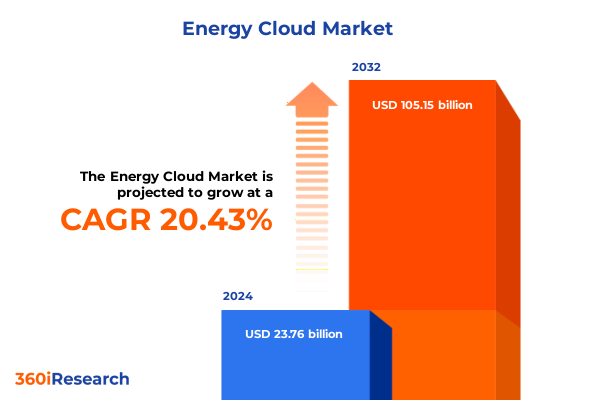
The Energy Cloud Market size was estimated at USD 28.53 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 34.27 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 20.48% to reach USD 105.15 billion by 2032.
Shaping the Future of Energy Management Through Cloud-Enabled Intelligence and Sustainable Infrastructure for a Resilient Grid
The evolution of energy systems has transcended traditional infrastructure models to embrace a paradigm centered on cloud-enabled platforms and digital intelligence. Energy Cloud represents the fusion of grid architecture with scalable cloud computing resources, enabling utilities, grid operators, and energy service providers to manage, analyze, and optimize energy flows in real time. By leveraging the virtually unlimited storage, processing power, and advanced analytics capabilities of the cloud, organizations can transform raw telemetry from distributed assets into actionable insights that drive efficiency and resilience across the energy value chain.
This shift is underpinned by the convergence of multiple technological trends. Rapid expansion of Internet of Things connectivity has multiplied the volume of data generated by sensors and smart devices across generation, transmission, distribution, and consumption points. Concurrently, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms have empowered predictive maintenance, demand forecasting, and anomaly detection at scales previously unattainable. Regulations and decarbonization targets have further incentivized investment in digital solutions that can facilitate renewable integration, reduce peak loads, and support dynamic tariff structures.
As organizations contend with aging infrastructure, increasing demand volatility, and the imperative to decarbonize, the ability to harness cloud-native architectures becomes not merely advantageous but essential. Real-time visibility into energy flows enables rapid fault isolation and grid balancing, while modular cloud services facilitate streamlined deployment of new applications. By establishing a robust digital foundation, energy providers position themselves to innovate new services, improve customer engagement, and maintain operational continuity amid evolving market dynamics.
Unveiling the Pivotal Technological and Market Dynamics Redefining Energy Networks with AI Optimization and Renewable Integration
The traditional energy sector is undergoing profound transformation as digital technologies redefine how power systems are designed, operated, and monetized. Automation and real-time monitoring solutions, once confined to isolated piloting environments, are now being embedded into core grid operations. This digital overlay allows operators to move from manual interventions to software-driven orchestration, where network reconfiguration, load balancing, and outage restoration can occur with minimal human oversight. Such shifts not only enhance operational efficiency but also unlock the potential for more flexible market participation by enabling granular visibility into supply and demand dynamics.
In parallel, novel market constructs are emerging to leverage distributed resources and prosumers. Virtual power plants aggregate diverse assets-including rooftop solar, battery storage, and controllable loads-into a single dispatchable entity. Demand response programs are increasingly dynamic, allowing real-time price signals to guide consumption patterns. These new service models rely on the cloud’s inherent scalability to integrate data streams from thousands, if not millions, of endpoints, while ensuring secure and reliable control. Consequently, stakeholders across the value chain are collaborating to design interoperable frameworks that can accommodate peer-to-peer energy trading, localized balancing areas, and grid-supportive DER operations.
