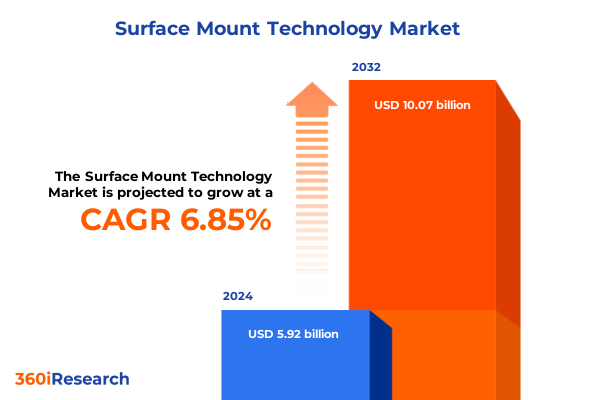
The Surface Mount Technology Market size was estimated at USD 6.30 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 6.72 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 6.91% to reach USD 10.07 billion by 2032.
Executive overview of surface mount technology as the foundational engine of next generation electronics design, assembly quality, and manufacturing resilience
Surface mount technology has evolved from a production innovation into the core manufacturing philosophy of modern electronics. It underpins everything from compact smartphones and advanced automotive driver assistance systems to high‑reliability aerospace controls and industrial automation platforms. As component densities rise and form factors shrink, this manufacturing approach is no longer a tactical choice-it is the default for designing and assembling competitive electronic systems.
The current environment surrounding surface mount assemblies is shaped by converging forces. On one side, there is relentless pressure for higher performance, lower power consumption, and greater functional integration, driving increasingly complex board layouts and multi‑layer assemblies. On the other, manufacturers must deliver consistent quality at high speed while keeping production flexible enough to accommodate shorter product lifecycles and more frequent design revisions. This tension between complexity and agility defines the strategic context in which equipment vendors and electronics manufacturers now operate.
At the same time, structural changes in global trade and industrial policy are reshaping the economics of surface mount production. United States tariff actions, new industrial subsidies, and shifts in regional trade agreements are prompting companies to rethink long‑established supply chains. Decisions about where to source components, where to locate lines, and which equipment platforms to standardize on increasingly reflect not just cost and capability, but also regulatory and geopolitical risk.
Against this backdrop, an executive‑level view of surface mount technology must go beyond technical detail. It must interpret how equipment categories, assembly methods, and application segments interact with trade policy and regional dynamics to create both constraints and opportunities. The following sections synthesize these interactions, focusing on the structural shifts that matter most for board‑level and C‑suite decision‑making.
Transformative shifts in surface mount technology driven by intelligent automation, process integration, and sustainability requirements across global electronics
The surface mount landscape is undergoing a profound transition driven by advances in automation, inspection, and data utilization. Placement platforms are increasingly defined not just by raw speed or component range, but by their ability to operate as intelligent nodes in a connected factory. Modern machines integrate high‑resolution vision, real‑time feedback loops, and software analytics that tune processes dynamically, allowing lines to adjust for subtle board or component variations without human intervention. This transforms surface mount lines from static, recipe‑driven assets into adaptive systems capable of optimizing yield continuously.
Inspection and testing have similarly moved from end‑of‑line gatekeeping to embedded process control. Automated optical and X‑ray inspection systems now capture large volumes of image and measurement data at multiple points in the line. When combined with machine learning algorithms, this data enables defect pattern recognition, early detection of drift in printing or placement, and rapid root‑cause analysis. The result is a shift from reactive quality management to predictive and preventive strategies, significantly reducing scrap and rework while supporting the tighter tolerances of miniaturized assemblies.
Another transformative shift involves the integration of printing, soldering, and cleaning into holistic process architectures. Screen printing equipment increasingly supports finer apertures and more consistent deposition for advanced solder pastes, while soldering systems are engineered to minimize thermal stress and voids for complex component packages. Cleaning platforms are calibrated to remove ever‑smaller residues associated with dense assemblies, supporting long‑term reliability in harsh environments such as automotive power electronics and aerospace controls. These developments reflect a broader move toward viewing the entire surface mount line as an integrated ecosystem rather than a collection of discrete steps.
Digitalization also extends into the way factories are planned and operated. Virtual commissioning, digital twins of lines, and simulation of board flows enable manufacturers to test changeovers, new products, or alternative equipment configurations before physically modifying the line. This reduces downtime, improves right‑first‑time performance during new product introduction, and supports more frequent reconfiguration to respond to demand shifts. As talent shortages in manufacturing persist, such tools are becoming essential to maintaining high utilization with fewer experienced engineers on site.
Finally, sustainability considerations are beginning to influence equipment selection and process design in a more systematic way. Energy efficiency of reflow ovens, chemistry usage in cleaning processes, and material utilization in printing are receiving more scrutiny as manufacturers work toward corporate climate and environmental targets. Vendors that can document lower energy consumption, reduced emissions, or safer chemistries are gaining traction, particularly among global customers with formal sustainability reporting requirements. This introduces a new set of decision criteria alongside throughput and technical capability, reshaping how investment in surface mount infrastructure is justified internally.
