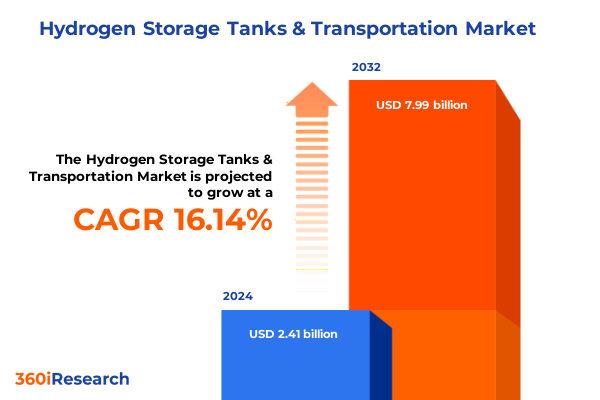
The Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation Market size was estimated at USD 2.41 billion in 2024 and expected to reach USD 2.78 billion in 2025, at a CAGR of 16.14% to reach USD 7.99 billion by 2032.
Hydrogen storage tanks and transportation at the heart of a resilient, low‑carbon energy ecosystem reshaping global logistics
Hydrogen is gaining prominence as a flexible energy carrier that can connect renewable generation, hard‑to‑abate industries, long‑distance transport, and seasonal power balancing. Yet, the value of hydrogen ultimately depends on how efficiently it can be stored and moved between production sites, intermediate hubs, and end‑use locations. Hydrogen storage tanks and transportation solutions therefore sit at the heart of the emerging hydrogen value chain, enabling both distributed deployment and large‑scale projects.
Across mobility, industrial, and utility applications, tanks and associated logistics assets must reconcile demanding requirements for safety, energy density, durability, and cost. The industry is transitioning from early demonstration projects to more standardized deployments, with growing emphasis on high‑pressure composite tanks, cryogenic liquid storage, and multimodal transport concepts that can handle increasing hydrogen volumes. As technology options mature, stakeholders are looking beyond stand‑alone engineering metrics to evaluate how particular tank designs, materials, pressure ratings, and transport modes align with specific business models and regulatory frameworks.
At the same time, policy support for low‑carbon hydrogen is intensifying, particularly in regions targeting net‑zero emissions. Infrastructure incentives, clean‑fuel standards, and public procurement commitments are catalyzing investments in new fueling networks, industrial feedstock pathways, and backup power systems that all rely on reliable storage and transportation. Against this backdrop, the hydrogen storage tanks and transportation landscape is undergoing rapid strategic repositioning, with companies and policymakers seeking to secure supply chains, drive down delivered costs, and harmonize safety and performance standards across borders.
This executive summary provides a high‑level synthesis of the most important dynamics shaping the space today. It explores the transformative shifts underway in technology and infrastructure, assesses how the evolving United States tariff regime through 2025 is reshaping cost structures and sourcing strategies, examines key segmentation patterns across tank type and end‑use sectors, and highlights regional and competitive insights that are most actionable for senior decision‑makers.
Transformative shifts in hydrogen storage tank technologies and transport networks under climate ambition, digitalization and safety regulation
The landscape for hydrogen storage tanks and transportation is being reshaped by concurrent shifts in technology, regulation, and market structure. On the technology side, the industry is steadily moving from traditional metal pressure vessels to advanced composite solutions as performance and lifecycle economics improve. Type I and Type II configurations, based primarily on metal cylinders or metal liners with partial reinforcement, remain relevant for lower‑pressure and cost‑sensitive applications. However, Type III and Type IV tanks, which use lightweight composite overwraps and, in the case of Type IV, polymer liners, are increasingly favored in mobility and high‑performance stationary systems, where gravimetric efficiency and corrosion resistance are critical.
Material innovations are central to these shifts. Carbon fiber is becoming the material of choice in advanced tanks, enabling higher pressure ratings and weight reduction, while glass fiber and metal options retain importance where cost and robustness take precedence over ultra‑lightweight design. Improved resin systems, liner materials, and manufacturing processes are allowing suppliers to refine performance envelopes while gradually reducing unit costs. At the same time, design evolution is broadening the use of cylindrical tanks, rectangular tanks, and spherical tanks depending on integration constraints, space utilization needs, and safety analyses within vehicles, industrial sites, and transport containers.
