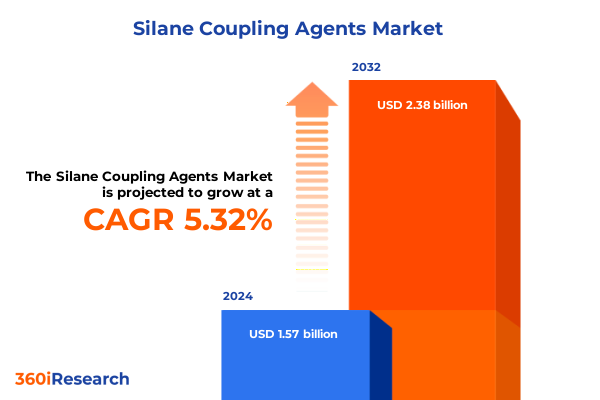
The Silane Coupling Agents Market size was estimated at USD 1.62 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 1.71 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 5.94% to reach USD 2.43 billion by 2032.
Silane coupling agents at the crossroads of advanced materials innovation, sustainability, and high-performance manufacturing across global industries
Silane coupling agents sit at the core of modern materials engineering, quietly enabling the performance that end-users now take for granted. These organosilicon molecules typically feature a hydrolyzable group that bonds with inorganic substrates and a non‑hydrolyzable organic group that anchors into polymers, creating durable bridges between phases that otherwise interact poorly. This interfacial chemistry improves adhesion, mechanical strength, moisture resistance, and long-term durability in systems ranging from structural sealants to high-voltage insulation and fiber-reinforced composites.
As industries push for lighter, stronger, and more sustainable products, the role of these agents has expanded sharply. In construction, they enhance the performance of concrete treatments, sealants, and glass façades exposed to harsh weather. In electrical and electronics, they support reliable insulation, encapsulation, and miniaturized circuitry. In automotive and transportation, silane-treated composites and rubber formulations underpin lightweight body structures, reduced rolling resistance in tires, and durable glazing systems. Healthcare, energy, and advanced chemical processing increasingly rely on silane-based surface modification to achieve biocompatibility, chemical resistance, or high-purity interfaces.
At the same time, the strategic context surrounding silane coupling agents is becoming more complex. Electrification of transport, accelerated infrastructure renewal, and rapid growth in renewable energy are amplifying demand for high-performance adhesion and surface treatment technologies. Parallel regulatory pressures on emissions, hazardous substances, and product stewardship are reshaping acceptable chemistries. Overlaying these factors, shifting trade policies and tariffs are prompting reassessment of global supply chains. This report’s subsequent sections unpack how these intertwined forces are redefining the landscape for silane coupling agents across technologies, segments, regions, and competitive positions.
Transformative technological, regulatory, and demand shifts redefining the role of silane coupling agents in coatings, composites, and engineered surfaces
The landscape for silane coupling agents is undergoing a profound transformation driven by converging technological, regulatory, and demand-side shifts. On the demand side, the global push toward electrified and lightweight vehicles is structurally increasing the importance of advanced composites and high-performance rubber systems. Electric car sales approached fourteen million units in 2023 and continue to grow, with electric models now representing a rapidly rising share of new vehicle sales worldwide. These vehicles use composite-intensive architectures and rely heavily on glass- and carbon-fiber reinforcements, where silane coupling agents are indispensable for achieving the necessary mechanical, thermal, and electrical performance.
Parallel trends are reshaping construction, infrastructure, and energy. Stricter building envelopes, façade durability expectations, and the need for long-lived concrete structures are increasing adoption of silane-based treatments and sealant systems. In wind energy and solar power, composite blades, encapsulants, and cabling all benefit from optimized silane interfaces to withstand cyclic loads, UV exposure, and extreme climates over long service lives. As grid modernization and distributed generation expand, the electrical and electronics sector is also using more sophisticated insulators, printed circuit boards, and encapsulants that depend on carefully selected silane chemistries.
