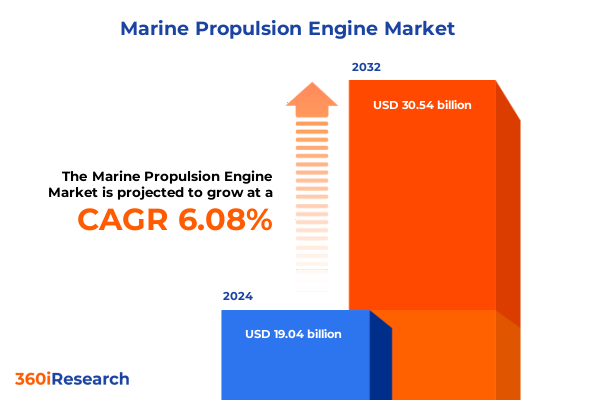
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market size was estimated at USD 20.14 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 21.33 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 6.12% to reach USD 30.54 billion by 2032.
Introduction to Indonesia’s marine propulsion dynamics where legacy diesel demand and emergent low-emission technologies converge amid supply-chain and regulatory pressures
Indonesia’s marine propulsion engine landscape sits at the intersection of traditional maritime demand and rapid technological disruption, creating a challenging yet opportunity-rich environment for shipowners, engine manufacturers, and systems integrators. Demand drivers in the archipelago are multifaceted: a sustained need for replacement and retrofit in coastal and riverine fleets, expansion in offshore support activity, persistent growth in domestic cargo movement, and a buoyant leisure and tourism sector that supports higher-margin recreational and passenger builds. Meanwhile, legacy diesel architectures coexist with emergent low-emission platforms, producing a heterogeneous fleet profile that requires flexible supply chain and service strategies.
Transitioning from legacy practices toward more modular, electrified, and fuel-diverse propulsion systems is reshaping procurement and maintenance cycles. Across Indonesia, shipyards and operators face competing priorities: reducing lifecycle fuel costs, meeting stricter emissions and port regulations, and maintaining operational reliability in remote operating areas. These pressures are translating into greater interest in alternative powertrains and hybridization as well as selective repowers of existing hulls. At the same time, global supply chain realignments and geopolitical dynamics are increasing emphasis on local content, secure sourcing of critical materials for propulsion systems, and clarity on import duties and compliance. For Indonesian stakeholders, the imperative is to balance near-term uptime and cost pressures with medium-term investment in decarbonization-ready architectures.
Consequently, commercial strategies must be both pragmatic and forward-looking. Operators that prioritize modular system architectures, create clear lifecycle TCO models, and invest in targeted crew and shore-side capabilities will be better positioned to capture efficiencies from fuel switching, hybridization, and incremental electrification. In parallel, manufacturers and integrators that can deliver retrofit kits, flexible power modules, and robust service networks tailored to the geographic and operational realities of Indonesian waters will gain a distinct competitive advantage.
Rapid technological and regulatory shifts are turning product competition into systems competition where integration, lifecycle services, and local supply resilience determine market winners
The marine propulsion landscape is undergoing transformative shifts driven by technology, policy, and evolving vessel economics. Advances in energy-dense batteries, higher-efficiency electric motors, and progress in hydrogen and fuel-cell systems are expanding the technical feasibility envelope for hybrid and zero-emission propulsion, particularly on short-haul, passenger, and inland segments. As battery energy density improves and charging or charging-alike infrastructure develops, operators are able to contemplate architectures that were previously constrained to trial projects. Concurrently, incremental improvements in diesel engine efficiency, digital engine management, and exhaust aftertreatment remain critical for work-intensive commercial and offshore classes where power density and range are non-negotiable.
Policy and port-level regulation are increasingly shaping technology adoption pathways. Emission control areas, IMO guidelines, and regional port initiatives are nudging vessel operators to consider low-emission alternatives and retrofits earlier in vessel life cycles. Financial instruments and green financing for cleaner ships and repowers are maturing, linking cost of capital to demonstrable emissions performance and retrofit readiness. From an industry structure perspective, partnerships between OEMs, integrators, battery suppliers, and power-electronics specialists are proliferating, reflecting the need for cross-disciplinary systems integration to deliver reliable hybrid solutions at scale. Local service and parts ecosystems are also evolving; where previously OEM aftersales dominated, a broader ecosystem of certified integrators and local service partners is emerging to support hybrid and modular system deployments.
