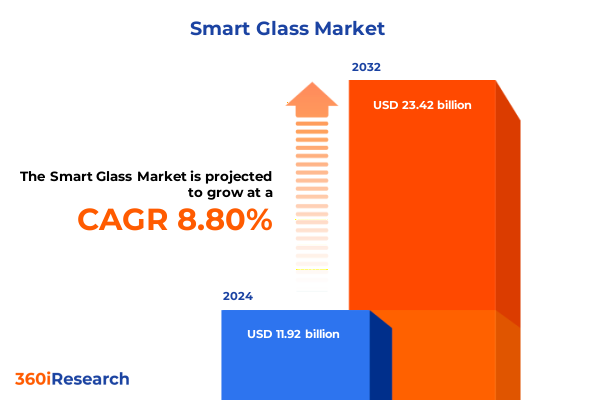
The Smart Glass Market size was estimated at USD 12.88 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 13.95 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 8.91% to reach USD 23.42 billion by 2032.
Positioning smart glass as a strategic convergence technology reshaping energy performance privacy user experience and supply chain resilience across China’s markets
The Chinese smart glass landscape sits at the intersection of advanced materials science, digital control systems, and accelerating demand for energy‑efficient, privacy‑enabled surfaces across built and mobile environments. In urban China, rising regulatory attention to building energy performance, combined with increasing sophistication in architectural design, has elevated smart glass from a niche novelty to a viable component of integrated façade systems. Concurrently, mobility sectors and consumer electronics manufacturers are exploring electroactive glazing and light‑management technologies to enhance passenger comfort, reduce HVAC loads, and enable new user experiences.
This introduction frames smart glass not merely as a product category but as a platform technology that mediates light, heat, and visual access. As a result, adoption drivers must be evaluated across multiple vectors: material capability, control systems, installation complexity, and long‑term operational benefits. Strategic decision‑makers should therefore shift focus from point purchases to systems thinking-prioritizing product designs that deliver demonstrable energy performance gains, compatibility with building automation systems, and scalable supply chains.
Finally, the competitive imperative in China is defined by speed to scale and channel sophistication. Domestic manufacturers have matured their capabilities in large‑area coating, laminated assemblies, and integrated control modules, while global component suppliers continue to influence material innovation and intellectual property. Understanding where product differentiation creates durable value-whether through improved switching speed, lifecycle energy performance, or integration with digital building controls-will determine which companies capture long‑term enterprise and consumer demand.
Identifying the pivotal technological regulatory commercial and supply chain shifts that are driving rapid evolution in China’s smart glass industry and adoption dynamics
Several transformative shifts are converging to reconfigure the competitive and adoption landscape for smart glass in China. First, material and manufacturing advances have reduced barriers to producing larger, more reliable electrochromic and suspended particle devices, enabling architects and OEMs to specify active glazing for projects that previously relied on static tinted glass. This technological maturation is coupled with improved control electronics and IoT connectivity, which allow glazing to respond to occupancy sensors, daylight harvesting logic, and remote building management systems, thereby creating measurable operational benefits.
Second, regulatory trends in China and in major export markets are aligning to favor low‑energy building envelopes and climate‑responsive design. Standards that emphasize thermal performance and lighting quality are increasingly cited in procurement criteria for large commercial projects, and renewable generation policies are incentivizing integrated solutions that reduce overall building loads. These regulatory drivers are accelerating specification decisions where initial capital costs can be justified by operational savings and improved occupant outcomes.
Third, customer expectations have shifted from single‑function glass to multifunctional glazing - combining daylight control, privacy, acoustic attenuation, and, in some cases, photovoltaic integration. This broadening of value propositions creates new partnerships between glass manufacturers, coating specialists, electronics integrators, and systems installers. Such partnerships are reshaping go‑to‑market models, with stakeholders prioritizing bundled solutions over component sales.