Regulation and safety standards are evolving in parallel, reinforcing the move toward more sophisticated tank technologies and integrated transport solutions. Authorities are sharpening requirements for pressure testing, leak detection, fire resistance, and lifecycle traceability, particularly for high‑pressure systems used in road transport or within densely populated areas. These requirements encourage deployment of digital monitoring capabilities in both tanks and logistics assets, such as sensors for real‑time pressure, temperature, and structural health monitoring. Digitalization also supports predictive maintenance, fleet optimization, and transparent compliance reporting, which are increasingly valuable as networks scale.
Finally, value chains are becoming more integrated. Instead of treating production, storage, and transport as discrete silos, project developers are designing end‑to‑end systems that co‑optimize electrolyzer capacity, storage tank sizing, and multimodal logistics. Road transport currently dominates many regional hydrogen movements, but interest is rising in rail transport for bulk inland corridors, marine transport for export‑oriented projects, and, in niche high‑value segments, air transport. As these modes develop, the interface between tank technology and transport asset design will be a defining competitive arena, influencing both operating economics and regulatory acceptance.
Assessing cumulative impacts of United States tariffs through 2025 on hydrogen storage tanks, materials and cross‑border transportation
Trade policy has become an increasingly important variable in the economics of hydrogen storage tanks and transportation, particularly as the United States tightens tariffs on strategic materials and clean‑technology goods. Recent Section 301 actions have raised duties on a range of Chinese‑origin products, including steel and aluminum products, semiconductors, batteries, and various critical minerals, many of which play a role in the hydrogen value chain. Tariffs on certain steel and aluminum imports have been lifted to around 25%, while solar cells now face duties near 50%, with higher rates on electric vehicles and lithium‑ion batteries.
For hydrogen storage tank manufacturers, these measures affect cost structures through multiple channels. Type I and Type II tanks rely heavily on steel or other metal components, which become more expensive when sourced from tariff‑affected suppliers. Composite Type III and Type IV tanks, while less metal‑intensive, still depend on metallic bosses, liners in some configurations, and specialized valves and fittings that may fall within affected tariff categories. In parallel, electronics used in monitoring and control systems can incorporate semiconductors subject to higher duties starting in 2025.
Transportation solutions also feel the impact. Road trailers, rail cars, and marine transport modules often incorporate steel structures, aluminum alloys, and precision‑engineered components sourced from global supply chains. As tariffs add friction to imports of these materials from specific countries, operators are reassessing sourcing strategies, exploring reshoring and near‑shoring options, and seeking to diversify suppliers across regions not subject to elevated duties. These adjustments, while supportive of domestic manufacturing goals, can lengthen lead times and introduce transitional cost pressures for hydrogen logistics projects.
By 2025, the cumulative effect of these tariff changes is likely to manifest in a more localized and strategically diversified supply base for hydrogen storage tanks and associated transport equipment serving the United States. Some manufacturers are evaluating new facilities or partnerships within the Americas to mitigate tariff exposure and take advantage of broader industrial policy support for clean energy manufacturing. Others are renegotiating long‑term contracts and adjusting product designs to reduce dependence on tariff‑sensitive inputs, for example by optimizing the use of carbon fiber and other composite materials where technically feasible.
At the same time, downstream customers in automotive and transportation, utilities, and industrial sectors must factor tariff‑driven cost variability into project planning. While policy incentives for low‑carbon hydrogen production may offset some of these increases, stakeholders that proactively model tariff scenarios, build flexible sourcing strategies, and standardize tank and module interfaces will be better positioned to maintain project viability. Thus, United States tariffs through 2025 represent not only a cost headwind but also a catalyst for more resilient, strategically aligned supply chains in hydrogen storage and transportation.
Unpacking demand patterns across tank types, materials, designs and use cases shaping hydrogen storage and transportation decisions
Understanding the hydrogen storage tanks and transportation landscape requires a granular view of how demand and technology choices distribute across key segments. Based on tank type, the market is studied across Type I, Type II, Type III, and Type IV, and these categories map closely to differing performance needs. Type I and Type II tanks, with their more traditional metal‑based architectures, tend to serve lower‑pressure, cost‑sensitive environments, such as certain industrial backup systems or early‑stage infrastructure. By contrast, Type III and Type IV architectures dominate where weight, corrosion resistance, and higher pressure capability are paramount, as in fuel cell vehicles or compact refueling modules that must maximize hydrogen delivered per unit mass.
