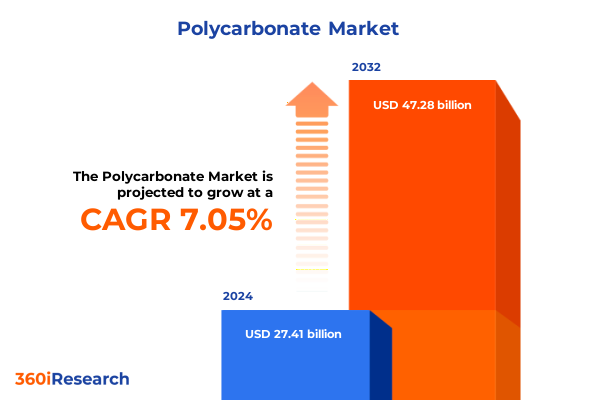
The Polycarbonate Market size was estimated at USD 29.27 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 31.26 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 7.08% to reach USD 47.28 billion by 2032.
Polycarbonate at the center of advanced materials innovation and cross industry transformation in a rapidly shifting global landscape
Polycarbonate has become one of the most versatile engineering thermoplastics underpinning modern industrial systems, combining optical clarity, impact resistance, dimensional stability, and heat resistance in a way few materials can match. Its ability to substitute glass, metal, and conventional commodity plastics across demanding environments makes it central to innovation in mobility, building technologies, electronics, medical devices, and industrial equipment. At the same time, the material is directly exposed to shifting regulatory expectations, evolving trade policy, and accelerating sustainability commitments from global brands.
As value chains adapt to decarbonization and circular economy goals, polycarbonate stands at a critical juncture. On one side, its durability, light weight, and design flexibility support more efficient vehicles, safer buildings, and compact high performance electronics. On the other, scrutiny of feedstocks such as bisphenol A, rising expectations around recycled or bio based content, and heightened attention to end of life management are reshaping how producers, converters, and users think about product selection and long term material strategies.
This executive summary provides a structured view of the current polycarbonate landscape, emphasizing qualitative insight rather than numerical projections. It highlights how product forms, processing routes, performance grades, applications, and end use industries interact with regional dynamics and policy change. It also explores how emerging technologies, particularly in chemical recycling and advanced compounding, are beginning to redefine what is technically and economically feasible. Together, these themes create a framework that helps senior stakeholders evaluate risk, prioritize opportunity, and position polycarbonate within broader material portfolios in the years ahead.
Structural shifts redefining polycarbonate demand across mobility construction electronics and sustainable design in the new industrial era globally
The polycarbonate ecosystem is undergoing structural shifts driven by sustainability, electrification, digitalization, and stricter regulatory oversight. Major brands across automotive, electronics, construction, and consumer goods now embed emissions reduction and circularity into product design decisions, pushing resin producers and compounders to develop low carbon and recycled content grades. Advances in depolymerization technologies, including mechanochemical methanolysis, carbon dioxide catalyzed alcoholysis, and nickel catalyzed reductive processes that recover bisphenol A from end of life polycarbonate and blends, have moved quickly from laboratory curiosity toward scalable pilot concepts, signaling that chemical recycling is likely to become a meaningful complement to mechanical routes over time.
Simultaneously, the shift toward electric and connected vehicles, advanced driver assistance, and vehicle to everything communication is increasing the demand for lightweight glazing, robust lighting systems, sensor housings, and complex interior components that combine mechanical durability with tight dimensional tolerances. Polycarbonate and its blends are well placed in this context, as they can be injection molded or extruded into intricate geometries, co extruded into optical grade sheets, and tuned through additives for flame retardancy, high heat performance, or ultraviolet stability. Similar dynamics play out in smart building solutions, where multiwall and solid sheet constructions are used in transparent roofs, facades, and noise barriers, often coupled with coatings or films to manage solar gain and weathering.
Another transformative trend is the digitalization of design and manufacturing, which favors materials that respond predictably to simulation and support high automation levels in molding and extrusion. Polycarbonate’s rheological behavior and compatibility with precise process control make it attractive for high volume, just in time production models in electronics, medical components, and industrial machinery. As additive manufacturing matures, pellets and specialty formulations optimized for three dimensional printing are also emerging, enabling rapid prototyping and, in some cases, low volume production of customized parts. These forces collectively shift the competitive landscape away from purely price based competition toward a more nuanced race focused on application specific performance, regulatory compliance, and demonstrable sustainability credentials.