Lastly, strategic sourcing and supply‑chain resilience have become critical competitive dimensions. Procurement teams are evaluating nearshoring, diversified supplier portfolios, and vertical integration for critical subcomponents to mitigate geopolitical and logistics risks. The combination of these technological, regulatory, commercial, and supply‑chain shifts is producing a market environment in which the pace of adoption will be governed as much by integration capability and installation economics as by raw product performance.
Analyzing the cumulative effects of United States tariff measures and reciprocal trade actions in 2025 on Chinese smart glass supply chains component sourcing and export dynamics
U.S. trade policy developments in 2024 and 2025 introduced new layers of tariff risk that materially affect component sourcing, cost stacks, and cross‑border value chains for smart glass producers and their customers. In December 2024, the Office of the U.S. Trade Representative announced increases in Section 301 tariff rates on select products, including a substantive increase for solar wafers and polysilicon that took effect on January 1, 2025, which illustrates the USTR’s focus on strategic energy‑related inputs. These adjustments signal that components tied to clean energy and high‑tech supply chains are receiving heightened tariff scrutiny, creating direct implications for smart glass variants that integrate photovoltaic layers or rely on polysilicon‑based supply chains.
During the spring of 2025, diplomatic engagements and executive actions produced a temporary reconfiguration of reciprocal duties between the United States and China. Effective May 14, 2025, the U.S. modified an additional ad valorem rate to 10 percent for a defined 90‑day period as part of a tranche of adjustments intended to facilitate negotiations and reduce immediate market disruption. This action resulted in a short‑term downward adjustment of the elevated reciprocal duty layer, but it did not remove existing product‑specific measures such as Section 301 tariffs or the fentanyl‑related ad valorem duties, which continue to stack with base MFN tariffs. The temporary nature of that modification introduced near‑term relief but also reinforced the risk of tariff re‑escalation once the reprieve period concludes.
Practically, these layered tariffs produce two cumulative effects for China‑based smart glass manufacturers and exporters. First, procurement economics for critical inputs such as coated films, interlayers, and any photovoltaic components (which are linked to wafer and polysilicon tariffs) face elevated landed costs if final assembly or component fabrication occurs across jurisdictions subject to additional duties. Second, price pass‑through into end users and OEMs becomes less predictable, complicating bidding for large architectural and automotive contracts that are often price‑sensitive. The combined result is an incentive to re‑examine sourcing strategies, accelerate localization of tariff‑sensitive inputs, or redesign product architectures to minimize exposure to tariffed subcomponents.
It is also important to note that regulatory and diplomatic developments after May 2025 continued to evolve. Exclusions and extensions were issued for certain Section 301 tariff items during 2025 to provide targeted relief or to allow for administrative review, and those adjustments created windows of opportunity for importers to reclassify or phase shipments strategically. For example, the U.S. extended specific exclusions in mid‑2025 as part of an effort to balance national security and industrial policy objectives with commercial continuity. While these adjustments provided tactical breathing room, they did not eliminate structural tariff risk, leaving supply chains vulnerable to renewed policy shifts.
Given this policy environment, industry players must treat tariff exposure as a multi‑dimensional cost and strategic risk. Companies that internalize tariff scenarios into product design, that qualify alternative suppliers outside affected tariff classifications, or that engage in proactive customs classification and tariff engineering will be positioned to protect margins and maintain competitive pricing in core markets. Conversely, organizations that rely on single‑source imports of tariffed inputs without contingency plans will face acute margin pressure and competitive disadvantage when duties are enforced or re‑stacked.
Translating segmentation intelligence into practical product strategy by examining type functionality application and end user vectors specific to China’s smart glass market
A segmentation‑driven lens reveals where commercial opportunity and technical differentiation intersect for smart glass in China. From a product type perspective, the market separates into active and passive technologies; active smart glass delivers dynamic control and includes electrochromic devices, liquid crystal variants, and suspended particle devices (SPD), each offering unique switching characteristics and integration pathways. Passive smart glass relies on material response to environment and includes photochromic and thermochromic solutions that remain cost‑effective for certain retrofit and consumer applications. Recognizing these distinctions is essential because specification decisions are ultimately driven by required control fidelity, lifecycle expectations, and installation complexity.
