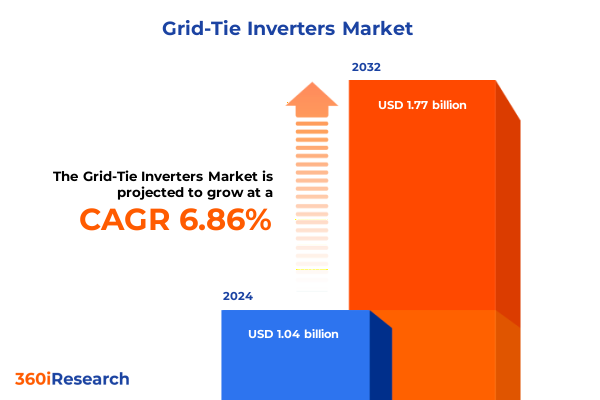
The Grid-Tie Inverters Market size was estimated at USD 1.11 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 1.19 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 6.84% to reach USD 1.77 billion by 2032.
Introducing the State-of-the-Art Developments in Grid-Tie Inverter Technology Shaping Modern Solar Energy Integration and Efficiency Gains
In recent years, grid-tie inverters have become the linchpin of modern solar energy systems, translating direct-current power generated by photovoltaic arrays into alternating-current electricity compatible with utility grids. As global solar adoption accelerates, the significance of inverter performance and reliability has surged, positioning these devices as critical enablers of renewable energy integration. Not only do inverters impact overall system efficiency, but they also serve as intelligent nodes for monitoring and control, ensuring grid stability and facilitating bi-directional energy flows. In parallel, advancements in power electronics have driven continuous improvements in conversion efficiencies, thermal management, and hardware miniaturization, allowing inverters to meet increasingly stringent performance standards. Furthermore, evolving grid codes and interconnection agreements demand inverters with enhanced functionalities such as reactive power support, ride-through capabilities, and anti-islanding protection. Consequently, manufacturers are investing heavily in research and development to balance cost, reliability, and feature complexity. As we explore the subsegments and shaping forces in the grid-tie inverter realm, it is essential to understand how technological innovation and regulatory developments intertwine to set new benchmarks. This introduction establishes the foundation for a nuanced examination of market shifts, policy impacts, segmentation insights, regional variances, and strategic imperatives poised to guide stakeholders toward informed decision-making.
Unveiling the Pivotal Technological and Policy-Driven Transformations Redefining the Grid-Tie Inverter Market Landscape for Next Generation Energy Ecosystems
Throughout 2024 and into 2025, the grid-tie inverter market has witnessed transformative shifts driven by both technological breakthroughs and policy realignments. On the technology front, rapid advances in semiconductor materials, including silicon carbide and gallium nitride, have unveiled unprecedented efficiency gains and thermal performance, enabling inverters to handle higher voltage densities with reduced losses. Coupled with integrated digital control algorithms powered by machine learning, these innovations are enhancing predictive maintenance capabilities, reducing downtime, and extending equipment lifespan. Simultaneously, the proliferation of smart meter deployments and IoT platforms is cultivating an ecosystem where inverters not only convert power but also serve as intelligent data hubs, facilitating real-time grid management and customer engagement. From a policy perspective, heightened decarbonization targets and dynamic tariff structures are reshaping investment priorities, pushing both project developers and utilities to seek inverters capable of dynamic grid support and rapid response to demand-side signals. Incentive mechanisms such as time-of-use pricing and performance-based incentives are prompting a shift from conventional centralized systems toward more distributed architectures. As a result, market participants are forging strategic partnerships to co-develop second-generation solutions that bridge hardware and software, underscoring a more holistic approach to energy management. This interplay of cutting-edge materials, digitalization, and regulatory impetus constitutes a new paradigm for how grid-tie inverters will operate and evolve in the coming decade.