Material choices add another layer of differentiation. Based on material, the market is studied across Carbon Fiber, Glass Fiber, and Metal, and each material mix influences not only cost but also safety, recyclability, and inspection regimes. Carbon fiber enables higher pressure ratings and superior weight‑to‑capacity ratios, making it central to advanced mobility solutions and high‑performance stationary systems. Glass fiber can provide a useful balance of cost and mechanical performance in medium‑duty applications, while metal remains attractive for robust, lower‑pressure tanks where mass is less critical and well‑established manufacturing and inspection methods are valued. Strategic combinations of these materials, aligned with pressure and duty‑cycle requirements, are shaping product roadmaps.
Form factor and integration constraints drive further segmentation. Based on design, the market is studied across Cylindrical Tanks, Rectangular Tanks, and Spherical Tanks. Cylindrical tanks currently underpin most commercial systems because of their manufacturing maturity and predictable stress distributions, but rectangular tanks are gaining interest for applications where space utilization within vehicles or containers is crucial. Spherical tanks, traditionally associated with large‑scale cryogenic storage, maintain relevance in specialized installations where uniform stress distribution and thermal performance justify higher upfront complexity. These design decisions must be considered alongside logistics considerations. Based on transportation mode, the market is studied across Air Transport, Marine Transport, Rail Transport, and Road Transport, with each mode imposing distinct requirements on tank packaging, vibration tolerance, certification, and interface standards.
Pressure and storage technology are intimately connected. Based on pressure rating, the market is studied across High Pressure (> 700 bar), Low Pressure (< 350 bar), and Medium Pressure (350 bar – 700 bar). High‑pressure solutions are central to mobility and compact storage where space is constrained, whereas low‑pressure configurations often support large buffer storage or applications where volume is less limited. Medium‑pressure systems serve as a bridge, particularly in modular transport cases and certain industrial uses where trade‑offs between compression energy and tank cost must be carefully managed. At the same time, based on technology, the market is studied across Compressed Gas Storage and Cryogenic Storage, reflecting a fundamental choice between gaseous and liquid pathways. Compressed gas storage remains the most widely deployed for distributed and smaller‑scale systems, while cryogenic storage is pivotal in high‑volume applications such as export terminals, large industrial hubs, and emerging liquid hydrogen bunkering and aviation concepts.
Operational context further differentiates tank solutions. Based on installation location, the market is studied across Portable and Stationary, and this distinction influences design life, mobility requirements, and regulatory oversight. Portable systems, including swap‑and‑go modules and mobile refuelers, favor lighter, more ruggedized designs with integrated monitoring, whereas stationary systems prioritize long life, ease of inspection, and integration into broader site safety plans. Capacity range is also critical. Based on tank capacity, the market is studied across 10000-50000 Liters, 3000-10000 Liters, <3000 Liters, and >50000 Liters, spanning compact vehicle tanks and skid units through to large industrial and utility‑scale installations. Suppliers increasingly tailor offerings and service models to these capacity bands to address distinct procurement processes and maintenance expectations.
End‑use patterns pull all of these segmentation dimensions together. Based on end‑use, the market is studied across Aerospace & Defense, Automotive & Transportation, Chemical & Petrochemical, Oil & Gas, and Utilities, each with its own reliability thresholds, certification requirements, and commercial structures. Aerospace & Defense applications demand exceptionally high safety margins and often rely on advanced Type III or Type IV composites with stringent qualification protocols. Automotive & Transportation projects focus on balancing cost and weight at scale, pushing innovation in mass‑manufactured composite tanks and standardized transport modules. Chemical & Petrochemical and Oil & Gas operators emphasize compatibility with existing process infrastructure and rigorous hazardous‑materials regimes, often integrating hydrogen tanks into multi‑fluid logistics chains. Utilities, finally, are exploring how a mix of compressed and cryogenic storage, across pressure and capacity segments, can underpin grid support, backup generation, and sector‑coupling initiatives. Together, these segmentation insights reveal a market that is highly heterogeneous but increasingly structured around clear performance and use‑case archetypes.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Tank Type
- Material
- Design
- Transportation Mode
- Pressure Rating
- Technology
- Installation Location
- Tank Capacity
- End-Use
Regional dynamics in hydrogen storage tanks and transport infrastructure across the Americas, Europe, Middle East & Africa and Asia‑Pacific
Regional context strongly influences how hydrogen storage tanks and transportation solutions evolve, with regulatory frameworks, industrial structure, and infrastructure maturity all playing important roles. In the Americas, national and sub‑national incentives for clean hydrogen production and deployment are catalyzing new projects across mobility, industry, and power. The United States is advancing tax credits, infrastructure funding, and regional hydrogen hub initiatives that require coordinated investment in high‑pressure composite tanks, refueling networks, and bulk logistics assets. Canada is emphasizing both export opportunities and domestic decarbonization, creating demand for large‑capacity stationary storage and marine transport solutions. In Latin American markets, interest is growing in leveraging renewable resources for hydrogen and derivative exports, which is beginning to translate into feasibility studies for cryogenic storage and marine transportation corridors.