These shifts have direct consequences for product roadmaps and competitive positioning. Engine manufacturers that accelerate modular electrification pathways, develop retrofit-friendly interfaces, and support open diagnostics and maintenance protocols will increase relevance across newbuild and retrofit markets. At the same time, supply-chain resilience-particularly for critical inputs such as high-grade steel, power-electronics semiconductors, and battery-cell chemistries-will dictate which players can deliver on price and lead-time promises. In short, the market is moving from point-product competition to systems-led competition where integration capability, service footprint, and supply assurance matter as much as raw engine performance.
Analysis of how United States tariff adjustments in 2025 on steel, aluminum, and targeted technology inputs materially reshape component costs, supply chains, and procurement choices
Recent United States tariff actions in 2025 have raised the cost and complexity of imported raw materials and key components that underpin marine propulsion systems, with practical implications for global supply chains and regional sourcing strategies. Most notably, U.S. proclamations raised tariff rates on steel and aluminum imports, heightening the price risk for metal-intensive components and assemblies used in engine blocks, crankcases, shafts, couplings, and ancillary fabrications. Official U.S. actions in 2025 increased duties on certain steel and aluminum articles and broadened the scope of products subject to elevated rates, with effective dates in early June 2025 for higher-rate adjustments. These formal proclamations are publicly documented and reflect a deliberate policy to adjust import treatment for steel and aluminum articles.
Concurrently, targeted changes under Section 301 reviews adjusted tariffs on specific technology-related inputs, with increases that took effect at the start of 2025 for categories such as polysilicon, wafers, and certain tungsten products-inputs that are not direct propulsion components but are relevant to electrification and power electronics supply chains. The tariff adjustments under Section 301 increased protection on select categories to levels that materially alter cost comparisons for imported subsystems and spares. These actions create knock-on effects for manufacturers and integrators who source power-electronics modules, control semiconductors, and other components from impacted supply hubs.
The cumulative impact of these U.S. tariff actions is ecosystem-specific. For engine builds and major component assemblies where steel and aluminum form a substantial cost base, manufacturers exposed to North American supply routes face higher landed costs and compressed margin windows. For global suppliers and OEMs that rely on cross-border subassembly flows, the tariffs increase the incentive to re-route supply, localize fabrication, or absorb cost by negotiating new supplier terms. Operators and shipyards outside the U.S., including those in Indonesia, will not be directly subject to U.S. import duties, yet they will feel secondary effects through higher OEM pricing, constrained global capacity for specific grades of steel or aluminum, and rebalancing of trade flows. In practical terms, procurement professionals should reassess supplier contracts, contingency inventories, and component localization strategies to mitigate tariff-driven disruption and to capitalize on opportunities where re-shoring or regionalization improves lead times and price visibility. Reuters and official White House texts document the timing and scope of these tariff decisions and their stated policy intents, which industry stakeholders must fold into scenario planning.
Segment-specific insights showing why engine architecture, power class, placement, installation modality, speed class, vessel verticals, and end-user priorities define adoption pathways
Segment-level dynamics reveal differentiated trajectories for adoption, retrofit demand, and service economics, driven by engine architecture, power class, placement, installation type, speed class, vessel application, and end-user requirements. Engine type distinctions are foundational: diesel platforms continue to dominate heavy-duty and long-range applications and are themselves subdivided into high-speed, medium-speed, and low-speed variants with distinct maintenance rhythms and OEM ecosystems. High-speed diesels remain prevalent in smaller commercial, passenger, and recreational classes where compactness and responsiveness are priorities, while low-speed, medium-speed units underpin large cargo and tanker applications where fuel efficiency and multi-decade life cycles govern decision rules. Electrification and fuel cells are gaining traction where duty cycles and charging or fueling logistics allow predictable, repeatable operating windows; gas turbines and steam turbines retain niche relevance in specialized high-power or legacy installations.