Cumulative impact of evolving United States tariffs in 2025 on semiconductor sourcing, clean energy electronics, and strategic surface mount investments
United States tariff policy has become a defining external factor for surface mount decision‑makers, particularly through the evolution of Section 301 measures on imports from China. The four‑year review concluded by the trade authorities resulted in targeted tariff increases for strategic sectors, notably raising tariffs on semiconductors to 50 percent by 2025. While many surface mount components are sourced from a globally distributed base, these higher duties on chips and related products amplify cost pressures for manufacturers that continue to depend heavily on China‑origin devices.
The same review extended elevated tariffs to elements of the clean energy supply chain, including wafers, polysilicon, and certain tungsten products, with higher rates taking effect from January 1, 2025. For surface mount stakeholders, this adds complexity for photovoltaic inverters, power optimizers, and other electronics embedded in solar and energy management systems. Manufacturers must now evaluate not only the component cost itself but also the combined effect of energy‑related tariffs and electronics‑focused duties when designing boards and selecting suppliers.
At the same time, authorities have used targeted exclusions to modulate the impact of these measures on domestic industry. Exclusions granted for certain China‑origin goods have been extended multiple times, with renewals in May and August 2025 pushing the current expiry for specific exemptions to late November 2025. For surface mount operations, these exclusions have provided temporary relief on selected manufacturing inputs and capital equipment, enabling some companies to proceed with planned investments while monitoring the policy trajectory.
Policy developments in 2025 also include a renewed focus on the enforcement of prior trade agreements and investigations into compliance with commitments relating to intellectual property and technology transfer. While not targeted exclusively at electronics, these actions underscore the likelihood of continued use of tariffs and related tools to influence technology supply chains. For surface mount manufacturers, this environment increases the value of diversified sourcing strategies, dual qualification of suppliers across multiple regions, and closer collaboration with distributors to manage potential disruptions.
The cumulative result of these tariff actions is a more differentiated cost landscape for components, materials, and in some cases capital equipment. Companies with the ability to nearshore or onshore surface mount assembly closer to end markets can partially offset higher component costs through logistics savings, reduced lead times, and better control over inventory. Meanwhile, suppliers in regions not subject to the same duties-such as parts of Southeast Asia, Mexico, and certain European locations-are strengthening their position as alternate sourcing hubs. Decision‑makers now increasingly integrate tariff scenarios into return‑on‑investment calculations for new placement, printing, and soldering lines, treating trade policy not as a short‑term disruption but as a structural factor in network design.
Key segmentation insights reveal how equipment types, components, assembly modes, and applications interact to shape surface mount investment priorities
Viewed through the lens of equipment categories, surface mount investment patterns reveal distinct priorities. Cleaning equipment is seeing heightened attention in applications where reliability is paramount, including aerospace, defense, automotive power electronics, and critical medical devices, as residues that were once acceptable now pose risk in finer pitch designs. Inspection equipment, both optical and X‑ray, has become central to process governance, serving not only high‑volume consumer lines but also lower volume, high‑mix environments where rapid detection of setup errors is critical. Placement equipment remains the strategic centerpiece of most lines, with decisions about platform family and feeder ecosystems effectively locking in future flexibility. Repair and rework equipment plays a growing role in sustainability and cost containment strategies, enabling targeted recovery of high‑value boards. Screen printing equipment has evolved to support finer apertures and more challenging pastes, while soldering equipment-spanning inline printing‑related systems and more standalone, flexible configurations-defines the thermal envelope within which advanced components can be reliably assembled.
Component characteristics continue to drive process requirements as well. Within the analytical framework used here, the active components segment encompasses capacitors, inductors, and resistors. These parts, although electrically passive in a strict engineering sense, dominate board real estate and placement counts, making their handling, packaging formats, and placement speeds decisive for line throughput. The passive components segment, defined for this analysis to include diodes, integrated circuits, and transistors, brings a different set of challenges. Diodes and discrete transistors require careful management of orientation and thermal performance, while integrated circuits introduce complex packages such as fine‑pitch QFNs, BGAs, and system‑in‑package formats that stress both printing and soldering processes. Together, these groups force manufacturers to balance ultra‑high‑speed chip shooting with the precision and verification required for advanced semiconductors.
Assembly type is another critical dimension shaping investment choices. Fully automated assembly has become the benchmark for high‑volume consumer electronics, networking devices, and automotive control units, where consistent quality, high utilization, and traceability justify the capital intensity. These lines typically integrate closed‑loop printing, high‑speed placement, reflow with advanced thermal profiling, and multi‑stage inspection in a seamless flow, often monitored via centralized manufacturing execution systems. Semi‑automated assembly retains a vital role in lower volume, high‑mix production such as specialized industrial controls, bespoke medical devices, and some aerospace subsystems. In these environments, flexible fixtures, operator‑assisted loading, and modular workcells allow manufacturers to handle frequent changeovers and complex customizations without excessive idle time.