Analyzing the Comprehensive Impact of 2025 United States Tariffs on Grid-Tie Inverter Supply Chains and Competitive Dynamics
In 2025, the United States government implemented a series of tariffs aimed specifically at photovoltaic components, which have rippled through the grid-tie inverter supply chain. Initially introduced under Section 301 and subsequently expanded by the Department of Commerce, these duties target inverters and related power electronics imported from select regions, raising import levies by up to 15-20 percent. As a direct outcome, many system integrators and EPC contractors have faced cost surges on imported units, leading to a renewed focus on domestic manufacturing incentives and localization strategies. In response, original equipment manufacturers have accelerated plans to establish or expand assembly facilities within the U.S., aiming to circumvent tariff constraints and leverage domestic workforce development programs. Concurrently, sourcing strategies have diversified to include regions with favorable trade agreements, while research teams are optimizing design architectures to reduce reliance on tariff-impacted components without compromising performance. Despite the immediate cost pressures, the tariff landscape has stimulated innovation in value engineering, prompting manufacturers to refine supply chains, adopt modular component strategies, and negotiate long-term procurement contracts. Over time, this tariff-driven realignment is expected to fortify the resilience of the U.S. inverter market, laying the groundwork for a more balanced interplay between imported technologies and homegrown solutions. Stakeholders must continue to evaluate policy trajectories and adjust sourcing as new rulings and extensions emerge through the year.
Deriving Strategic Insights from Inverter Type End-User Phase Capacity and Communication Technology Segmentation Dimensions Shaping Market Differentiation Patterns
A detailed examination of market segmentation reveals nuanced dynamics that can inform product development, sales strategies, and partnership decisions. When considering inverter types, central inverters still serve large-scale utility projects with robust power conversion needs, microinverters excel in residential arrays by maintaining module-level optimization and fault isolation, and string inverters-both transformer-based and transformerless variants-offer a balance of cost efficiency and performance adaptability. In the residential segment, the choice between ground-mounted installations and roof-mounted configurations influences inverter sizing, installation complexity, and balance-of-system costs, while commercial operations gravitate toward scalable string architectures that can integrate advanced monitoring. Single-phase systems remain prevalent in smaller installations due to simpler electrical layouts, while three-phase configurations dominate in larger commercial and utility-scale deployments, offering uninterrupted power delivery and enhanced load balancing. Capacity segmentation, spanning from under 100 kilowatts through 100 to 250 kilowatts, and extending beyond 250 kilowatts into 250–500 kilowatt and above 500 kilowatt ranges, underscores the need for modular growth paths that facilitate facility expansions and grid code compliance. Finally, communication protocols such as Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and Zigbee underpin remote monitoring, over-the-air updates, and interoperability with building management systems, shaping how system operators leverage data analytics. These intertwined segmentation dimensions highlight the importance of flexible, interoperable solutions tailored to specific application profiles and end-user requirements.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Grid-Tie Inverters market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Inverter Type
- End User
- Phase
- Capacity
- Communication
Highlighting Regional Market Dynamics Across Americas Europe Middle East Africa and Asia-Pacific Solar Ecosystems to Identify Growth Trajectories
Regional market dynamics vary significantly across the Americas, Europe, Middle East & Africa, and Asia-Pacific, each influenced by distinct regulatory frameworks, infrastructure maturity, and renewable energy adoption trajectories. In the Americas, federal incentive programs and state-level mandates drive strong uptake of advanced grid-tie inverters, particularly in the United States where renewable portfolio standards and investment tax credits channel capital toward both centralized solar farms and rooftop solar initiatives. Latin American markets, led by Brazil and Chile, are emerging as high-growth corridors thanks to competitive solar tariffs and grid modernization efforts. Over in Europe, Middle East, and Africa, the REPowerEU plan and regional clean energy strategies in GCC nations have ignited demand for grid-supportive inverters with black-start capabilities and reactive power management. North African countries, grappling with grid stability challenges, are leveraging hybrid configurations that combine solar generation with energy storage, reinforcing the need for bidirectional inverter functionalities. Asia-Pacific remains the world’s largest installer of grid-tie inverters, led by China’s robust domestic manufacturing ecosystem and India’s ambitious solar capacity targets. Southeast Asian nations increasingly rely on advanced inverters to manage grid congestion and voltage fluctuations amid rapid urbanization. Each of these regions presents unique entry barriers and partnership opportunities, underscoring the necessity for manufacturers to adapt product portfolios, service models, and distribution networks to local market conditions.