Power output categories exert a meaningful influence on technology choices and lifecycle trade-offs. Engines in the up-to-1000 kW band favor compact, high-speed diesels and hybrid-electrified architectures, enabling owners to prioritize fuel flexibility and simplified repower paths. The midband from 1000 to 3000 kW is a battleground where hybridization, selective electric-assist, and advanced diesel platforms compete on total cost of operation and regulatory compliance. Above 3000 kW remains the domain where energy density and continuous power favor diesel and gas turbine solutions, although modular hybridization for auxiliary loads is becoming common.
Placement and installation choices also shape product and service demand. Inboard and outboard architectures present differing maintenance access and retrofit complexity, while sterndrive and jet-drive platforms influence integration of propulsion control and ancillary systems. Newbuild programs versus retrofit/repower decisions are central to adoption timelines: newbuilds allow native integration of alternative powertrains while retrofit pathways require modular interfaces, clear certification processes, and short installation windows to minimize downtime.
Engine speed classes, ranging from high-speed to low-speed categories, correlate directly with maintenance intervals, spare parts cadence, and operator skill requirements. Vessel segmentation further refines priorities: commercial cargo classes favor durability and fuel economy; offshore support vessels prioritize redundancy and rapid maintainability; passenger and recreational segments emphasize noise, emissions, and onboard comfort; defense operators weight reliability, mission endurance, and domestic sourcing constraints. Finally, end-user categories-commercial, defense, and recreational-create distinct procurement time horizons and risk tolerances, with defense procurement typically prioritizing security-of-supply and certification while commercial actors focus on lifecycle economics and deployment flexibility. Taken together, these segmentation lenses indicate that a one-size-fits-all product or service strategy is unlikely to succeed; winning approaches will be calibrated to engine class, vessel mission, and installation modality.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Marine Propulsion Engine market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Engine Type
- Power Output
- Engine Placement
- Installation Type
- Engine Speed Class
- Vessel Type
- End User
Regional dynamics and procurement corridors explain why Asia-Pacific proximity, Americas service networks, and EMEA regulatory regimes collectively shape Indonesian sourcing and retrofit decisions
Regional dynamics matter in translating global trends to commercial outcomes for Indonesia, because supply chains, financing access, regulatory regimes, and vessel mixes vary significantly across geographies. In the Americas, infrastructure investment cycles, a high concentration of aftermarket service networks, and proximity to North American OEMs influence procurement patterns; the region’s policy choices on import duties also shape where manufacturers route supply and set pricing. Europe, the Middle East and Africa display heterogenous demand: stringent European emissions expectations and an active shipbuilding and retrofit market create early-adopter niches for low-emission technologies, while the Middle East’s investment in offshore sectors and Africa’s coastal trade expansion present specialized opportunities for medium- and large-bore engines. Asia-Pacific is the most directly relevant geographic cluster for Indonesian stakeholders, featuring dense shipbuilding capacity, a strong supplier base for engine components, and rapid adoption of hybrid and alternative fuel programs in several neighboring markets.
For Indonesia specifically, proximity to Asia-Pacific suppliers confers advantages in lead time and regional collaboration, yet domestic content requirements and port infrastructure gaps create local constraints on the pace of electrification and repower projects. Cross-regional supply realignments triggered by tariff actions or critical minerals policies can shift sourcing corridors, making it essential for Indonesian operators to monitor supplier footprints across the Americas, Europe/Middle East/Africa, and Asia-Pacific. Engagement with regional certification authorities and financiers is also important, as regionally tailored financing or incentives can materially change the economics of repower or newbuild programs. Ultimately, a regionalized sourcing strategy that leverages Asia-Pacific manufacturing strength while maintaining contingency access to Western suppliers for specialty components will offer the best balance of cost, lead time, and technical capability.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Marine Propulsion Engine market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Supplier and competitor landscapes are shifting to favor integrators that combine modular hardware, software-driven fleet services, and certified regional service footprints to win Indonesian contracts
Competitive and supplier landscapes are converging toward an ecosystem view where engine OEMs, power-electronics firms, battery suppliers, and integrators bid to provide integrated propulsion solutions. Established engine manufacturers continue to protect market positions in heavy-duty segments through scale, certification expertise, and broad service networks. At the same time, new entrants and specialized integrators are capturing share in hybrid and electrified niches by offering modular systems, software-driven energy management, and retrofit packages optimized for constrained dockside windows. Strategic partnerships between engine OEMs and battery or fuel-cell suppliers are accelerating time-to-market for hybrid platforms, while digitalization initiatives-predictive maintenance, remote diagnostics, and digital twin simulations-are becoming core differentiators for aftermarket service contracts.