Evolving trade policy and layered tariff regimes reshaping polycarbonate sourcing competitiveness and strategic planning for United States stakeholders
United States trade policy in plastics and chemicals has entered a new phase characterized by layered tariffs and frequent policy adjustments, and polycarbonate is caught within this evolving framework. Existing Section three hundred one duties on many Chinese origin products, including a range of plastic resins and intermediates, continue to apply, while a separate set of duties imposed under emergency powers has targeted commodity plastics and chemicals more broadly. In twenty twenty five, these measures have been supplemented by an additional reciprocal duty applied to virtually all goods of Chinese origin, as well as a separate surcharge linked to fentanyl related national security concerns, with both stacking on top of baseline most favored nation and Section three hundred one rates.
At the same time, the trade authority has extended certain product specific exclusions on Chinese imports into late twenty twenty five, providing temporary relief for selected inputs while preserving the overarching tariff architecture. An appeals court decision in mid twenty twenty five allowed the government to maintain nearly all of the newer plastic and chemical tariffs while litigation over presidential authority proceeds, removing the near term prospect of a broad rollback and reinforcing the need for companies to plan around sustained higher duty burdens. These overlapping layers, alongside evolving negotiations with China that have slightly modified certain tariff rates without dismantling the structure, create a complex landscape in which effective duty rates can vary widely depending on product classification, origin, and eligibility for exclusions or special programs.
For polycarbonate stakeholders, the cumulative effect is visible across the value chain. Importers of resins, additives, or precursors are experiencing structurally higher landed costs and increased administrative complexity around classification, documentation, and exclusion management. Converters relying on imported sheet, film, or molded components face pressure either to absorb higher costs, eroding margins, or to pass them through to downstream customers in automotive, construction, electronics, and medical sectors, where competitive intensity and cost sensitivity are high. These conditions are accelerating efforts to diversify sourcing toward alternative Asian producers, regional suppliers in the Americas and Europe, and in some cases domestic capacity expansions. They also encourage closer collaboration between procurement, engineering, and finance teams to redesign parts, optimize grades, and adjust inventory strategies in order to mitigate tariff exposure without compromising performance or compliance. While policy trajectories remain fluid, the clear implication for twenty twenty five and the near term horizon is that tariff risk is now a structural factor in polycarbonate strategy rather than a temporary disturbance.
Segmentation insights revealing performance differentiation innovation hotspots and application specific opportunities across the polycarbonate value chain globally today
Understanding polycarbonate’s role across forms reveals distinct performance and positioning dynamics. Pellets remain the backbone of the market, feeding injection molding and extrusion operations in automotive interiors, electrical housings, medical devices, and consumer goods where precise control of melt flow and mechanical properties is essential. Rod and tube formats, encompassing hollow tube and solid rod, are increasingly specified for safety guards, transparent protective enclosures, and fluid handling components in industrial and machinery settings, as designers seek materials that combine impact resistance with machinability and reduced weight compared with glass or metal. Sheet and film forms, spanning co extruded sheet, multiwall sheet, and solid sheet, anchor applications in architectural glazing, roofing, skylights, noise barriers, and signage, where optical clarity, weatherability, and thermal insulation must be tailored to climate and building code requirements.
Process segmentation adds another layer of insight. Injection molding remains fundamental for high volume parts in automotive, transportation, consumer electronics, and medical applications, where complex geometries, overmolding with elastomers, and integration of decorative or functional films demand tight process control. Blow molding serves specialized uses such as containers, housings, and select medical or industrial packaging designs where impact strength and transparency are critical. Extrusion, including downstream shaping into pipes and profiles, underpins continuous production of structural glazing elements, protective covers, lighting diffusers, and mechanical components for industrial systems. The ability to move seamlessly between these processing routes allows converters to optimize part design, cycle times, and material utilization while leveraging a common resin family.
Performance grades demonstrate how segmentation aligns with regulatory and application specific demands. Standard grades meet many general purpose needs, but flame retardant formulations are indispensable in electrical and electronics applications and in building products that must satisfy stringent fire codes, including consumer electronics housings, industrial control enclosures, power generation components, and telecommunications infrastructure. High heat resistance grades enable under hood parts in passenger and commercial vehicles, as well as thermal management elements in electric vehicle battery systems and rail and mass transit interiors. Ultraviolet stabilized grades support outdoor applications from roofing and glazing in residential and commercial construction to infrastructure and public space installations such as shelters, canopies, and noise barriers.