Functionality further refines product strategy by articulating core value propositions. Energy efficiency remains a primary functionality vector, where subcapabilities such as heat insulation and low‑energy consumption determine operational savings and compliance with thermal performance regulations. Light control is the second functionality axis, where attributes like brightness adjustability and UV absorption influence occupant comfort and interior asset preservation. Privacy enhancement is the third axis, encompassing both sound insulation and visual obscuration characteristics that appeal to high‑security commercial projects and premium residential segments. Successful product roadmaps explicitly map type to functionality-selecting electrochromic or SPD platforms when precise brightness control and rapid switching are required, and choosing passive photochromic or thermochromic options when simplicity and lower cost to install are the primary constraints.
Application segmentation clarifies commercial routes to scale. Architectural and construction projects remain a dominant deployment channel for large‑format glazing, while automotive and avionics applications prioritize weight, reliability, and certification pathways. Consumer electronics and smart homes demand thin, low‑power films or laminated units that can integrate with user interfaces, and solar power applications explore dual‑use glazing that contributes to building energy generation. Each application carries distinct qualification cycles and procurement cadences; architectural projects require long specification lead times and multi‑disciplinary approvals, whereas consumer electronics favor rapid iteration and high‑volume manufacturing throughput.
Finally, end‑user segmentation determines distribution strategy and value chain partnerships. Commercial real estate and enterprises/industrial customers focus on total cost of ownership, regulatory compliance, and integration with building management systems. Individual consumers prioritize aesthetics, privacy, and ease of installation, often driving demand for retrofit‑friendly passive systems. Public utilities and infrastructure projects look for durability, standardized interfaces, and predictable lifecycle performance. Translating segmentation intelligence into targeted product development, channel selection, and service models enables firms to move beyond one‑size‑fits‑all approaches and to construct value propositions that match buyer procurement behavior and risk tolerance.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Smart Glass market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Type
- Functionality
- Application
- End User
Decoding regional trade dynamics and demand centers across the Americas Europe Middle East & Africa and Asia Pacific to inform market access and partnership strategy
Regional dynamics exert a strong influence on both demand formation and trade policy exposure for smart glass manufacturers in China. Within the Americas, procurement decision‑making is influenced by retrofit economics, architectural trends favoring daylighting, and increasingly stringent energy codes in major U.S. and Canadian urban centers. At the same time, tariff policies and supply‑chain due diligence create sourcing complexity for exports targeted at North American OEMs and construction projects, necessitating robust customs classification and contingency logistics.
In Europe, Middle East & Africa, specification drivers emphasize sustainability credentials, building certification compliance, and performance under diverse climate conditions. European buyers often require third‑party performance verification and lifecycle analyses, which favors suppliers that can demonstrate measurable energy savings and standardized testing protocols. In Middle Eastern markets, solar load management and privacy features may dominate specification choices, while African markets are attentive to cost, reliability, and local installation capacity.
Across the Asia‑Pacific region, demand heterogeneity is notable. Advanced economies in East Asia and Oceania increasingly adopt high‑performance glazing as part of smart building mandates and premium automotive features, while Southeast Asian markets balance cost sensitivity with rising interest in comfort and energy efficiency. Regional manufacturing clusters in Asia‑Pacific also provide a logistics advantage for exporters, enabling faster delivery and closer collaboration with regional OEMs. The combined regional picture emphasizes that market access strategies must be calibrated for regulatory requirements, procurement cycles, and local value propositions in each geography, rather than relying on a uniform export approach.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Smart Glass market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Profiling incumbent and emerging corporate strategies that are defining competitive advantage in manufacturing IP integration and channel development within China’s smart glass ecosystem
Competitive dynamics in the smart glass ecosystem are shaped by a combination of manufacturing scale, intellectual property in coatings and control systems, channel relationships, and the ability to deliver integrated solutions. Leading manufacturers that have invested in large‑area coating lines, automated lamination, and modular control electronics enjoy a cost and quality advantage for architectural projects requiring full‑height glazing. At the same time, specialist firms focused on electrochromic stacks or SPD technologies leverage proprietary materials and process know‑how to command premium positioning for high‑end mobility and commercial projects.