For Indonesian stakeholders, supplier selection will increasingly reward firms that can demonstrate proven integration capability, local service support, and flexible warranty frameworks that accommodate mixed-power architectures. Firms that invest in certified local assembly or authorized service centers in the region will gain preference from operators looking to minimize downtime and import complexity. Additionally, companies that offer end-to-end transition services-technical feasibility assessments, engineering packages for repower, crew training courses, and operational monitoring platforms-will capture more value than those that sell discrete components alone. The competitive field therefore favors players who can combine product excellence with systems-level integration and a credible regional service footprint.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Marine Propulsion Engine market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- Anglo Belgian Corporation NV
- Bergen Engines AS
- Brunswick Corporation
- Caterpillar Inc.
- Cummins Inc.
- Everllence SE
- GE Aerospace
- Guascor Energy S.A.U.
- Haluan Group
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- MPS GROUP
- PT Antakesuma Inti Raharja
- PT Jagad Mandiri Marine
- PT Marmin
- PT Trayagantha Pinasthika
- PT. Daya Pioneer International
- Rolls-Royce plc
- Samudra Diesel
- Scania CV AB
- Steyr Motors AG
- TEKNO Group
- Volvo Group
- Weichai Holding Group Co.,Ltd.
- Wärtsilä Corporation
- Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd.
- YANMAR HOLDINGS CO., LTD.
Actionable strategic moves for industry leaders to hedge tariff risk, accelerate modularization, and build regional service and financing models that secure competitive advantage
To preserve competitiveness and manage risk in a rapidly changing landscape, industry leaders should prioritize a set of actionable moves that balance short-term continuity with longer-term transformation. First, companies should conduct a focused component-exposure audit that maps their reliance on tariff-sensitive inputs-particularly steel, aluminum, and key electronic components-and then develop prioritized mitigation measures such as multi-sourced procurement, regional fabrication partnerships, and selective stockpiling for critical spares. Second, accelerate modularization of powertrain platforms to simplify retrofit interfaces, shorten installation time, and enable staged electrification; modular designs will also de-risk supplier transitions and make product lifecycles more flexible.
Third, invest in regional service capabilities in Indonesia and neighboring Asia-Pacific centers through authorized service partnerships or localized assembly to reduce lead times and improve warranty responsiveness. Fourth, expand offerings beyond hardware by bundling engineering services, financing options, and performance-based maintenance contracts that align incentives with operators’ fuel and emissions goals. Fifth, align product roadmaps with regulatory trajectories and port requirements to ensure certification pathways are cleared ahead of deployment windows. Finally, adopt scenario-based planning that explicitly models tariff shock cases, raw-material supply disruptions, and accelerated regulatory shifts to test the resilience of sourcing and pricing strategies. Implementing these moves in parallel-procurement hedging, modular product design, service localization, and commercial model innovation-will put industry leaders in a position to protect margin while capturing new growth from retrofit and low-emissions adoption.
A decision-grade mixed-methods approach combining primary interviews, component exposure mapping, and scenario-based trade-policy simulations to validate practical impacts for Indonesia
This research applies a blended methodology combining qualitative stakeholder interviews, component-level technical analysis, and scenario-based supply-chain stress testing to produce rigorous, decision-grade insights. Primary inputs include structured interviews with OEM product managers, shipyard procurement leads, ship operators, and regional service providers to capture real-world constraints and adoption barriers; secondary inputs comprise technical whitepapers, publicly available regulatory texts, tariff proclamations and notices, and manufacturer specification sheets to validate engineering assumptions. Component exposure mapping was performed by decomposing representative propulsion platforms into bill-of-materials categories and assessing sensitivity to input cost shocks such as steel and aluminum tariff uplifts.