Applications and end use industries complete the picture. Within automotive and transportation, both original equipment manufacturers and the aftermarket rely on polycarbonate for lighting systems, glazing, interior trim, and exterior components in passenger vehicles, commercial vehicles, and rail and mass transit. Building and construction applications span glazing, insulation panels, and roofing across residential construction, commercial construction, and public infrastructure, where energy efficiency, impact resistance, and design flexibility are valued. Electrical and electronics uses cover consumer electronics, industrial electronics, power generation, and telecommunications hardware that must balance miniaturization with safety. Beyond these segments, polycarbonate is embedded in consumer goods and appliances, encompassing household appliances and personal care and lifestyle products, in medical and healthcare applications from hospitals and clinics to diagnostics, laboratories, and home healthcare, in packaging for food and beverage, industrial and institutional products, and consumer packaging, and in industrial and machinery contexts such as manufacturing equipment and safety and protection systems. Together, this segmentation illustrates how polycarbonate’s versatility is activated differently across the value chain, providing multiple avenues for innovation and differentiation rather than a single monolithic market.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Polycarbonate market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Form
- Process
- Grade
- Application
- End-Use Industry
Regional dynamics in the Americas Europe Middle East Africa and Asia Pacific shaping risk resilience and opportunity for polycarbonate stakeholders
Regional dynamics shape the risk profile and opportunity set for polycarbonate in distinct ways. In the Americas, the United States and Canada anchor demand with well established automotive, construction, electronics, and medical sectors, supported by sophisticated molding and extrusion capabilities. Trade policy plays an outsized role, as tariff regimes influence sourcing decisions for resins and intermediates from Asia and Europe, and sustainability regulations at federal, state, and provincial levels gradually tighten expectations around recycling, product stewardship, and disclosure of substances of concern. Latin American economies add a layer of cyclical demand tied to infrastructure spending, construction, and automotive production, alongside emerging opportunities in renewable energy installations where polycarbonate is used in protective housings and balance of system components.
Across Europe, Middle East, and Africa, the environment is equally diverse. Europe remains a key hub for high performance polycarbonate innovation, driven by strict chemical and product regulations that accelerate the phaseout of certain additives, incentivize closed loop models, and favor energy efficient building materials. Automotive and rail industries in Western and Central Europe continue to specify advanced glazing, interior, and lighting solutions that rely on tailored polycarbonate grades, while the region’s leadership in industrial automation and renewable power reinforces demand for robust, flame retardant electrical and electronics components. In the Middle East, competitive access to feedstocks supports regional resin production and attracts investment in downstream conversion facilities. African markets, while smaller, are gradually increasing consumption through urbanization, expansion of power and telecommunications infrastructure, and development of healthcare facilities that require durable, easy to sanitize materials.
Asia Pacific, however, remains the gravitational center for polycarbonate, combining large scale manufacturing ecosystems with fast growing end use sectors. China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan host major resin production assets, advanced compounders, and extensive electronics and automotive supply chains, while Southeast Asian economies and India are building capacity in both resin production and downstream processing. Regional policy trends include strengthening waste management regulations, voluntary corporate commitments to recycled and low carbon content, and a growing focus on domestic innovation in chemical recycling to reduce dependence on imported fossil feedstocks. As trade relations evolve, shifts in tariff regimes and non tariff barriers between Asia, the Americas, and Europe will continue to influence investment decisions, plant footprints, and long term supply agreements, making regional diversification a central strategic consideration for polycarbonate stakeholders.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Polycarbonate market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Strategic directions of leading polycarbonate producers compounders and converters as competition intensifies around technology and sustainability globally today
The competitive landscape for polycarbonate is defined by a relatively concentrated group of integrated resin producers complemented by a wide network of compounders, sheet and film manufacturers, and specialized converters. Large chemical companies with strong positions in polycarbonate production continue to optimize their portfolios through capacity debottlenecking, feedstock integration, and selective investment in new facilities, often aimed at serving fast growing applications in mobility, construction, and electronics. These firms are increasingly differentiating through advanced grades that offer higher heat performance, improved flame retardancy with lower halogen content, enhanced ultraviolet resistance, or tailored optical properties for lighting, displays, and automotive glazing.
Sustainability has become a core strategic theme for leading players. Many are advancing pilot and commercial initiatives in chemical recycling, leveraging catalytic depolymerization methods that efficiently recover monomers such as bisphenol A from virgin and end of life polycarbonate and even complex blends, and then re polymerize them into high quality resins. Partnerships with technology startups, research institutes, and equipment manufacturers are common, as companies seek scalable solutions that reduce carbon footprints, meet brand owner requirements for recycled content, and align with future regulatory frameworks. At the same time, producers are exploring bio based feedstocks and low carbon power sources at major production sites to further reduce embedded emissions.