Regulation and sustainability expectations are simultaneously pushing the industry toward cleaner formulations. Across Europe and the United Kingdom, regulators are advancing restrictions on persistent substances such as PFAS and tightening scrutiny of chemistries with problematic toxicological profiles, which is encouraging users to favor lower-volatility, lower-toxicity silane systems and to optimize dosage levels. At the same time, corporate climate and circularity commitments are prompting closer evaluation of silane life-cycle impacts, including energy intensity of production and potential emissions in application and end-of-life.
Technological innovation is responding to these pressures. Producers are expanding portfolios of multifunctional silanes that combine, for example, adhesion promotion with hydrophobicity or improved weathering, reducing formulation complexity for customers. Advancements in amino, epoxy, methacryloxy, vinyl, sulfur, and alkyl silane chemistries are increasingly tuned to specific fillers, fibers, and substrates. Digital design tools, application laboratories, and advanced analytical techniques allow suppliers to co‑develop tailored solutions with customers more quickly, shortening qualification cycles and improving performance predictability.
Finally, the supply side is being reshaped by capacity investments and regionalization. Asia-based manufacturers have strengthened their presence in standard grades and cost-sensitive applications, while European, North American, and Japanese producers emphasize high-purity, specialty, and sustainability-oriented solutions. As the following section details, evolving tariff regimes and trade policies are accelerating these structural changes by altering relative cost positions and encouraging closer-to-market production footprints.
Navigating the cumulative impact of evolving United States tariffs in 2025 on silane coupling agent trade flows, sourcing strategies, and profitability
The tariff environment in the United States during 2025 is exerting a cumulative, rather than singular, influence on the silane coupling agent value chain. At the broadest level, the country continues to participate in the Chemical Tariff Harmonization Agreement, under which most basic chemical imports fall in a relatively low bound duty band, typically at or below single-digit percentages. However, this baseline is now layered with a complex overlay of country- and sector-specific measures that have material implications for silane producers, importers, and downstream users.
Section 232 actions on steel and aluminum, which now impose duties of around fifty percent on many products, directly increase the cost of the metal-intensive infrastructure that underpins silane manufacturing and logistics, such as reactors, pressure vessels, storage tanks, and bulk transport containers. In parallel, a twenty-five percent tariff on imported automobiles and many auto parts affects the economics of vehicle manufacturing in the United States, with knock-on effects for tire, composite, and glazing demand-all key outlets for sulfur, amino, and epoxy silane coupling agents.
Section 301 tariffs on Chinese-origin goods remain a critical factor for the specialty chemical segments into which many silane coupling agents fall. Lists covering chemicals and industrial inputs continue to carry additional duties, often at rates near twenty-five percent, with selected strategic sectors facing even higher levels. While some product-specific exclusions have been extended into late 2025, these remain temporary and subject to revision, introducing planning uncertainty for import-reliant buyers of silane intermediates or finished coupling agents sourced from China.
The administrative burden of navigating this landscape has also increased. The Harmonized Tariff Schedule has undergone numerous revisions in 2025, forcing companies to monitor classification changes, update customs documentation, and ensure that their silane coupling agents and precursors remain correctly coded. Concurrently, proposed changes to de minimis rules aim to limit duty-free entry for small parcels that are already subject to Section 232 or Section 301 tariffs. This development affects companies that previously relied on frequent low-value shipments of specialty silane grades via e-commerce and courier channels.
Looking forward, potential eco-tariff initiatives such as the proposed Foreign Pollution Fee Act, which would levy import charges based on embedded emissions intensity, signal an additional vector of risk for energy-intensive chemical products. For silane coupling agent producers and users, the net effect of all these measures is a strong incentive to evaluate alternative sourcing strategies, including increased reliance on North American or allied-country supply, re‑engineering formulations to reduce exposure to tariff-affected intermediates, and closer coordination between procurement, trade compliance, and technical teams. Companies that proactively model tariff scenarios and bake them into product and capacity planning will be better positioned than those that view tariffs as a purely transactional issue at the border.