Scenario analysis simulated multiple trade-policy trajectories-including elevated tariffs on steel and aluminum, targeted technology tariffs, and critical-minerals restrictions-to estimate practical impacts on lead time, landed cost, and retrofit feasibility. The research triangulated findings through cross-checks with global procurement trends and regional shipbuilding activity to ensure relevance to Indonesia’s fleet composition. Where applicable, specialist technical reviewers validated assumptions on engine speed classes, installation complexity, and integration timelines. The methodology privileges transparency: assumptions, data sources, and scenario parameters are documented and available in appendices to support client validation and internal replication.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Marine Propulsion Engine market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Marine Propulsion Engine Market, by Engine Type
- Marine Propulsion Engine Market, by Power Output
- Marine Propulsion Engine Market, by Engine Placement
- Marine Propulsion Engine Market, by Installation Type
- Marine Propulsion Engine Market, by Engine Speed Class
- Marine Propulsion Engine Market, by Vessel Type
- Marine Propulsion Engine Market, by End User
- Marine Propulsion Engine Market, by Region
- Marine Propulsion Engine Market, by Group
- Marine Propulsion Engine Market, by Country
- United States Marine Propulsion Engine Market
- China Marine Propulsion Engine Market
- Indonesia Marine Propulsion Engine Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 20]
- List of Tables [Total: 2400 ]
Conclusion emphasizing pragmatic dual-track execution to protect operations today while investing in modular electrification and supply resilience for the future
In conclusion, the Indonesian marine propulsion engine market is confronting a period of constructive disruption where technology evolution, regulatory pressure, and geopolitical trade actions intersect to reshape product economics and supply reliability. Diesel platforms retain foundational importance across high-power and long-range applications, but a clear and growing role exists for hybrid, electric, and alternative-fuel solutions where operating profiles and infrastructure permit. Tariff actions originating from major markets in 2025 add a new layer of procurement complexity by increasing cost volatility for metal-intensive components and for select electrification inputs, underscoring the need for proactive supplier strategies and regional service investments.
Stakeholders that adapt through modular product design, pragmatic localization of service and fabrication, and innovative commercial models-such as performance-based maintenance and bundled financing-will find opportunities to improve margins, accelerate retrofit adoption, and capture differentiated share. Conversely, firms that treat these shifts as incremental rather than structural risk ceding advantage to more integrated competitors. The path forward requires balanced execution: protect short-term operational continuity while allocating measured investments toward electrification-readiness and supply-chain resilience. This dual focus will enable operators and suppliers in Indonesia to navigate tariff-driven disruptions and to participate in the broader transition toward lower-emission maritime operations.
Secure a tailored briefing and purchase path with the Associate Director of Sales & Marketing to unlock the complete Indonesian marine propulsion engine market study and custom deliverables
For decision-makers seeking immediate, defensible intelligence and a practical route to commercial advantage, acquiring the full market research report is the most effective next step. The report delivers comprehensive coverage across engine types, power classes, placement strategies, installation options, speed classes, vessel verticals, and end-user segments, enabling procurement, engineering and commercial teams to align investments with regulatory and supply-chain realities. It also contains detailed supplier matrices, component-level exposure analyses, and scenario-based playbooks tailored to Indonesia’s shipbuilding and retrofit markets.
If you would like a tailored briefing, a sample executive dashboard, or a proposal that maps the report’s insights to your organization’s specific priorities in Indonesia, reach out to Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing. Ketan can arrange a custom briefing, share a limited preview of the report’s table of contents, and discuss licensing options and bespoke add-ons such as custom data extracts or competitor benchmarking. Engaging directly will accelerate your access to granular tables, vendor risk scores, and actionable roadmaps that are not available in summary form.
Investing in the full study will shorten your decision cycle by converting broad market signals into prioritized tactical actions for procurement, engineering roadmaps, JV negotiations, and aftermarket strategy. To initiate a purchase or to request a tailored briefing, contact Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing, and mention your interest in the Indonesian marine propulsion engine market report to arrange next steps and timing.

- How big is the Marine Propulsion Engine Market?
- What is the Marine Propulsion Engine Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