Downstream, compounders and converters play a pivotal role by translating base resin capabilities into application specific solutions. This includes development of blends with acrylonitrile butadiene styrene or other polymers for improved impact balance, color stable formulations for exterior automotive or building components, and specialty sheets with coatings that deliver abrasion resistance, anti fog performance, or controlled light transmission. Many of these companies are repositioning themselves as solution providers rather than simple material suppliers, offering design assistance, finite element analysis support, and collaborative prototyping with original equipment manufacturers in sectors ranging from passenger vehicles and rail systems to medical devices, household appliances, industrial machinery, and safety and protection systems. Competitive advantage increasingly depends on the ability to integrate material science, processing expertise, and regulatory knowledge into cohesive value propositions that help customers manage cost, performance, and compliance simultaneously.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Polycarbonate market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- 3A Composites GmbH
- Arla Plast AB
- Brett Martin Ltd.
- Chi Mei Corporation
- Covestro AG
- DS Smith
- Evonik Industries AG
- Gallina India
- Koscon Industrial S.A.
- LG Chem
- Mitsubishi Gas Chemical Company, Inc.
- Palram Industries Ltd.
- Plazit Polygal
- SABIC
- Spartech
- Suzhou Omay Optical Materials Co., Ltd.
- Teijin Limited
- Trinseo
Actionable strategic priorities for industry leaders seeking to strengthen polycarbonate portfolios navigate disruption and capture emerging demand worldwide
Industry leaders looking to strengthen their polycarbonate portfolios in this environment should prioritize actions that build resilience while enabling differentiation. A first imperative is to align material strategies with corporate sustainability goals by actively incorporating recycled and low carbon grades, working with suppliers that demonstrate credible progress in chemical recycling and emissions reduction, and designing products with end of life recovery in mind. Close collaboration between procurement, engineering, marketing, and sustainability teams is essential to ensure that new formulations meet regulatory requirements, maintain performance, and support brand narratives around environmental responsibility.
In parallel, organizations should take a more integrated approach to managing trade and tariff exposure. Rather than treating tariffs as a purely transactional cost, leading companies are embedding trade scenarios into long term capacity planning, supplier qualification, and tooling decisions. This means evaluating the resilience of supply chains for pellets, sheets, films, and critical additives, considering alternative sourcing in the Americas, Europe, Middle East, Africa, and Asia Pacific, and exploring local or regional manufacturing options when volumes and strategic importance justify investment. Scenario based planning can help clarify when to hold inventory, when to redesign parts to utilize grades with more favorable duty treatment, and when to negotiate long term agreements that share tariff risks with suppliers or customers.
Finally, innovation efforts should focus on application spaces where polycarbonate delivers unique value. This includes lightweight glazing and structural elements in electric vehicles and rail and mass transit, impact resistant and energy efficient building components in residential, commercial, and infrastructure projects, advanced housings and connectors for consumer and industrial electronics, and robust, easy to sanitize devices for hospitals, clinics, diagnostic laboratories, and home healthcare. By combining deep segmentation insight with close engagement of original equipment manufacturers and end users, companies can identify unmet needs in passenger and commercial vehicles, household appliances, personal care and lifestyle products, food and beverage and industrial packaging, and manufacturing equipment and safety systems. Executing against these opportunities with disciplined project selection and cross functional governance enables organizations to turn the complexity of the polycarbonate landscape into a source of competitive advantage.
Robust research methodology underpinning the polycarbonate market assessment with integrated qualitative insights and data driven validation throughout study
The insights summarized in this document are grounded in a structured research methodology designed to balance breadth of coverage with depth of technical and strategic understanding. Primary research has involved extensive engagement with stakeholders across the polycarbonate value chain, including resin producers, compounders, sheet and film manufacturers, injection molders, extruders, original equipment manufacturers in automotive and transportation, building and construction, electrical and electronics, medical and healthcare, packaging, and industrial and machinery, as well as consultants, technology developers, and academic researchers working on polycarbonate processing and recycling technologies. These interactions provided direct perspectives on evolving application requirements, regulatory drivers, supply chain constraints, and innovation priorities.
Complementing this, secondary research has drawn on a wide range of publicly available information such as company reports, regulatory filings, patent databases, technical journals, conference proceedings, trade statistics, and standards documents. Particular attention has been given to recent advances in chemical recycling, depolymerization chemistry, and catalyst development for polycarbonate, as well as to official communications on trade policy, tariffs, and environmental regulation in key regions. Data points from these sources have been cross checked where possible and interpreted with care, recognizing the rapid pace of change in both technology and policy.