Europe, Middle East & Africa displays a different, but complementary, pattern. European Union climate legislation and hydrogen strategies are driving rapid standardization of safety rules, performance benchmarks, and certification protocols for tanks and transport assets. This regulatory clarity supports accelerated deployment of road and rail‑based distribution networks and fuels strong demand for both portable and stationary tank systems across industrial clusters. In the Middle East, several countries are positioning themselves as major producers and exporters of low‑carbon hydrogen and derivatives, prompting investments in large‑scale cryogenic storage, export terminals, and marine transport solutions. African economies are at earlier stages but are increasingly featured in long‑term supply scenarios, creating opportunities for modular storage and transport solutions that can scale as projects progress from pilot to commercial phases.
Asia-Pacific is emerging as both a demand center and a technology testbed for hydrogen storage and transportation. Japan and South Korea continue to advance hydrogen strategies that emphasize fuel cell mobility, distributed power, and, in the longer term, hydrogen or ammonia imports, all of which require sophisticated storage tanks and multimodal logistics infrastructure. Australia is developing large renewable hydrogen and derivative projects aimed at export markets, spurring design work on cryogenic storage and marine transport concepts that can bridge long distances to Asian and European offtakers. Other Asia-Pacific economies, including China and India, are exploring domestic deployment at scale, with growing attention to localized manufacturing of tanks, composite materials, and associated logistics equipment.
Across the Americas, Europe, Middle East & Africa, and Asia-Pacific, regional policy choices and industrial strategies are thus generating distinct, yet interconnected, demand patterns for hydrogen storage tanks and transportation. Multinational companies that can align their product portfolios and partnership models with these regional trajectories-while respecting local safety codes and content requirements-are best placed to capture emerging opportunities and manage risk as the global hydrogen trade begins to take shape.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Strategic moves by leading tank manufacturers, materials suppliers and logistics innovators defining competitive advantage in hydrogen storage
Competitive dynamics in hydrogen storage tanks and transportation are intensifying as established industrial players and specialized innovators converge on this growth area. Large industrial gas and engineering companies are leveraging decades of experience in cryogenic storage, industrial gases logistics, and safety systems to offer integrated solutions that span production, storage, and transport. Their strengths lie in the ability to design turnkey projects, secure long‑term offtake and supply agreements, and navigate complex permitting processes, making them preferred partners for large industrial clusters and utility‑scale projects.
At the same time, dedicated tank manufacturers and composite specialists are pushing the frontier of Type III and Type IV technologies. These companies focus on optimizing carbon fiber usage, refining filament winding and liner technologies, and validating designs under stringent automotive and aerospace standards. Many are forming alliances with vehicle manufacturers, system integrators, and fuel retailers to co‑develop onboard storage and refueling modules tailored to specific fleets and duty cycles. Vertical integration is becoming more common, with some players moving upstream into material development or downstream into maintenance and digital monitoring services to capture more of the value chain.
Logistics and infrastructure operators, including firms active in road, rail, and marine segments, are also asserting a stronger role. By co‑designing tank modules with trailer, rail wagon, and vessel platforms, they aim to improve load factors, reduce handling times, and ensure compliance across jurisdictions. Digital platforms are emerging to monitor tank fleets, optimize routing, and manage maintenance, enabling operators to differentiate on service quality and reliability rather than capacity alone. As competitive intensity increases, companies that can combine technical excellence in tank design with robust execution capabilities in transportation and infrastructure deployment are best positioned to secure long‑term contracts and build defensible positions in key regions and end‑use segments.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- A M S Composite Cylinders Limited
- BAGLIONI S.p.A.
