map the findings to your context. From there, a structured plan can align stakeholders on timelines, risks, and value realization.
Connect with Ketan to purchase the report and schedule a customized debrief that accelerates your 12‑ to 24‑month roadmap. With the right information at the right time, you can move decisively while others are still interpreting the landscape.

- How big is the DNA Sequencing Market?
- What is the DNA Sequencing Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




