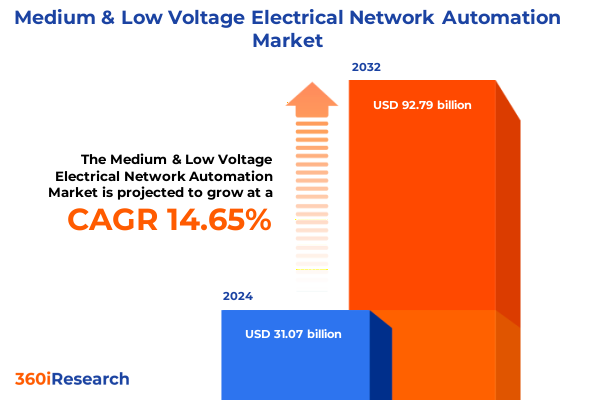
The Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation Market size was estimated at USD 35.64 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 40.11 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 14.64% to reach USD 92.79 billion by 2032.
Exploring the Critical Role of Automation in Modern Medium and Low Voltage Electrical Networks to Drive Operational Efficiency Reliability and Grid Resilience
Exploring the Critical Role of Automation in Modern Medium and Low Voltage Electrical Networks to Drive Operational Efficiency Reliability and Grid Resilience
The electrical grid of today faces an unprecedented array of challenges, ranging from aging infrastructure and evolving regulatory mandates to the integration of distributed energy resources and the need for greater fault tolerance. Automation at the medium and low voltage levels has emerged as a foundational pillar to address these demands, offering network operators real‐time visibility into asset health and enabling rapid response to system anomalies. By embedding digital controls, intelligent sensors, and advanced communication protocols at strategic nodes across the grid, utilities can transition from reactive maintenance cycles to predictive and condition‐based strategies that extend asset lifecycles and minimize unplanned outages.
Moreover, as decarbonization initiatives accelerate globally, the grid’s ability to accommodate solar, wind, and storage assets at the distribution level becomes critical. Automated platforms that orchestrate voltage regulation, fault isolation, and service restoration are essential for integrating variable renewable resources without compromising power quality. In tandem with stringent reliability standards, these systems support two‐way power flows, enabling prosumers and microgrids to operate within a broader grid ecosystem seamlessly. Consequently, investments in medium and low voltage automation are not simply about replacing legacy relays and switches; they represent a strategic transformation towards a more resilient, flexible, and intelligent electrical network.
Navigating Transformative Shifts in the Electrical Automation Landscape with Digitization Integration and Advanced Data Analytics Fueling Grid Evolution
Navigating Transformative Shifts in the Electrical Automation Landscape with Digitization Integration and Advanced Data Analytics Fueling Grid Evolution
The landscape of medium and low voltage network automation is undergoing a profound transformation driven by the convergence of digitization, cloud computing, and big data analytics. Traditionally, supervisory control and data acquisition systems and distribution management solutions operated in silos, isolated from predictive maintenance platforms and enterprise asset management tools. Today, these disparate systems are being unified under open‐architecture frameworks that facilitate real‐time data exchange, enhance situational awareness, and enable intelligent decision support across utility control centers and field operations.
In parallel, advancements in edge computing have empowered remote terminal units and intelligent electronic devices to perform localized analytics, reducing latency and preserving network bandwidth. Machine learning algorithms applied to streaming sensor data can now detect incipient equipment faults, forecast loading conditions, and optimize voltage setpoints with minimal human intervention. This shift towards smarter, distributed intelligence not only improves system reliability but also defers capital investments by maximizing the utilization of existing assets.
Furthermore, the rise of interoperable communication standards such as IEC 61850 and DNP3 over secure channels has mitigated protocol fragmentation, enabling seamless integration between network elements from different manufacturers. As a result, utilities can adopt a heterogeneous portfolio of automation products without sacrificing performance or consistency. Taken together, these developments mark a new era in which data‐driven insights, modular architectures, and resilient communications converge to deliver next‐generation grid capabilities.