Decoding silane coupling agent segmentation to uncover product, form, application, end-use, and channel niches with outsized strategic relevance
Understanding where value accrues within the silane coupling agents space requires a nuanced view of how chemistry, form, application, and route to market intersect. At the product level, amino silanes remain foundational across many applications because of their strong reactivity with both inorganic surfaces and organic resins. Within this family, monoamino silane coupling agents are widely used where controlled reactivity and fine-tuned adhesion are paramount, such as in structural sealants and certain fiber treatments, while diamino silane coupling agents offer higher functionality for demanding composite interfaces and high-fill formulations. Epoxy silanes form a second critical pillar; glycidoxy silane coupling agents are particularly valued in coatings and adhesives that must combine robust adhesion with chemical resistance, whereas cycloaliphatic epoxy silane coupling agents are increasingly specified for high-voltage insulation and UV‑resistant systems where thermal and dielectric stability are essential.
Sulfur silanes have carved out a strategically important niche, especially in rubber and tire applications. Monosulfide silane coupling agents support balanced dynamic properties in high-performance rubber compounds, while polysulfide silane coupling agents are a cornerstone of modern “green tire” technology, facilitating strong silica–rubber interaction that enables lower rolling resistance and improved wet grip. Vinyl silanes are indispensable in cable insulation, wire and cable jacketing, and moisture-curable systems, where their ability to graft onto polyolefins underpins long-term reliability in harsh environments. Methacryloxy silanes bridge into radiation-curable and high-crosslink-density systems used in advanced coatings and dental or medical composites, and alkyl silanes play a critical role in imparting hydrophobicity and stain resistance to mineral substrates in construction and stone treatment.
Form factors also shape adoption patterns. Liquid silanes dominate in many high-volume industrial processes because they can be easily metered, mixed, and sprayed, supporting in-line treatment of fillers, fibers, and surfaces. However, solid silane forms, including powders and pellets, are gaining traction where ease of handling, safety, and dosing accuracy are prioritized, such as in rubber compounding and thermoplastic masterbatches. These solid forms can reduce worker exposure to volatiles, improve storage stability, and simplify integration into automated dosing systems.
Applications provide another lens on value concentration. Coatings and adhesives represent a broad and technically demanding arena, with silane coupling agents used to improve adhesion to glass, metals, and concrete, extend durability, and enhance chemical and weather resistance. Composite materials, including glass- and carbon-fiber reinforced polymers, rely on carefully selected silanes to optimize fiber–matrix bonding and maintain performance under thermal cycling and moisture ingress. Fiber treatment remains a major consumption pool, especially in glass fiber sizing formulations for automotive, construction, and electrical components. Glass ceramics draw on silanes to bond glazes, sealants, and functional layers to substrates, while rubber plastics applications focus on dynamic properties in tires, vibration isolation, footwear, and industrial components.
End-use industries pull these chemistries and applications together in distinct ways. Automotive and transportation customers emphasize sulfur and amino silanes in rubber plastics for tires and mounts, epoxy and vinyl silanes in composite materials and fiber treatment for lightweight structures, and specialized grades in coatings and adhesives for body-in-white and glazing. Building and construction stakeholders focus heavily on alkyl and methacryloxy silanes in water repellents, sealants, and façade systems. Electrical and electronics manufacturers prioritize vinyl, epoxy, and amino silanes in cables, encapsulants, and circuit board materials. Energy and chemical operators draw on a mix of silane types to harden coatings and composites that face corrosive or high-temperature environments, and healthcare applications increasingly call for highly pure, biocompatible methacryloxy and amino silanes in dental and medical devices.
