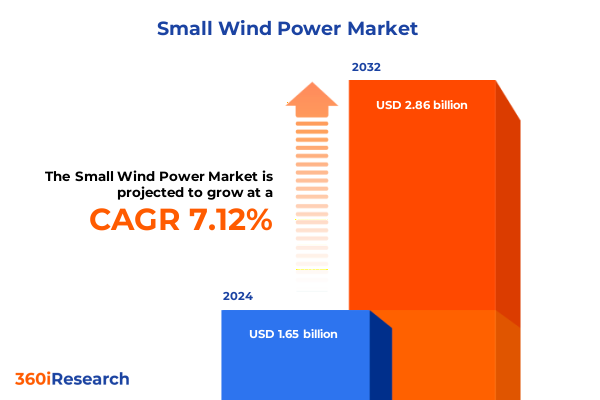
The Small Wind Power Market size was estimated at USD 1.76 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 1.88 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 7.16% to reach USD 2.86 billion by 2032.
Setting the Stage for Small Wind Power Innovation with an Overview of Its Role in Decentralized Renewable Energy Ecosystems
The small wind power segment has emerged as a pivotal component of modern renewable energy portfolios, offering decentralized generation capabilities that complement larger-scale utility installations. In recent years, the rapid maturation of turbine technologies, combined with declining capital costs and heightened policy support for distributed energy resources, has elevated small wind systems from niche applications to mainstream energy solutions. This introduction sets the stage by outlining how these compact turbines integrate into residential, commercial, and off-grid installations to deliver resilience, sustainability, and economic benefits.
As communities and businesses seek to fortify their energy independence, small wind installations have become synonymous with innovation. Advances in rotor design, control electronics, and grid interconnection hardware have unlocked new performance thresholds, while modular manufacturing approaches have improved scalability. Moreover, evolving incentive structures at federal and state levels have incentivized adoption, enabling end users to access favorable financing mechanisms and tax credits. By framing small wind power within the broader context of distributed energy resources, this section establishes a foundation for understanding the dynamic interplay of technology, policy, and market forces that underpin its growing relevance.
Unfolding Technological and Regulatory Transformations That Are Redefining Competitive Dynamics and Investment Priorities in Small Wind Energy
Over the past decade, transformative shifts in regulatory frameworks and technological breakthroughs have reshaped the small wind power landscape. The integration of digital monitoring and predictive maintenance solutions has enhanced operational efficiency, enabling remote diagnostics and proactive asset management. Concurrently, the advent of advanced composite materials has driven down weight and manufacturing costs, allowing manufacturers to optimize turbine performance across diverse wind regimes.
On the regulatory front, streamlined permitting processes and the emergence of community-based renewable energy programs have lowered entry barriers for system installers and developers. Furthermore, the convergence of small wind with energy storage and smart grid platforms has created hybrid configurations that mitigate intermittency, improve load matching, and enable dynamic grid services. As these shifts unfold, market participants are adapting by forging strategic partnerships, investing in vertically integrated supply chains, and pursuing standardization efforts to accelerate deployment.
Analyzing How Recent United States Tariff Policies Have Reshaped Cost Structures Supply Chains and Deployment Strategies for Small Wind Systems
The imposition of Section 232 tariffs on imported steel and aluminum in the United States has reverberated through the small wind power sector, driving up component costs and complicating procurement strategies. Turbine towers, nacelle frameworks, and key subassemblies are heavily reliant on these materials, and the cumulative tariffs introduced since 2018 have added complexity to global supply chains. In response, leading manufacturers have pursued diversified sourcing models, negotiating long-term agreements with domestic mills and exploring alternative alloy formulations to mitigate input price volatility.
These tariff dynamics have triggered operational adjustments across the value chain. Some turbine producers have localized assembly operations closer to end markets to reduce cross-border shipping expenses, while others have accelerated research into low-cost, recyclable composites that bypass traditional metal dependencies. Moreover, developers and project financiers have incorporated tariff contingencies into contract structures, ensuring that cost escalations do not erode project viability. As US policy evolves, small wind stakeholders continue to monitor prospective tariff reviews and trade negotiations for signals that could alleviate or intensify current pressures.
Unveiling Critical Market Segmentation Insights by Turbine Type Components Installation Modalities Capacity Ranges and Diverse End Use Scenarios
A nuanced segmentation framework reveals distinct performance trajectories and adoption patterns across the small wind market. When categorizing by turbine type, horizontal axis designs predominate in high-wind zones due to their aerodynamic efficiencies, whereas vertical axis machines have gained traction in urban or turbulent environments owing to their omni-directional capture capabilities. Examining component segmentation highlights the nacelle as a focal point for innovation, where advances in gearbox engineering, control electronics, and yaw systems are driving reliability gains, while rotor blade and hub enhancements optimize energy yield and reduce maintenance demands.