Assessing the Cumulative Impact of US 2025 Tariffs on Supply Chains Procurement Strategies and Technological Adoption in Medium and Low Voltage Automation
Assessing the Cumulative Impact of US 2025 Tariffs on Supply Chains Procurement Strategies and Technological Adoption in Medium and Low Voltage Automation
Over the past year, a series of tariff impositions by the United States government on imported steel, aluminum, and selected electrical components has reverberated throughout the medium and low voltage automation sector. The cumulative effect of these measures has been to elevate raw material costs and introduce volatility into the global supply chain. Project planners have responded by accelerating orders, hedging material purchases, and renegotiating contracts to lock in prices before further tariff escalations.
Moreover, the procurement strategies of technology OEMs and system integrators have shifted towards diversifying vendor bases, including cultivating domestic foundries and forging alliances with non‐traditional suppliers in regions unaffected by US policy. These adjustments have triggered a rebalancing of lead times and inventory carrying costs, prompting some organizations to localize critical component manufacturing closer to end markets. In turn, this localization trend has improved supply chain resilience but has required significant investments in automation equipment and quality‐assurance processes domestically.
Consequently, the tariff environment has also influenced the pace at which certain advanced automation technologies are adopted. Projects with tight capital budgets have deferred upgrades to digital substations and advanced analytics platforms, while others have pivoted towards retrofit solutions that maximize return on existing assets. As utility executives navigate this complex policy backdrop, the ability to model total cost of ownership, account for import duties, and secure alternative sourcing channels has become integral to sustaining modernization roadmaps.
Unveiling Critical Insights into How Automation Types Voltage Levels Components Communication Methods Installation Models and End Users Drive Market Evolution
Unveiling Critical Insights into How Automation Types Voltage Levels Components Communication Methods Installation Models and End Users Drive Market Evolution
The medium and low voltage network automation market is inherently multifaceted, shaped by several key segmentation dimensions that influence technology selection and deployment strategies. Based on automation type, utilities and service providers allocate resources across asset management platforms that encompass condition monitoring, life cycle management, and predictive maintenance; distribution automation functions such as fault location, isolation, and service restoration alongside network reconfiguration and volt‐var optimization; feeder automation modules including feeder monitoring, remote terminal units, and switchgear automation; network management systems that integrate distribution management and SCADA capabilities; as well as substation automation solutions spanning communication, control, monitoring, and protection automation.
Voltage level segmentation further delineates offerings between low voltage systems typically deployed within commercial, industrial, and utility distribution networks and medium voltage platforms that operate at higher thresholds to facilitate substation-to-grid connectivity. Component-wise, the automation ecosystem relies on actuators-both motor and solenoid operated-controllers such as intelligent electronic devices, PLCs, and RTUs, alongside relays (control, numerical, and protective), sensors (current, temperature, voltage), and switchgear elements including circuit breakers, disconnectors, and load break switches.
Communication technologies represent another critical axis, with Ethernet, fiber optic, powerline communication, satellite links, and wireless solutions-spanning cellular, microwave, and RF mesh-supporting real‐time data exchange and remote control. At the end‐user level, commercial sectors (spanning buildings, data centers, hospitals), industrial domains (manufacturing, mining, oil & gas, water & wastewater), and utilities each demand tailored automation approaches. Finally, installation models range from greenfield projects focused on new distribution networks and substations to retrofit initiatives-both full and partial-that modernize legacy equipment. Together, these segmentation drivers illustrate the diversity and complexity inherent in designing future‐ready electrical networks.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Automation Type
- Voltage Level
- Component
- Communication Technology
- Installation Type
- End User
Delivering Regional Perspectives on How the Americas EMEA and AsiaPacific Are Driving Innovation Adoption and Resilience in Electrical Network Automation
Delivering Regional Perspectives on How the Americas EMEA and AsiaPacific Are Driving Innovation Adoption and Resilience in Electrical Network Automation
In the Americas, utility modernization has been propelled by federal and state incentives aimed at grid hardening, renewable integration, and cybersecurity enhancements. The United States market, in particular, has witnessed extensive pilot programs for advanced distribution management and mobile response units equipped with real‐time analytics. Meanwhile, utility operators in Canada have prioritized grid stability across remote and harsh terrain, deploying robust network management systems and leveraging satellite communications to maintain reliability.