Analytical techniques applied include qualitative trend analysis, mapping of value chain structures, assessment of competitive positioning, and scenario based thinking around tariffs, regulatory trajectories, and technology adoption. Rather than presenting quantitative forecasts or specific market size estimates, the study emphasizes patterns, directional shifts, and strategic implications, with an emphasis on how segmentation by form, process, grade, application, end use industry, and region interacts with macroeconomic, regulatory, and technological forces. This approach is intended to provide decision makers with a robust, evidence based narrative that complements internal data and planning tools, while remaining flexible enough to accommodate new information as the polycarbonate landscape continues to evolve.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Polycarbonate market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Polycarbonate Market, by Form
- Polycarbonate Market, by Process
- Polycarbonate Market, by Grade
- Polycarbonate Market, by Application
- Polycarbonate Market, by End-Use Industry
- Polycarbonate Market, by Region
- Polycarbonate Market, by Group
- Polycarbonate Market, by Country
- United States Polycarbonate Market
- China Polycarbonate Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 17]
- List of Tables [Total: 2862 ]
Conclusion on the evolving role of polycarbonate as a critical enabler of lightweight durable and sustainable solutions across global industries
Polycarbonate continues to occupy a pivotal role in modern material portfolios, offering a rare combination of transparency, impact resistance, thermal performance, and design flexibility that supports innovation across a wide range of industries. At the same time, the environment in which the material is produced, processed, and specified has become far more complex. Regulatory scrutiny, especially in relation to chemical content, fire performance, and environmental impact, is intensifying. Trade policy shifts and layered tariff regimes are altering cost structures and supply patterns. Technological advances in depolymerization and chemical recycling are opening new pathways for circularity, while electrification, digitalization, and urbanization are creating new applications and raising the bar for performance.
This complexity does not diminish the importance of polycarbonate; rather, it elevates the importance of informed and proactive strategy. Segmentation by form, process, grade, application, end use industry, and region reveals a mosaic of opportunities, from specialized hollow tubes and solid rods in industrial machinery and safety systems to multiwall and solid sheets in energy efficient building envelopes, from high heat and flame retardant grades in electric vehicles, power generation, and telecommunications equipment to ultraviolet stabilized solutions in infrastructure and public spaces. Across passenger vehicles, commercial vehicles, rail and mass transit, residential and commercial construction, household appliances, personal care and lifestyle products, hospitals, clinics, diagnostics, home healthcare, food and beverage and industrial packaging, and manufacturing equipment, polycarbonate continues to solve problems that alternative materials struggle to address.
As organizations plan for the coming years, those that integrate a nuanced understanding of tariffs and regional dynamics, invest in sustainability and recycling technologies, and collaborate closely across the value chain to develop application specific solutions will be best positioned to succeed. The material’s inherent versatility, combined with rapid advances in processing and recycling, suggests that polycarbonate will remain a cornerstone of high performance, sustainable design. However, realizing its full potential will depend on the ability of industry leaders to navigate uncertainty with clarity, agility, and a willingness to challenge legacy assumptions about how and where the material is produced and used.
Next steps to unlock deeper polycarbonate intelligence through direct engagement and tailored access to comprehensive executive level insights
Maximizing the strategic value of this executive summary requires turning insight into informed decision making, and the most efficient way to do that is by accessing the full depth of analysis behind it. The complete polycarbonate report provides significantly greater granularity on product level dynamics, tariff exposure by trade lane, technology roadmaps in recycling and advanced compounding, and emerging use cases in areas such as electric mobility, smart infrastructure, and next generation electronics.
By engaging directly with Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales and Marketing, decision makers can secure tailored access to this intelligence and align it with their specific strategic objectives. A direct discussion enables clarification of key findings, exploration of custom cuts by form, process, grade, application, or end use industry, and identification of optional add on deliverables such as workshop style briefings or internal stakeholder presentations. This level of engagement helps senior teams rapidly translate complex market narratives into clear priorities for investment, procurement, technology development, and regional expansion.
Prospective buyers are encouraged to connect with Ketan to explore licensing options, discuss organization wide access for commercial, technical, and finance teams, and identify how the report’s datasets and qualitative insights can complement existing internal planning tools. Taking this step ensures that the organization is not relying on partial information, but is instead equipped with a comprehensive and rigorously validated view of the polycarbonate landscape that supports confident decisions in an increasingly uncertain operating environment.

- How big is the Polycarbonate Market?
- What is the Polycarbonate Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