Installation modalities further differentiate market dynamics: grid-connected configurations benefit from feed-in tariffs and net-metering regimes, whereas off-grid systems serve remote or islanded applications, often coupling with storage to deliver uninterrupted power. Power capacity breakdowns underscore the importance of modular scalability, with sub-1 kW systems catering to standalone residential use, mid-range turbines addressing commercial loads, and larger bracketed units supporting agricultural and small industrial requirements. Finally, application segmentation reveals that utility and commercial deployments leverage scale economies and technical expertise, while residential installations emphasize ease of integration and system self-sufficiency.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Small Wind Power market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Type
- Component
- Installation Type
- Power Capacity
- Application
- End-User
Exploring Regional Nuances and Growth Drivers across Americas Europe Middle East Africa and Asia Pacific Small Wind Power Markets
Regional nuances play a defining role in shaping small wind power adoption and innovation trajectories. In the Americas, a blend of supportive renewable energy targets, rural electrification initiatives, and incentive programs has propelled growth across North and South American markets. Investment in microgrid projects and resilience solutions has elevated small wind as a viable complement to solar and battery arrays, particularly in off-grid communities.
Contrastingly, Europe, the Middle East, and Africa exhibit a heterogeneous landscape. Western Europe’s ambitious decarbonization goals and streamlined permitting processes have fostered pilot deployments in urban and agricultural settings, while emerging markets in the Middle East and North Africa explore small wind for water pumping and remote infrastructure. Sub-Saharan Africa leverages decentralized wind to address power access gaps, coupling turbines with donor-funded microgrids and hybrid renewable systems. Meanwhile, policy fragmentation across countries underscores the need for flexible business models.
In Asia-Pacific, escalating energy demand, coupled with government mandates for distributed generation, has sparked early-stage commercial interest in small wind systems. Island economies and off-shore territories are evaluating vertical axis prototypes for their adaptability to variable wind conditions, and partnerships between local enterprises and international OEMs are catalyzing market entry. As regional stakeholders prioritize sustainable electrification, small wind power emerges as a strategic complement to dominant solar solutions.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Small Wind Power market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Highlighting Leading Industry Participants Pioneering Innovation and Strategic Collaborations in the Small Wind Power Value Chain Worldwide
Industry participants are actively shaping the small wind power ecosystem through targeted innovation and collaborative ventures. Several turbine manufacturers have expanded R&D investments to enhance rotor aerodynamics and gearbox durability, while power electronics providers are integrating advanced inverters with grid support functionalities to facilitate seamless interconnection. Strategic alliances between component specialists and full-system integrators have emerged, enabling co-development of turnkey offerings that streamline customer adoption curves.
At the same time, service providers focused on predictive analytics and digital twin technologies have carved out vital roles in asset management, offering subscription-based platforms that optimize performance and reduce downtime. Financing institutions and development banks are also stepping into the fray, establishing dedicated funding lines and risk-mitigation instruments to underwrite community-scale and remote deployments. Collectively, these efforts underscore a shift from commoditized equipment sales toward value-added ecosystem solutions that address technical, financial, and operational barriers simultaneously.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Small Wind Power market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- Aeolos Wind Energy Ltd.
- Aeromine Technologies, Inc.
- APRS World, LLC
- Avant Garde Innovations Pvt. Ltd.
- Be-Wind LLC
- Bergey Windpower Co.
- BORNAY AEROGENERADORES SLU
- City Windmills Limited
- Ducted Wind Turbines, Inc.
- Ecotricity Group Ltd.
- ENESSERE S.r.l.
- Envision Group
- Eocycle Technologies Inc.
- Freen OÜ
- Guangzhou HY Energy Technology Limited
- Kestrel Wind Turbines by Eveready (Pty) Ltd.
- Kingspan Group PLC
- Kliux Energies International Inc.
- Northern Power Systems Corp.
- Royall Products, LLC.
- Ryse Energy (UK) Ltd.
- SD Wind Energy Limited.
- Senwei Energy Technology Inc.
- Shanghai Ghrepower Green Energy Co., Ltd.
- Superwind GmbH
- TUGE Energia
- Unitron Energy Systems Pvt. Ltd.
- Vestas Wind Systems A/S
- VORTEX BLADELESS, SL
- VWT Power Limited
- WEG S.A.