At the intersection of these trends lies the integration of electric vehicles and renewable generation into the grid. As fleets of EVs become ubiquitous, charging infrastructure must be managed to avoid peak load spikes and maximize renewable utilization. Cloud-based platforms are facilitating intelligent charging schedules, vehicle-to-grid services, and energy arbitrage opportunities. Meanwhile, renewable assets such as solar and wind farms leverage cloud-hosted predictive analytics to anticipate weather-driven generation patterns, synchronize with storage systems, and participate more effectively in wholesale markets. The confluence of edge computing and centralized cloud processing creates a hybrid model that balances low-latency decision making with the computational heft required for large-scale optimization.
Assessing the Aggregate Consequences of 2025 U.S. Section 301 Tariffs on Clean Energy Supply Chains and Technology Deployment
In response to concerns over supply chain vulnerabilities and unfair trade practices, the U.S. government implemented significant tariff increases effective January 1, 2025, targeting imports from China of key energy components. Rates on solar wafers and polysilicon surged from 25 percent to 50 percent, while duties on certain tungsten products rose to 25 percent under Section 301 provisions. This latest action concluded the four-year statutory review, reflecting a continued emphasis on bolstering domestic manufacturing and safeguarding critical technology inputs for clean energy projects.【turn0search0】
Beyond solar materials, the broader Section 301 measures also impact semiconductors, electric vehicles, and battery-related goods. Tariffs on EVs escalated up to 100 percent, while lithium-ion battery cells and battery parts encountered new duties in the 25 percent range. Such increases compound existing levies on a range of renewable energy and grid modernization components-wind turbine parts, smart meters, and power electronics-introducing heightened cost pressures across the clean energy supply chain and prompting manufacturers to reassess sourcing strategies and pricing models.【turn0search3】
These cumulative tariff impacts have accelerated logistics complexities, delayed equipment deliveries, and spurred manufacturers to impose surcharge adjustments to offset elevated input costs. Utilities and project developers face lengthened procurement cycles and cost uncertainty, inhibiting rapid deployment of grid modernization initiatives. As stakeholders navigate these headwinds, the imperative for resilience has never been more acute, with market participants diversifying supplier bases and exploring nearshoring opportunities to mitigate the risk of further trade policy shifts.
Extracting Strategic Sectoral Insights from Multilayered Segmentation to Illuminate Key Drivers and Opportunities in Energy Cloud Solutions
A nuanced understanding of market segmentation reveals the diverse factors shaping the Energy Cloud landscape. Across components, hardware offerings-ranging from communication modules and gateways to sensors and smart meters-form the physical foundation for distributed monitoring and control. Complementing these are managed and professional services that guide system deployment and ongoing optimization, alongside software solutions spanning analytics platforms, application software, and cloud-native platforms that integrate disparate data streams into coherent insights.
Deployment models also dictate how solutions are consumed and managed. Public and private cloud architectures provide organizations with flexible scaling options and accelerated time to market, while on-premises deployments continue to serve use cases demanding rigorous data sovereignty, reduced latency, or heightened cybersecurity controls. Layered on top of these infrastructure choices are service delivery models such as IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, each presenting distinct value propositions for integration, customization, and operational expense management.
Critical applications further segment the market by function and end use. Demand response initiatives, offered through both incentive and price-based mechanisms, harness real-time signals to modulate energy consumption. Energy management systems extend from building-level solutions to distributed energy resource orchestration and virtual power plant configurations. EV charging management must accommodate commercial, public, and residential charging patterns, while grid modernization programs encompass distribution automation, network monitoring, and smart grid automation. Renewable integration spans energy storage, solar, and wind interfaces, enabling seamless coordination of variable resources across commercial, industrial, and residential environments in use cases as varied as education, healthcare, manufacturing, and multi-family residential complexes. Underpinning these segments is an ecosystem of communication technologies-including IoT protocols such as LoRaWAN, NB-IoT, and Zigbee, wired connectivity through Ethernet and fiber optics, and wireless networks leveraging cellular, RF mesh, or satellite links-to ensure ubiquitous, reliable data exchange.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Energy Cloud market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Component
- Offering
- Communication Technology
- Deployment Model
- Application
- End Use
Decoding Regional Energy Cloud Adoption Trends Across Pan-American, EMEA, and Asia-Pacific Markets for Informed Strategic Positioning
In the Americas, the United States and Canada remain at the forefront of Energy Cloud adoption, driven by substantial investments in grid modernization, supportive regulatory frameworks, and advancing renewable mandates. Latin American countries are increasingly turning to cloud-based platforms to overcome infrastructure constraints, enhance utility performance, and address growing electrification needs in urban and remote regions. Collaborative initiatives between public entities and private technology providers are laying the groundwork for more resilient, data-centric power networks across the hemisphere.