Integration capability-particularly software and systems interoperability-has emerged as a differentiator. Suppliers that offer open APIs, certified BMS integrations, and remote commissioning services reduce adoption friction for building owners and systems integrators. This shift places a premium on cross‑disciplinary teams that can manage both materials engineering and software development. Another competitive vector is aftermarket and service models; warranty terms, field service networks, and performance monitoring subscriptions influence long‑term customer economics and help sustain recurring revenue.
Strategic alliances and channel partnerships are central to market expansion. Glass manufacturers that cultivate relationships with façade contractors, automotive OEMs, and smart home OEMs accelerate specification and procurement. Conversely, firms that focus narrowly on component manufacture without channel engagement risk commoditization. Finally, for companies navigating the tariff environment, flexible manufacturing footprints and diversified supplier lists are essential to preserve margin and continuity of supply. Those that proactively redesign supply chains and that invest in tariff engineering and customs optimization create defensible advantages over less nimble competitors.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Smart Glass market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- AGC Inc.
- AGP Group
- Carl Zeiss AG
- ChromoGenics AB
- Compagnie de Saint-Gobain S.A.
- Corning Incorporated
- Dream Glass Group
- EssilorLuxottica
- Gauzy Ltd.
- General Motors Company
- Gentex Corporation
- Glasstronn
- Google LLC by Alphabet Inc.
- Guardian Industries Holdings by Koch Industries, Inc.
- LG Electronics Inc.
- LTI Smart Glass, Inc.
- Meta Platforms, Inc.
- Miru Smart Technologies
- Nippon Sheet Glass Co., Ltd.
- Pleotint LLC
- Polytronix, Inc.
- PPG Industries, Inc.
- Pro Display Group
- Pulp Studio, Inc.
- RavenWindow
- Rev Interactive SDN. BHD.
- Seiko Epson Corporation
- Shenzhen Yuguang New Material Co., Ltd.
- Skyline Design
- Smart Glass Group
- Smart Window Company, Inc.
- Smartglass International Ltd.
- SmartGlassCountry
- Tejj Sons
- VELUX A/S
- View, Inc.
Action oriented strategic imperatives for industry leaders to accelerate commercialization secure resilient sourcing and capture value across the Chinese smart glass ecosystem
Leaders seeking to convert market insight into commercial advantage should prioritize a short list of action‑oriented initiatives. First, institute a rigorous component risk assessment that maps tariff exposure, supplier concentration, and lead‑time sensitivity across all bill‑of‑materials items. This assessment should inform a prioritized program of supplier qualification, near‑sourcing, or vertical integration where critical inputs create disproportionate exposure.
Second, accelerate integration capabilities by bundling glazing hardware with control electronics and software services. Demonstrable interoperability with common building automation platforms and clear commissioning protocols reduce adoption friction for large projects. Firms should invest in modular product architectures that can be configured for different functionality mixes-energy efficiency, light control, or privacy enhancement-without requiring full redesigns.
Third, align product roadmaps with regulatory and certification timelines. Attaining recognized performance certifications and producing transparent lifecycle and test data will unlock requirements‑driven procurement channels in commercial real estate and public infrastructure. Where photovoltaic integration or energy‑harvesting capabilities are part of the roadmap, ensure early engagement with energy regulators and grid interconnection stakeholders to preempt technical and permitting obstacles.
Fourth, develop commercial models that reflect total cost of ownership rather than simple capital price comparisons. Performance‑based contracting, longer warranties, and performance monitoring services can shift buyer focus toward lifecycle value, enabling premium positioning for higher‑performing systems. Fifth, maintain active customs and trade counsel engagement to monitor tariff developments, secure favorable classifications, and exploit legitimate exclusions that reduce landed cost.
Implementing these measures in a coordinated program-with cross‑functional leadership and clear KPIs-will strengthen resilience in the face of policy volatility and accelerate adoption where value propositions are most compelling.