Overlaying these technical and sectoral dynamics, the sales channel dimension is changing how value is captured. Online sales, both through broad eCommerce platforms and dedicated company websites, are now common for small and medium-sized buyers seeking rapid access to standard silane grades, technical datasheets, and sample logistics. Offline sales remain dominant for large accounts and custom solutions, with direct sales teams working closely with formulators and end-users, and distributors providing regional inventory, credit, and technical support. The balance between these routes varies by region and product complexity, but overall, companies that can synchronize their product type, form, application focus, end-use targeting, and mix of online and offline channels are best positioned to occupy the most lucrative niches within the silane coupling agents landscape.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Silane Coupling Agents market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Product Type
- Form
- Application
- End-Use Industry
- Sales Channel
Regional dynamics across the Americas, Europe, Middle East & Africa, and Asia-Pacific shaping innovation clusters in silane coupling agents
Regional dynamics strongly influence how silane coupling agents are specified, sourced, and consumed, starting with the Americas. In North America, the combination of robust automotive and transportation industries, a large installed base of aging infrastructure, and a sophisticated electronics and energy ecosystem creates a broad and technically demanding customer base. Automakers and their suppliers are intensifying efforts around vehicle lightweighting and electrification, which raises the importance of composite materials, advanced coatings, and high-performance rubber plastics that depend on optimized amino, epoxy, sulfur, and vinyl silanes. Infrastructure renewal programs and stricter performance expectations for bridges, tunnels, and buildings drive demand for durable concrete treatments, sealants, and façade systems using alkyl and methacryloxy silanes. At the same time, tariff policies and reshoring initiatives are encouraging greater reliance on regional silane production and more diversified sourcing strategies. In Latin America, growing construction activity and a maturing automotive base are expanding demand for mid-range silane technologies in coatings, adhesives, and rubber, often served through distributor-led offline channels.
Across Europe, Middle East & Africa, regulatory ambition and sustainability commitments are powerful demand shapers. European policy initiatives on climate, circularity, and hazardous substances-including ongoing efforts to restrict PFAS and other persistent chemicals-are pushing the market toward lower-emission, lower-toxicity silane systems and tighter control of emissions during application. The region’s strong adoption of electric vehicles and energy-efficient buildings amplifies demand for high-end epoxy, vinyl, and sulfur silanes in tires, cables, composites, and structural sealants. Major multinational producers headquartered in Europe are also leveraging local innovation clusters to advance bio-based or otherwise more sustainable silane technologies. In the Middle East, investments in petrochemical complexes and downstream conversion into plastics and rubber components are boosting consumption of silane coupling agents for both export-oriented and local manufacturing. Emerging African markets, while smaller today, are seeing rising use of silane technologies in construction materials, automotive components, and basic electrical infrastructure as urbanization and industrialization progress.
Asia-Pacific remains the gravitational center for both production and consumption of silane coupling agents. China, Japan, South Korea, and increasingly India host extensive manufacturing capacity for silanes and downstream rubber, plastic, composite, and electronic components. The region’s dominant role in global electric vehicle production and battery value chains creates strong pull for sulfur silanes in green tires, amino and epoxy silanes in composite structures, and vinyl silanes in cable and busbar insulation. Rapid infrastructure expansion across Asia-Pacific also demands durable construction materials and protective coatings, further supporting uptake of alkyl and methacryloxy silanes. However, the region is not insulated from regulatory and trade headwinds; export-oriented producers must navigate tightening environmental rules at home while adapting to evolving tariff and non-tariff measures in destination markets. Companies that can align regional production strengths with global compliance expectations and customer performance requirements are reshaping supply chains in ways that will reverberate through the silane coupling agents market for years to come.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Silane Coupling Agents market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Competitive landscape insights on leading silane coupling agent producers, regional specialists, and emerging innovators in functional surface chemistry
The competitive landscape in silane coupling agents is characterized by a blend of diversified chemical multinationals and specialized regional producers, each occupying distinct roles along the value spectrum. Global leaders such as large European, North American, and Japanese chemical companies leverage broad silicon chemistry platforms, deep application expertise, and extensive technical service networks. Their portfolios typically span the full range of amino, epoxy, sulfur, vinyl, methacryloxy, and alkyl silanes, supported by application labs that collaborate closely with tire manufacturers, automotive OEMs, construction chemicals formulators, and electronics producers. These companies are increasingly differentiating through sustainability, emphasizing lower-VOC systems, reduced residual monomers, and life-cycle assessments that help customers meet tightening regulatory and corporate ESG requirements.