Transitioning to Europe, the Middle East, and Africa (EMEA), regulatory mandates under the European Union’s Clean Energy Package have accelerated the adoption of automated voltage control and demand‐response mechanisms. In the Gulf region, sovereign wealth funds have underwritten smart city initiatives that incorporate substation automation and extensive use of fiber optics. Conversely, in Africa, electrification programs have emphasized cost-effective, modular automation packages that combine solar microgrids with protective relays and basic SCADA functions to extend service to underserved communities.
In Asia-Pacific, rapid urbanization and industrial expansion are key growth drivers. China’s state-owned utilities continue to deploy IEC 61850-compliant substations at scale, while India’s government-sponsored renewable energy corridors rely on feeder automation and fault isolation technologies to maintain grid stability amidst high variability. Japan remains a leader in life cycle management systems for transformers and switchgear, and Australia’s focus on bushfire mitigation has spurred investment in satellite-linked monitoring and automated sectionalizers.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Highlighting Leading Technology Providers Distributors and Integrators Defining Competitive Strategies and Partnerships in Medium and Low Voltage Network Automation
Highlighting Leading Technology Providers Distributors and Integrators Defining Competitive Strategies and Partnerships in Medium and Low Voltage Network Automation
The competitive arena for medium and low voltage network automation is characterized by established multinational firms partnering with innovative niche players to deliver end‐to‐end solutions. Leading global original equipment manufacturers have enhanced their portfolios through strategic acquisitions of software analytics start-ups, thereby integrating cloud platforms with traditional relay and switchgear offerings. Moreover, system integrators have formed alliances with telecommunications providers to bundle wireless connectivity, edge gateways, and managed services, creating turnkey deployment models that reduce implementation complexity.
In parallel, several emergent technology vendors are disrupting conventional value chains by commercializing plug-and-play automation modules equipped with embedded intelligence. These providers can quickly address retrofit scenarios, offering containerized solutions that communicate over existing powerline or broadband networks. At the regional level, distributors have sharpened their focus on localized engineering and after-sales support, ensuring that utilities have rapid access to spare parts and expert troubleshooting.
Furthermore, partnerships between cybersecurity firms and automation specialists have taken center stage as threats to industrial control systems escalate. Joint offerings that embed anomaly detection algorithms directly into programmable logic controllers and protective relays exemplify the trend towards security‐by‐design. Collectively, these strategic initiatives reflect a market in which collaboration and cross-industry convergence are imperatives for sustaining competitive advantage.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- ABB Ltd.
- Beckwith Electric Co., Inc.
- Chint Group Co., Ltd.
- Eaton Corporation plc
- Entec Electric & Electronic Co., Ltd.
- Fuji Electric Co., Ltd.
- G&W Electric Company
- General Electric Company
- Hubbell Incorporated
- Larsen & Toubro Limited
- Legrand SA
- Liyond (Changzhou) Co., Ltd.
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- NR Electric Co., Ltd.
- People Electric Appliance Group Co., Ltd.
- Rockwell Automation, Inc.
- Schneider Electric SE
- Siemens AG
- Socomec Group S.A.
- Sécheron Holding SA
- Toshiba Corporation
Offering Actionable Recommendations to Industry Leaders for Accelerating Deployment Enhancing Interoperability and Cyber Resilience in Network Automation
Offering Actionable Recommendations to Industry Leaders for Accelerating Deployment Enhancing Interoperability and Cyber Resilience in Network Automation
To harness the full potential of medium and low voltage network automation, industry leaders should prioritize the adoption of open‐architecture frameworks that facilitate seamless integration between devices and platforms. By aligning on interoperable communication standards and leveraging middleware abstraction layers, utilities can avoid vendor lock‐in and expedite the deployment of new functionalities without costly rip-and-replace projects. Additionally, embedding cybersecurity best practices-such as network segmentation, zero-trust policies, and continuous threat monitoring-directly into automation architectures is critical for safeguarding critical infrastructure against evolving adversaries.