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Grid-Tie Inverters market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Profiling Leading Global Grid-Tie Inverter Manufacturers Driving Innovation Collaboration and Market Leadership Strategies Shaping Competitive Advantage
The competitive landscape of grid-tie inverters features several leading technology providers that have defined market trajectories through innovation, strategic alliances, and diversified product portfolios. SMA Solar Technology has long been recognized for pioneering transformerless string inverters with integrated power management features and has recently expanded its offerings to include advanced energy management software. Huawei has leveraged its telecommunications expertise to deliver inverters with embedded AI-driven optimization algorithms and robust cybersecurity protocols, partnering with utilities to pilot distributed energy resource management systems. SolarEdge Technologies continues to gain traction with its power optimizers and centralized inverters, coupling module-level monitoring with cloud-based analytics to enable dynamic performance tuning. Enphase Energy leads the microinverter segment by refining per-module power conversion units that simplify system design and enhance resilience against shading and module mismatches. Schneider Electric integrates grid-tie inverters into broader building energy management solutions, capitalizing on its experience in industrial controls to offer holistic automation capabilities and seamless integration with energy storage systems. Emerging specialists are also entering the fray, focusing on niche applications such as off-grid hybridization, bidirectional V2G readiness, and utility-scale turnkey solutions. This diverse competitive ecosystem drives continual feature enhancements and incentivizes deeper collaboration between electronics engineers, software developers, and energy service providers.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Grid-Tie Inverters market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- ABB Ltd
- Adani Solar Energy Systems Ltd
- Delta Electronics, Inc.
- Enphase Energy, Inc.
- Exide Industries Limited
- FIMER S.p.A.
- Fronius International GmbH
- GoodWe Power Supply Technology Co., Ltd.
- Growatt New Energy Technology Co., Ltd.
- Hopewind Co., Ltd.
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Luminous Power Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
- Microtek International Pvt. Ltd.
- Power Electronics S.L.
- SMA Solar Technology AG
- SolarEdge Technologies, Inc.
- Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd.
- Swelect Energy Systems Limited
- TMEIC Corporation
- UTL Solar Pvt. Ltd.
Actionable Strategic Recommendations for Industry Leaders to Navigate Technological Policy and Supply Chain Complexities and Capitalize Emerging Opportunities
To maintain a leadership position amid rapid market evolution and policy flux, industry participants should prioritize a multifaceted strategy blending technological innovation, supply chain resilience, and proactive regulatory engagement. Firstly, accelerating development of semiconductor-based architectures that leverage silicon carbide and gallium nitride materials will yield measurable efficiency improvements while reducing thermal footprint. Parallel investing in modular hardware and scalable firmware upgrades can lower lifetime ownership costs and extend product roadmaps. Secondly, companies must diversify sourcing to mitigate tariff-induced risks, establishing or strengthening local assembly and leveraging free trade agreements to balance cost optimization with compliance. Forming strategic alliances with logistics partners and component suppliers will further enhance agility in responding to sudden policy shifts. Thirdly, engaging early with regulators and grid operators to co-define technical standards, interoperability frameworks, and tariff structures will facilitate smoother interconnection processes and unlock advanced functionalities such as dynamic reactive power dispatch. Additionally, partnering with software firms and research institutions to embed artificial intelligence, predictive analytics, and cybersecurity measures can differentiate offerings in a crowded market. Finally, enhancing service models-through remote monitoring platforms, performance-based contracts, and training programs-will help sustain long-term client relationships and establish a recurring revenue stream that complements hardware sales.