Specialty and regional players-particularly in China, broader Asia-Pacific, and parts of Europe-contribute agility and cost competitiveness. Many focus on specific product families such as sulfur silanes for tire and rubber applications, amino and epoxy silanes for glass fiber sizing and resins, or vinyl silanes for wire and cable. Their strengths often lie in rapid custom synthesis, responsiveness to local customer needs, and the ability to scale capacity quickly for fast-growing segments. Some of these producers are evolving from contract or toll manufacturers into branded suppliers, investing in quality systems, regulatory dossiers, and export-oriented distribution partnerships.
Downstream, several major tire and rubber companies have deepened their engagement with silane technology, either through long-term supply and development agreements or, in some cases, through backward integration into silane production. This close coupling of raw material innovation with application development has accelerated progress in green tire performance, enabling lower rolling resistance and improved wet grip in line with regulatory labeling schemes and OEM efficiency targets. Similar dynamics are emerging in high-performance composites, where aerospace, wind energy, and automotive stakeholders collaborate with silane suppliers to fine-tune adhesion at the fiber–matrix interface.
An additional axis of competition centers on service and data. Leading companies increasingly differentiate not only on product properties but also on their ability to provide formulation guidance, process optimization support, and digital tools that model silane performance in end-use conditions. This includes predictive models for adhesion, durability, and moisture ingress, as well as digital platforms that simplify product selection across complex portfolios. As regulatory and trade environments grow more complex, suppliers that combine high-performance chemistry with reliable supply, regulatory support, and data-rich customer interfaces are emerging as preferred partners for global and regional customers alike.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Silane Coupling Agents market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- 3M Company
- Advanced Polymer Inc
- Anhui Sinograce Chemical Co., Ltd
- Arkema S.A.
- Clariant AG
- Dow Inc.
- Evonik Industries AG
- Gelest, Inc.
- Hexpol Compounding HQ SA
- Hubei Jianghan New Materials Co., Ltd.
- Jiangxi Chenguang New Materials Co., Ltd.
- JNC Corporation
- KBG Corporation
- KCC Corporation
- Merck KGaA
- Momentive Performance Materials Inc.
- Nanjing SiSiB Silicones Co., Ltd.
- Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd.
- RAYTON CHEMICALS CO., LTD
- Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Taizhou Huangyan Donghai Chemical Co.,Ltd.
- Tangshan Sunfar Silicon Industries Co., Ltd.
- Tianjin Shengbin Chemical Engineering
- Wacker Chemie AG
- WD Silicone Co., Ltd
Strategic actions for executives to capture value, mitigate risk, and accelerate innovation in the evolving silane coupling agent ecosystem
Industry leaders navigating the silane coupling agents arena must increasingly adopt an integrated perspective that spans chemistry, regulation, trade, and customer strategy. A first priority is to reassess supply chains in light of evolving tariff regimes and geopolitical risks. Rather than relying on single-source imports of critical silane grades or precursors, companies should map their exposure by origin and tariff category, then develop diversified sourcing strategies that consider regional manufacturing partnerships, tolling arrangements, and selective capacity investments closer to key customer clusters. Incorporating scenario-based landed-cost modeling into procurement and strategic planning will help ensure that portfolio decisions remain robust under plausible shifts in duties and trade policies.