- BayoTech, Inc.
- BNH Gas Tanks LLP
- CALVERA HYDROGEN S.A.
- Chart Industries, Inc.
- Cummins Inc.
- Doosan Mobility Innovation
- Energiepark Bad-Lauchstaedt
- Everest Kanto Cylinder Limited
- FABER INDUSTRIE SPA
- Hexagon Purus ASA
- INOX Group
- Iwatani Corporation
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Linde PLC
- LOTTE Chemical Corporation.
- Luxfer Holdings PLC
- L’AIR LIQUIDE S.A.
- McDermott International, Ltd.
- NPROXX B.V.
- OPmobility SE
- Plug Power Inc.
- Quantum Fuel Systems LLC
- Shijiazhuang Enric Gas Equipment Co., Ltd. by CIMC Enric Holdings Limited
- Steelhead Composites, Inc.
- Tenaris S.A.
- Toyoda Gosei Co., Ltd.
- Umoe Advanced Composites
- Voith GmbH & Co. KGaA
- Weldship Group
- Worthington Cylinders GmbH
Actionable strategic priorities for hydrogen storage tank and transportation stakeholders navigating policy shifts, technology risk and capital allocation
Industry leaders seeking to shape the future of hydrogen storage tanks and transportation should prioritize a combination of technology, supply‑chain, and partnership strategies. On the technology front, organizations need clear roadmaps that align tank type, material selection, and pressure rating with target applications and regulatory environments. Investing in advanced Type III and Type IV platforms where weight and performance advantages are decisive, while maintaining selective capabilities in Type I and Type II solutions for cost‑sensitive or lower‑pressure uses, can provide a balanced portfolio. Parallel development of compressed gas storage and cryogenic storage options, along with modular designs that can be deployed in both portable and stationary configurations, will enhance flexibility as demand patterns evolve.
Supply‑chain resilience is equally critical in light of shifting trade policies and tariffs. Executives should map their dependencies on tariff‑sensitive inputs, such as steel, aluminum, selected electronics, and critical minerals, and identify alternative sourcing strategies within and beyond the Americas. Long‑term contracts with diversified suppliers, combined with localized manufacturing or final assembly where feasible, can mitigate exposure to cost volatility and regulatory change. Adopting design‑for‑supply‑chain principles-such as standardizing interfaces across 3000-10000 Liters and 10000-50000 Liters capacity bands, or designing modules that can be easily reconfigured between road transport and rail transport-can further reduce risk and improve asset utilization.
Partnerships and ecosystem engagement round out the set of actionable priorities. Collaboration with automotive and transportation, Aerospace & Defense, Chemical & Petrochemical, Oil & Gas, and Utilities customers early in project development ensures that tank and transport solutions reflect real‑world operating conditions and maintenance capabilities. Engagement with standards organizations and regulators can help shape pragmatic safety and performance rules that support innovation while maintaining public confidence. Finally, embedding digital capabilities-such as asset tracking, predictive maintenance analytics, and automated compliance reporting-into tank and transport offerings can create differentiated value propositions and open new service‑based revenue streams.
Leaders who act now to integrate these priorities into corporate strategy will be better equipped to navigate the uncertainties of evolving hydrogen policy, tariff regimes, and technology competition. By focusing on robust technology platforms, resilient and adaptable supply chains, and collaborative ecosystem development, they can position their organizations to capture long‑term advantage as hydrogen storage and transportation infrastructure scales from early projects to critical national and regional systems.
Robust multi‑source research methodology integrating primary insight, secondary intelligence and analytical rigor on hydrogen storage and transport
The insights summarized in this executive overview are grounded in a structured research methodology designed to capture both the technical nuance and the commercial realities of hydrogen storage tanks and transportation. The research team combined extensive secondary analysis with targeted primary engagement to build a coherent view of technology pathways, regulatory developments, and competitive positioning across regions and end‑use segments.
Secondary research drew on a broad range of publicly available information, including company reports, investor presentations, regulatory filings, technical standards, academic publications, trade statistics, and policy documents from national and regional authorities. Particular attention was paid to developments in material science for composite tanks, updates to safety and pressure vessel standards, and policy measures affecting clean energy infrastructure and trade, such as evolving tariff schedules on strategic materials and technologies.