- Windflow Technology Ltd.
- Zephyr Corporation
Delivering Actionable Strategic Recommendations to Guide Industry Leaders through Investment Operational and Policy Engagement Decisions
To navigate the evolving small wind landscape, industry leaders should pursue a multifaceted strategy that balances technological investment with policy engagement and stakeholder partnerships. Prioritizing R&D in novel materials and modular designs will be essential for reducing capital intensity and expanding feasibility across diverse site conditions. Concurrently, investing in digital monitoring and advanced control systems will unlock operational efficiencies, improve asset longevity, and enable new revenue streams through grid ancillary services.
Engagement with regulatory bodies and standard-setting organizations is equally critical; by contributing to the development of streamlined permitting protocols and performance benchmarks, companies can accelerate market access and foster customer confidence. Moreover, forming alliances with energy storage vendors and microgrid solution providers will open pathways toward hybrid project offerings, enhancing resilience and broadening end-user appeal. Finally, building flexible financing models that integrate tariff hedges and performance guarantees can mitigate price volatility risks, ensuring project bankability and sustained market growth.
Detailing Rigorous Research Methodology Emphasizing Data Triangulation Expert Consultations and Comprehensive Supply Chain Analysis
This analysis is grounded in a rigorous research methodology designed to deliver comprehensive insights into the small wind power sector. Primary data collection involved in-depth interviews with technology developers, project developers, policymakers, and financial institutions across key geographies. Complementing these qualitative insights, extensive secondary research was conducted through industry reports, trade publications, and regulatory databases to map policy frameworks and market dynamics.
Data triangulation techniques were applied to validate supply chain cost structures and performance benchmarks, while scenario analysis was utilized to assess the implications of tariff fluctuations and technological shifts. A dedicated advisory panel of renewable energy experts provided ongoing guidance, ensuring that emerging trends and disruptive events were accurately reflected. The resulting framework offers a balanced perspective that integrates macroeconomic, technological, and regulatory dimensions, enabling stakeholders to make informed strategic decisions.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Small Wind Power market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Small Wind Power Market, by Type
- Small Wind Power Market, by Component
- Small Wind Power Market, by Installation Type
- Small Wind Power Market, by Power Capacity
- Small Wind Power Market, by Application
- Small Wind Power Market, by End-User
- Small Wind Power Market, by Region
- Small Wind Power Market, by Group
- Small Wind Power Market, by Country
- United States Small Wind Power Market
- China Small Wind Power Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 18]
- List of Tables [Total: 1431 ]
Drawing Conclusive Reflections on Key Trends Competitive Forces and Strategic Imperatives Shaping the Future Trajectory of Small Wind Power
The future of small wind power is characterized by converging forces that promise to redefine its role within global energy portfolios. Technological innovation in turbine design and digital controls will continue to enhance system reliability and cost competitiveness, while policy frameworks evolve to recognize the value of distributed generation in resilience and decarbonization agendas. Regional market dynamics will remain diverse, but overarching trends toward hybrid renewable configurations and community-oriented deployments are set to accelerate adoption.
As the sector advances, stakeholders who embrace ecosystem thinking-integrating hardware, software, financing, and regulatory engagement-will secure lasting advantages. The cumulative impact of tariffs underscores the importance of supply chain agility and material innovation, and successful market entrants will demonstrate the ability to adapt swiftly to policy shifts. Ultimately, the strategic imperatives outlined in this executive summary offer a roadmap for leveraging small wind power as a flexible, scalable solution capable of addressing the evolving needs of energy users worldwide.
Engage with Associate Director Ketan Rohom Today to Secure Comprehensive Market Intelligence and Unlock Strategic Advantages in Small Wind Energy
To explore how this meticulously curated research can empower your organization with unparalleled market clarity and strategic depth, reach out to Associate Director Ketan Rohom. His expertise in navigating the small wind power ecosystem ensures you gain the actionable intelligence necessary to align your business priorities with emerging opportunities and regulatory nuances. By engaging directly, you will receive tailored guidance on leveraging our holistic analysis across technological trends, tariff implications, competitive landscapes, and regional dynamics. Connect with Ketan to facilitate expedited access to the full report, schedule a personalized walkthrough of its insights, and discuss bespoke consulting packages that address your unique needs. This direct engagement promises to accelerate informed decision making, strengthen your market positioning, and optimize your investment planning within the dynamic small wind power sector. Act now to secure your organization’s competitive advantage and capitalize on the transformative potential of distributed wind energy solutions.

- How big is the Small Wind Power Market?
- What is the Small Wind Power Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