Moreover, organizations should invest in advanced analytics and artificial intelligence capabilities that transform voluminous streaming data into actionable insights. Establishing a phased roadmap that begins with condition monitoring and evolves towards prescriptive maintenance can maximize return on investment while building internal data science competencies. Engaging cross-functional teams that include field technicians, control engineers, and IT specialists early in the planning stages ensures that human-machine interfaces and reporting dashboards align with operational workflows.
Lastly, to improve supply chain resilience and reduce dependency on single‐source suppliers, companies should develop strategic alliances with regional manufacturing partners and explore on-shore production of critical components. Cultivating talent through targeted training programs in automation engineering, cybersecurity, and data analytics will further empower organizations to execute modernization initiatives with confidence and agility.
Outlining Research Methodology Built on Primary Expert Interviews Secondary Data Triangulation and Industry Validation to Ensure Comprehensive Report Accuracy
Outlining Research Methodology Built on Primary Expert Interviews Secondary Data Triangulation and Industry Validation to Ensure Comprehensive Report Accuracy
This report’s findings are underpinned by a rigorous research methodology designed to ensure validity and depth. The primary research phase involved extensive interviews with senior‐level stakeholders, including utility executives, control engineers, and technology providers, to capture firsthand insights on automation adoption, pain points, and future priorities. These discussions were complemented by detailed surveys of regional grid operators and system integrators to quantify technology preferences and deployment timelines.
In parallel, secondary research encompassed a systematic review of regulatory filings, industry whitepapers, patent databases, and technical journals to map the competitive landscape and track emerging technology trends. Data triangulation techniques were applied to reconcile discrepancies by cross-referencing multiple data sources, ensuring that conclusions reflect both qualitative perspectives and quantitative evidence. Finally, all key findings underwent validation workshops with subject-matter experts to refine assumptions and align interpretations with real-world practices. This multi-layered approach provides stakeholders with confidence in the report’s comprehensive coverage and actionable insights.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation Market, by Automation Type
- Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation Market, by Voltage Level
- Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation Market, by Component
- Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation Market, by Communication Technology
- Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation Market, by Installation Type
- Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation Market, by End User
- Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation Market, by Region
- Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation Market, by Group
- Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation Market, by Country
- United States Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation Market
- China Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 18]
- List of Tables [Total: 3498 ]
Summarizing Key Insights and Highlighting the Strategic Imperatives for Stakeholders in Medium and Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation
Summarizing Key Insights and Highlighting the Strategic Imperatives for Stakeholders in Medium and Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation
The convergence of digital technologies, regulatory pressures, and evolving energy landscapes has elevated medium and low voltage automation from a niche operational enhancement to a strategic imperative for utilities and industrial end users alike. By embedding advanced analytics, edge computing, and interoperable communication protocols, organizations can unlock new levels of grid reliability, safety, and adaptability. Meanwhile, the cumulative effects of trade policies underscore the importance of supply chain diversification and localized manufacturing to mitigate cost volatility and project delays.
Across market segments and regions, tailored strategies-whether focusing on condition‐based maintenance, fault isolation, or renewable integration-are essential for addressing unique regional challenges and end‐user requirements. Industry leaders that embrace open architectures, prioritize cybersecurity by design, and cultivate internal data‐science capabilities will be best positioned to capitalize on the opportunities presented by distributed energy resources and smart grid initiatives. Ultimately, the path forward hinges on cross‐industry collaboration, continuous innovation, and a steadfast commitment to future-proofing electrical networks.
Engage with Ketan Rohom to Secure Your Definitive Market Intelligence Report and Empower Strategic Decisions in Electrical Network Automation Today
To explore how these insights translate into a comprehensive strategic advantage and to secure the full market intelligence report covering medium and low voltage electrical network automation, reach out to Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing at our firm. He can provide you with tailored insights, address your specific industry challenges, and facilitate access to the data you need to make informed technology investments and accelerate project timelines. Engaging directly with Ketan ensures you gain actionable guidance, custom data extracts, and a detailed briefing on emerging trends shaping the future of grid automation.

- How big is the Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation Market?
- What is the Medium & Low Voltage Electrical Network Automation Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