A second imperative lies in innovation aligned with sustainability and regulatory trends. As regulators tighten controls on persistent and hazardous substances and as customers commit to ambitious environmental targets, demand is gravitating toward silane systems with lower toxicity profiles, reduced VOC content, and clearer end-of-life pathways. Senior executives should therefore prioritize R&D programs that refine existing amino, epoxy, sulfur, vinyl, methacryloxy, and alkyl silane chemistries for improved environmental performance, while also exploring bio-based feedstocks or novel functional groups that maintain efficacy at lower dosage levels. Close collaboration between R&D, regulatory affairs, and key customers can accelerate the path from lab-scale concepts to qualified commercial products.
At the same time, leaders should refine their segmentation strategies to focus resources where differentiation is most defensible. Not every product type or application warrants equal investment. For instance, sulfur silanes for high-performance tires, epoxy silanes for demanding electronics and infrastructure coatings, and highly pure methacryloxy silanes for healthcare and advanced composites often carry higher technical barriers and more stringent qualification requirements, favoring suppliers with strong technical support capabilities. Executives who align capital expenditure, marketing, and technical service around such high-value intersections of product type, form, application, and end-use sector can improve mix quality and strengthen competitive positioning.
Finally, strengthening the interface with customers and regulators is crucial. Proactive engagement with automotive, construction, electronics, energy, and healthcare customers through joint development programs, on-site process audits, and training can deepen relationships and uncover unmet needs. In parallel, active participation in standards bodies and industry associations allows companies to anticipate regulatory changes and contribute to practical implementation guidelines. Leaders who invest in these relationships, while simultaneously upgrading internal capabilities in trade compliance, data analytics, and digital customer support, will be best placed to convert the evolving silane coupling agent landscape into a source of durable competitive advantage.
Robust research methodology underpinning silane coupling agent insights through primary engagement, secondary intelligence, and expert validation
The insights presented in this report are built on a multi-layered research methodology designed to balance breadth of coverage with depth of technical and strategic detail. At the foundation, the research team conducted a structured review of primary information from across the silane coupling agents value chain. This included in-depth interviews and consultations with producers of silane coupling agents, suppliers of key silicon-based intermediates, formulators in coatings, adhesives, rubber, plastics, and composite materials, and downstream users in automotive and transportation, building and construction, electrical and electronics, energy and chemical, and healthcare sectors. These engagements illuminated practical challenges in formulation and processing, evolving specification requirements, and how tariff and regulatory developments are influencing procurement and investment decisions.
Complementing primary insights, the study integrates a broad range of secondary intelligence. Publicly available customs and trade databases, including detailed tariff schedules and revision histories from authorities such as the United States International Trade Commission and related tariff documentation, were analyzed to understand the changing duty environment affecting silane coupling agents and related chemistries. Regulatory texts, consultation documents, and news coverage on environmental and chemical policy-such as PFAS-related proposals and other emerging restrictions-were examined to capture the direction of future compliance requirements. Industry and academic publications on silane chemistry, adhesion science, and composite materials provided the technical context needed to interpret how product innovations are translating into performance gains in end-use applications.