Transparent explanation of research design primary and secondary data inputs validation processes and analytical frameworks used to derive the insights presented
The research underpinning this executive summary used a blended methodology that combined primary interviews, technical literature review, and supply‑chain mapping to ensure balanced, operationally relevant findings. Primary inputs included structured interviews with material scientists, façade engineers, procurement leads at major developers, and systems integrators active in China’s architectural, automotive, and consumer electronics sectors. These interviews informed an understanding of specification drivers, installation constraints, and service models.
Secondary research synthesized regulatory documents, standards publications, patent filings, and publicly available technical white papers to validate product‑level performance claims and to identify R&D trajectories. In addition, trade policy developments were cross‑referenced against official government releases and executive actions to ensure that tariff and trade risk observations reflect the authoritative policy record. Where possible, technical performance attributes-such as switching times, U‑values, and transmissivity ranges-were compared across vendor documentation to assess engineering trade‑offs.
Analytical frameworks applied included segmentation analysis (type, functionality, application, end user), scenario planning for tariff exposure and supply‑chain resilience, and a capability maturity model to evaluate commercialization readiness across manufacturers. Where data limitations existed, findings were conservatively framed and supported by qualitative corroboration from multiple stakeholders. The combination of primary and secondary methods provided both market context and tactical insight designed to be actionable for corporate decision‑makers.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Smart Glass market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Smart Glass Market, by Type
- Smart Glass Market, by Functionality
- Smart Glass Market, by Application
- Smart Glass Market, by End User
- Smart Glass Market, by Region
- Smart Glass Market, by Group
- Smart Glass Market, by Country
- United States Smart Glass Market
- China Smart Glass Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 16]
- List of Tables [Total: 1590 ]
Synthesis of strategic implications and near term inflection points that leaders must monitor to convert technological progress and policy shifts into commercial advantage
Smart glass in China has moved beyond proof‑of‑concept to a phase where technical differentiation, integration capability, and supply‑chain resilience determine commercial success. The confluence of improved material technologies, stronger regulatory emphasis on energy performance, and evolving customer expectations for multifunctional glazing creates a durable opportunity for suppliers that can execute on systems integration and provide verified performance outcomes.
However, policy volatility-particularly tariff dynamics that emerged in 2024–2025-introduces a structural variable that companies must manage proactively. Firms that incorporate tariff scenarios into product development, maintain flexible sourcing footprints, and offer performance‑oriented commercial models will be better positioned to capture demand as project pipelines normalize. For decision‑makers, the core implication is clear: competitive advantage will accrue to organizations that blend deep technical capability with disciplined supply‑chain and commercial execution.
Monitoring near‑term inflection points-regulatory updates, major project specifications, and advances in control‑system interoperability-will enable more agile responses. Ultimately, the path to scale in China’s smart glass market is paved by demonstrable operational benefits, robust integration with building and mobility systems, and the ability to adapt rapidly to policy and trade shifts.
Engage directly with Ketan Rohom Associate Director Sales & Marketing to acquire the detailed market research report and operationalize insights for commercial growth
To obtain the full market research report and translate these strategic insights into executable commercial initiatives, contact Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing. He can guide prospective buyers through the report’s detailed chapters, customization options, and licensing arrangements, and help align the deliverables with product roadmaps, procurement strategies, and regional go‑to‑market plans.
Engaging directly with the sales lead will fast‑track access to granular datasets, supplier and OEM profiles, regulatory impact appendices, and implementation playbooks that move analysis into action. For executive teams and business unit leaders preparing investment cases or supply‑chain realignments, a short briefing with the associate director can clarify which modules to prioritize, what bespoke analyses are available, and how to integrate the report’s findings into quarterly planning cycles.
A targeted purchase conversation also ensures timely delivery of any tailored scenario modeling or competitive benchmarking that your organization requires. If you are evaluating partnerships, local manufacturing expansion, or alternative sourcing strategies, initiating contact with the associate director will provide a clear path from insight to procurement and execution.

- How big is the Smart Glass Market?
- What is the Smart Glass Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