To complement this foundation, the team conducted structured discussions with industry participants where possible, including tank manufacturers, engineering firms, logistics operators, technology developers, and end‑users in sectors such as automotive and transportation, Chemicals & Petrochemicals, and Utilities. These engagements helped validate assumptions about adoption barriers, cost drivers, and practical operating constraints, and provided qualitative insight into how companies are responding to regulatory and trade policy shifts.
Analytical techniques included segmentation analysis across tank type, material, design, transportation mode, pressure rating, technology, installation location, tank capacity, and end‑use; scenario exploration around policy and tariff trajectories; and cross‑regional benchmarking to understand how local regulatory and industrial contexts shape infrastructure choices. Quality control steps, including internal peer review and consistency checks across data sources, were employed to enhance reliability. While the methodology does not rely on proprietary market sizing or forecasting models in this summary, it is designed to support such analyses in the full report, enabling decision‑makers to move from qualitative insight to quantified business cases as needed.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation Market, by Tank Type
- Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation Market, by Material
- Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation Market, by Design
- Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation Market, by Transportation Mode
- Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation Market, by Pressure Rating
- Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation Market, by Technology
- Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation Market, by Installation Location
- Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation Market, by Tank Capacity
- Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation Market, by End-Use
- Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation Market, by Region
- Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation Market, by Group
- Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation Market, by Country
- United States Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation Market
- China Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 21]
- List of Tables [Total: 1590 ]
Converging technology, policy and infrastructure trends position hydrogen storage tanks and transportation as critical enablers of energy transition
Hydrogen storage tanks and transportation systems are emerging as critical enablers of a more flexible, resilient, and low‑carbon energy architecture. As hydrogen moves from pilot deployments into larger‑scale industrial, mobility, and power applications, the ability to safely and economically store and transport the molecule will determine how quickly and efficiently projects can be realized. Technology trajectories in tank design, material innovation, and storage approaches are converging with regulatory evolution and infrastructure build‑out to create a rapidly changing, but increasingly structured, landscape.
At the same time, external forces such as trade policy, particularly United States tariffs affecting key materials and technologies, are reshaping supply chains and cost structures. These shifts, while challenging in the near term, are prompting a more deliberate approach to sourcing, localization, and design standardization that can ultimately strengthen the resilience of hydrogen infrastructure. Regional dynamics across the Americas, Europe, Middle East & Africa, and Asia-Pacific further diversify opportunities and risks, as different policy frameworks and industrial strengths generate distinct demand patterns.
For executives and policymakers, the implication is clear: storage and transportation considerations must be integrated into hydrogen strategies from the outset, not treated as downstream implementation details. Organizations that understand the nuances of segmentation-from tank type and material combinations to end‑use and regional specifics-and that proactively navigate regulatory and trade developments will be best positioned to convert hydrogen’s technical promise into durable competitive advantage. The path forward will favor those who combine technological insight with strategic agility and collaborative ecosystem engagement.
Partner with Ketan Rohom to unlock deeper hydrogen storage tank and transportation insights and accelerate informed investment decisions
Hydrogen storage tanks and transportation infrastructure are no longer peripheral considerations; they sit at the center of strategic energy and logistics planning for governments and corporations alike. Executives evaluating capital projects in mobility, industrial decarbonization, or large-scale power systems increasingly recognize that storage and transport constraints can limit the value of upstream production and downstream demand.
To move from high-level interest to concrete action, decision‑makers need structured, data‑rich insight that connects technology choices, tariff developments, regional regulations, and competitive dynamics. This executive summary provides that high-level orientation, but the full study goes several levels deeper into segment‑by‑segment benchmarks, technology roadmaps, and case‑based best practices.
Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing, is available to guide stakeholders through the full market research report and help align its findings with specific strategic questions. Whether the priority is selecting between Type III and Type IV tank platforms, stress‑testing investment plans against evolving United States tariff schedules, or understanding regional go‑to‑market options, he can point decision‑makers directly to the most relevant analyses.
Engaging with Ketan enables leadership teams to convert complex hydrogen storage and transportation developments into practical actions, from portfolio prioritization and supply‑chain design to partnership selection. By purchasing the full report and discussing its implications with him, organizations can shorten their learning curves, reduce execution risk, and ensure their hydrogen strategies are informed by rigorous, up‑to‑date market intelligence rather than fragmented anecdotal information.

- How big is the Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation Market?
- What is the Hydrogen Storage Tanks & Transportation Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