Data from these diverse sources were triangulated and normalized to build a coherent view of supply structures, trade flows, and demand drivers across the Americas, Europe, Middle East & Africa, and Asia-Pacific. Where quantitative indicators were available, they were analyzed in conjunction with qualitative feedback from market participants to validate directional trends and identify turning points, such as shifts in preferred silane chemistries within key applications. Scenario analysis was applied to explore the potential impact of tariff adjustments, regulatory tightening, and macroeconomic shifts on sourcing strategies and product development priorities. Throughout, the research team subjected findings to internal peer review and cross-checked key conclusions with selected external experts to enhance robustness. The result is a methodology that blends empirical data, expert judgment, and forward-looking scenario thinking to offer decision-makers reliable guidance in a complex and evolving market context.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Silane Coupling Agents market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Silane Coupling Agents Market, by Product Type
- Silane Coupling Agents Market, by Form
- Silane Coupling Agents Market, by Application
- Silane Coupling Agents Market, by End-Use Industry
- Silane Coupling Agents Market, by Sales Channel
- Silane Coupling Agents Market, by Region
- Silane Coupling Agents Market, by Group
- Silane Coupling Agents Market, by Country
- United States Silane Coupling Agents Market
- China Silane Coupling Agents Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 17]
- List of Tables [Total: 1749 ]
Synthesizing key themes to clarify the strategic trajectory of silane coupling agents amid material innovation, regulation, and supply realignment
Taken together, the foregoing analysis shows that silane coupling agents occupy a pivotal position in the transition toward lighter, more durable, and more sustainable materials across a wide array of industries. Their unique ability to bridge organic resins and inorganic substrates underpins critical performance attributes in coatings and adhesives, composite materials, fiber treatments, glass ceramics, and rubber plastics, making them indispensable in applications as diverse as high-efficiency tires, long-life infrastructure sealants, high-voltage insulation, and precision medical devices. As global priorities shift toward decarbonization, electrification, and resilience, the technical importance of well-chosen silane chemistries is only set to deepen.
At the same time, the operating environment for producers and users of silane coupling agents is growing more demanding. Rapid growth in electric vehicles, renewable energy installations, and advanced infrastructure is raising the bar on performance and reliability, while regulatory systems tighten controls on emissions and hazardous substances, prompting a move toward cleaner, lower-impact formulations. Layered on top of these structural forces, evolving tariff policies and geopolitical tensions are reshaping trade routes, cost structures, and sourcing strategies, particularly for companies with significant exposure to cross-border flows of specialty chemicals.
Within this context, a detailed understanding of segmentation and regional dynamics becomes a strategic asset. Differences among amino, epoxy, sulfur, vinyl, methacryloxy, and alkyl silanes, across liquid and solid forms, and among applications and end-use industries, create a rich set of opportunities for focused innovation and targeted commercial strategies. Regional variations in regulation, demand structure, and industrial capabilities across the Americas, Europe, Middle East & Africa, and Asia-Pacific further compound this complexity. Companies that can navigate this multi-dimensional landscape with clarity-backed by robust data, scenarios, and on-the-ground insight-will be well placed to capture attractive niches and to respond quickly as conditions evolve.
Ultimately, the trajectory of silane coupling agents will be shaped by the interplay of material science advances, environmental and trade policy, and changing end-user expectations. Organizations that invest now in understanding these forces in detail, and in aligning their portfolios, supply chains, and partnerships accordingly, will not only safeguard resilience but also unlock new avenues for growth in an increasingly interconnected and demanding global materials ecosystem.
Activate deeper decision-making with tailored silane coupling agent intelligence and connect now to secure your advantage with the full market report
Decision-makers who need to move quickly in this complex environment require more than a high-level overview. They need a structured, defensible evidence base that links policy, technology, and customer behavior to concrete strategic options across every product family, application, and region in the silane coupling agents space.
The full market research report delivers that level of depth. It translates regulatory shifts, such as evolving tariff regimes and environmental standards, into practical implications for product development, sourcing, and customer engagement. It also drills into the detailed behavior of amino, epoxy, sulfur, vinyl, methacryloxy, and alkyl silanes across forms, applications, end-use sectors, and sales channels, providing a level of granularity that internal teams rarely have the time or reach to assemble.
To turn these insights into a decisive competitive edge, engage directly with Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing. Ketan can guide you through the report’s structure, discuss how the findings align with your current portfolio and geographic footprint, and help you select the license configuration that best supports your planning, investment, and go-to-market objectives. Securing the complete report now ensures your organization is equipped with the actionable intelligence needed to steer silane coupling agent strategy with confidence over the coming planning cycles.

- How big is the Silane Coupling Agents Market?
- What is the Silane Coupling Agents Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