Meanwhile, Europe continues to build on its ambitious decarbonization goals by integrating energy cloud services into national climate strategies. The European Green Deal and successive directives on renewable integration have catalyzed the deployment of advanced grid management systems, with Middle Eastern nations also piloting cloud-enabled microgrid solutions to balance solar and gas-fired generation in desert environments. In Africa, nascent energy cloud projects leverage off-grid and hybrid power systems to extend reliable electricity access, demonstrating the technology’s potential to drive inclusive energy transitions.
Asia-Pacific exhibits perhaps the most diverse and high-growth dynamics in the Energy Cloud market. China’s strategic focus on self-reliant technology supply chains and digital infrastructure has accelerated large-scale adoption across generation and distribution networks. India is deploying cloud-based analytics to optimize coal, gas, and renewable plants, while Southeast Asian markets leverage cloud platforms for rural electrification and urban grid management. The region’s rapid urbanization and ambitious renewable targets underscore its critical role in shaping the future contours of Energy Cloud adoption and innovation.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Energy Cloud market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Profiling Leading Technology and Infrastructure Providers Shaping the Evolution of Energy Cloud Market Competitiveness and Innovation
Hyperscale cloud providers have emerged as pivotal enablers of Energy Cloud capabilities. Platforms from leading vendors offer pre-integrated services for data ingestion, storage, and advanced analytics, empowering utilities and third-party developers to deploy applications at scale. These providers continue to expand their specialized frameworks for energy management, incorporating industry-specific APIs and certification programs that streamline compliance with regulatory requirements and grid standards.
Traditional industrial technology companies have deepened their digital portfolios to secure market share in the evolving Energy Cloud ecosystem. By combining legacy expertise in grid equipment with software development and services delivery, these firms deliver end-to-end solutions that encompass hardware provisioning, system integration, and managed services. Such incumbents often leverage strategic partnerships and acquisitions to bolster their cloud offerings and accelerate time to value for enterprise clients.
A growing cadre of specialized software and analytics firms is also shaping competitive dynamics. Focused on niche segments-such as predictive maintenance, energy trading optimization, or peer-to-peer energy marketplaces-these players leverage cloud architectures to deliver modular, API-driven solutions. Collaborative alliances between these innovators and larger platform providers have proliferated, reflecting a broader trend toward ecosystem interoperability and co-innovation to address complex utility challenges.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Energy Cloud market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- ABB Ltd
- Amazon Web Services, Inc.
- AutoGrid Systems, Inc.
- Bloom Energy Corporation
- C3.ai, Inc.
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Enel X Way S.r.l.
- EnergyHub, Inc.
- Generac Grid Services, Inc.
- General Electric Company
- Google LLC
- IBM Corporation
- Itron, Inc.
- Microsoft Corporation
- Oracle Corporation
- Schneider Electric SE
- Siemens AG
- Trilliant Holdings, Inc.
- Uplight, Inc.
Implementing Tactical Strategic Imperatives and Investment Approaches to Capitalize on Energy Cloud Disruption and Strengthen Organizational Resilience
Industry leaders should prioritize investment in AI-driven analytics and machine learning capabilities to unlock deeper insights from vast, heterogeneous data sources. Enhancing grid observability through advanced anomaly detection and predictive algorithms enables proactive maintenance, reduces downtime, and optimizes asset utilization. Partnerships with data science specialists and cloud vendors can accelerate development cycles, ensuring that analytics modules remain current with evolving grid conditions and regulatory changes.