Elaborating a Robust Research Methodology Incorporating Primary Data Validation Secondary Analysis and Expert Triangulation
The research underpinning these insights employed a rigorous, multi-tiered methodology to ensure accuracy, relevance, and depth. Initially, a comprehensive secondary analysis scanned technical publications, regulatory filings, and industry white papers to map out existing knowledge and identify critical variables. This was followed by structured primary interviews with technology architects, operations managers, and regulatory stakeholders, capturing firsthand perspectives on emerging challenges and solution pathways. Data collected from these qualitative discussions were triangulated against quantitative datasets sourced from equipment registries, patent databases, and trade records, enabling validation through cross-referencing. To refine segmentation accuracy, the methodology incorporated both top-down and bottom-up approaches: macro-level analyses of deployment trends informed high-level categorization, while micro-level case studies of representative installations provided granular performance and cost benchmarks. An expert panel review stage then evaluated preliminary findings, ensuring methodological soundness and operational feasibility. Throughout the process, emphasis was placed on transparency and auditability, with data protocols, assumption logs, and anonymized interview transcripts maintained for quality assurance. This approach has yielded a robust foundation for the executive summary and associated strategic recommendations, providing stakeholders with a reliable framework for decision-making.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Grid-Tie Inverters market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Grid-Tie Inverters Market, by Inverter Type
- Grid-Tie Inverters Market, by End User
- Grid-Tie Inverters Market, by Phase
- Grid-Tie Inverters Market, by Capacity
- Grid-Tie Inverters Market, by Communication
- Grid-Tie Inverters Market, by Region
- Grid-Tie Inverters Market, by Group
- Grid-Tie Inverters Market, by Country
- United States Grid-Tie Inverters Market
- China Grid-Tie Inverters Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 17]
- List of Tables [Total: 1272 ]
Summarizing Key Insights Conclusions and Strategic Imperatives for Stakeholders in the Grid-Tie Inverter Domain Value Chain Navigability
This executive summary synthesizes key takeaways from an in-depth examination of the grid-tie inverter landscape, charting critical technological, regulatory, and market-driven factors that will define industry trajectories. Emerging semiconductor materials and digital control systems are poised to elevate performance benchmarks, while evolving tariff regimes and policy frameworks are reshaping supply chain strategies and competitive positioning. Segmentation insights underline the importance of tailoring inverter solutions to project scale, installation type, and communication requirements, reflecting a market where one-size-fits-all approaches are giving way to application-specific architectures. Regional analyses highlight distinct growth corridors, from mature markets in North America and Europe to high-potential deployments in Asia-Pacific and Latin America. Competitive profiling underscores the necessity for ongoing innovation and service excellence as market leaders vie for share in both centralized and distributed energy segments. Across these dimensions, five strategic imperatives emerge: embrace technology diversification, fortify supply chain agility, champion regulatory collaboration, integrate advanced analytics, and design scalable service models. Stakeholders who adopt a holistic, forward-looking posture will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities, navigate uncertainties, and drive sustainable growth. Ultimately, the grid-tie inverter domain is entering a new era of complexity and possibility, where strategic adaptability and technical leadership are the greatest assets.
Discover How to Secure In-Depth Grid-Tie Inverter Market Intelligence and Fuel Your Strategic Decisions with a Custom Research Report from Ketan Rohom Today
To gain a competitive edge in the fast-evolving grid-tie inverter landscape and inform your strategic roadmap, connect with Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing. He can provide direct access to the comprehensive market intelligence report designed to address your unique requirements, including detailed qualitative analyses, technology deep dives, and stakeholder perspectives. By reaching out today, you will unlock tailored insights that clarify emerging opportunities, mitigate policy and supply chain risks, and guide capital allocation. The report offers immediate recommendations, scenario-planning tools, and peer benchmarking data that empower executive teams to act decisively. Engage with Ketan Rohom to schedule a briefing, explore custom add-on modules, and secure priority delivery. Take the next step toward transforming your approach to grid-tie inverter investments and partnerships by leveraging world-class research curated for high-impact decision-making. Your strategic advantage begins with one conversation-contact Ketan Rohom now to elevate your market view and drive profitable growth strategies.

- How big is the Grid-Tie Inverters Market?
- What is the Grid-Tie Inverters Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