To mitigate supply chain disruptions and tariff-related cost escalation, organizations must cultivate diversified sourcing strategies and nearshore manufacturing partnerships. Developing transparent procurement frameworks that incorporate tariff forecasting, materials hedging, and multi-vendor qualification helps maintain project schedules and budget discipline. Alignment with government programs and incentives that support domestic manufacturing can further offset the financial impact of trade policy shifts and reinforce long-term supply resilience.
Adopting sustainable cloud practices and edge-computing architectures strengthens both environmental performance and system responsiveness. Edge computing nodes reduce latency for mission-critical operations and limit data egress fees in cloud environments, while green data center initiatives-leveraging renewable energy and advanced cooling techniques-can curtail operational carbon footprints. Firms should embed sustainability criteria into vendor selection and regularly measure carbon intensity metrics across their digital infrastructure.
Detailing Rigorous Multi-Source Research Methodologies Employed to Validate Data Integrity and Analytical Rigor for Energy Cloud Insights
This research synthesizes primary insights gathered through in-depth interviews with senior executives at utilities, grid operators, energy service providers, and technology vendors. Supplementary survey data from cross-functional teams-including engineering, IT, and regulatory affairs-provided quantitative validation of emerging trends, technology adoption rates, and strategic priorities across multiple regions.
Secondary research was conducted through systematic review of public financial filings, regulatory filings, policy white papers, industry consortium publications, and authoritative technical journals. Trade association reports and government communications offered a foundational understanding of evolving standards, tariff developments, and incentive structures that influence deployment decisions and supply chain configurations.
Data integrity and analytical rigor were upheld through triangulation of multiple data sources, quantitative modeling of technology adoption scenarios, and peer review by subject-matter experts. Methodological safeguards included data normalization protocols, sensitivity analysis to account for policy volatility, and iterative validation cycles with advisory board members. This approach ensures that findings are robust, transparent, and directly applicable to strategic decision-making in dynamic market conditions.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Energy Cloud market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Energy Cloud Market, by Component
- Energy Cloud Market, by Offering
- Energy Cloud Market, by Communication Technology
- Energy Cloud Market, by Deployment Model
- Energy Cloud Market, by Application
- Energy Cloud Market, by End Use
- Energy Cloud Market, by Region
- Energy Cloud Market, by Group
- Energy Cloud Market, by Country
- United States Energy Cloud Market
- China Energy Cloud Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 18]
- List of Tables [Total: 3339 ]
Concluding Reflections on Emerging Energy Cloud Paradigms and Strategic Imperatives Driving the Next Wave of Digital Transformation
The Energy Cloud paradigm represents a critical juncture in the evolution of power systems, where digitalization, decentralization, and decarbonization converge to redefine grid reliability, operational efficiency, and customer empowerment. Through comprehensive analysis of technological shifts, tariff impacts, segmentation dynamics, regional adoption patterns, and provider strategies, it becomes evident that organizations must embrace cloud-enabled architectures and advanced analytics to remain competitive. By integrating strategic investments, resilient supply chain practices, and sustainable infrastructure approaches, industry stakeholders will be better positioned to unlock the full potential of the Energy Cloud, driving innovation and delivering value across the energy ecosystem.
Engage Directly with Associate Director of Sales & Marketing to Secure Comprehensive Energy Cloud Market Intelligence and Support Strategic Decision Making
To explore this comprehensive analysis and understand how these insights can elevate your strategic planning, reach out directly to Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing at 360iResearch. Engaging with Ketan will ensure you receive the full market research report, complete with in-depth data, expert commentary, and actionable guidance tailored to drive your initiatives forward. Don’t miss the opportunity to equip your organization with the competitive intelligence necessary to navigate and lead in the evolving Energy Cloud landscape.

- How big is the Energy Cloud Market?
- What is the Energy Cloud Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