The mounting process itself has also diversified. Single‑sided surface mount assembly is prevalent where cost efficiency, simpler board construction, and moderate functional density suffice, including many power supplies, basic control boards, and cost‑sensitive consumer appliances. Double‑sided surface mount assembly, by contrast, enables much higher functional density within constrained form factors, supporting advanced driver assistance modules, compact telecom equipment, and portable medical devices. However, it imposes tighter constraints on profile design, solder paste selection, and component sequencing, driving demand for more sophisticated process simulation and thermal management capabilities.
Application segmentation reveals where these technical and process choices converge into distinct demand patterns. Aerospace and defense lines emphasize traceability, high‑reliability soldering, and rigorous inspection regimes, often operating with semi‑automated or hybrid configurations to accommodate diverse platforms and long product lifecycles. Automotive applications span driver assistance systems, where high compute density and sensor fusion drive complex, double‑sided boards, and infotainment systems, which must balance high‑volume consumer electronics economics with automotive durability standards. Consumer electronics remains the most visible user of cutting‑edge high‑speed placement and fully automated lines, covering audio and video systems, home appliances, mobile phones, personal computers, and storage devices, each with distinct cycle times and product refresh rhythms.
Healthcare applications divide between consumer medical devices, such as wearables and home diagnostics, where miniaturization and battery efficiency are critical, and medical imaging equipment, where boards are large, complex, and built for long‑term stability and serviceability. Industrial applications encompass industrial automation and motion control, mechatronics and robotics, photovoltaic systems, and power electronics, collectively driving demand for robust, often high‑power designs with strict thermal constraints. Finally, IT and telecommunication applications, including networking devices and telecom equipment, require a combination of high port densities, signal integrity at high frequencies, and strong thermal management, pushing both design and surface mount processes toward more intricate layouts and materials. Across these segments, equipment selection and line configuration are increasingly tailored to the specific reliability, lifecycle, and flexibility needs of each end‑use domain rather than treated as one‑size‑fits‑all.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Surface Mount Technology market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Product
- Component
- Assembly Type
- Mounting Process
- Application
Key regional insights highlight how Americas, EMEA, and Asia-Pacific manufacturing ecosystems reshape strategic choices in surface mount deployment
Regional dynamics in surface mount technology reflect both historic manufacturing strengths and recent policy‑driven shifts. In the Americas, the United States anchors demand through its concentration of high‑value design houses, system integrators, and critical industries such as aerospace, defense, advanced automotive, and cloud infrastructure. Investments in domestic semiconductor fabrication and electronics manufacturing incentives are encouraging closer integration between chip production and board assembly, particularly for strategic applications. Mexico has consolidated its role as a nearshore hub for consumer electronics, automotive electronics, and networking equipment, leveraging competitive labor costs and trade agreements to serve North American markets with reduced lead times. Canada and selected Latin American countries contribute specialized capacity, especially in industrial, energy, and niche consumer products.
Europe, the Middle East, and Africa present a diversified but evolving landscape. Western and Central European countries host a dense network of automotive, industrial automation, and medical equipment manufacturers that demand high‑reliability surface mount solutions and often lead in adopting advanced inspection, traceability, and sustainability features. Eastern and Southern European locations, supported by regional incentives and proximity to major end markets, are emerging as competitive manufacturing bases for both consumer and industrial electronics. In the Middle East, expanding telecom and infrastructure projects, along with nascent diversification into non‑hydrocarbon industries, are stimulating interest in local assembly capabilities. Across Africa, surface mount activity is at an earlier stage but gradually expanding, particularly in telecommunications, consumer devices assembly, and certain energy applications, often supported by regional integration initiatives and skills development programs.
Asia‑Pacific remains the gravitational center of global electronics assembly, and surface mount technology is deeply embedded across the region’s industrial fabric. Long‑established hubs in China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan continue to anchor production of smartphones, computers, networking hardware, and a broad spectrum of consumer and industrial devices, supported by extensive supplier ecosystems and highly optimized logistics. At the same time, rising labor costs, evolving tariff regimes, and supply chain resilience strategies are driving a redistribution of capacity toward Southeast Asian countries and India, where governments have launched initiatives to attract electronics manufacturing. This is creating a more multi‑polar production network in which regional clusters specialize in particular product categories or value chain stages.
Across all three regions, a common thread is the push to align surface mount investments with regional policy frameworks, from trade measures and local content rules to incentives for automation, digitalization, and low‑carbon manufacturing. Companies that understand how these regional dynamics interact with their product portfolios can better decide where to locate new lines, which equipment platforms to standardize globally, and how to configure cross‑regional supply chains that remain resilient in the face of regulatory change.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Surface Mount Technology market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Key company insights show equipment vendors evolving into data-centric partners delivering integrated surface mount hardware, software, and lifecycle services
The competitive landscape in surface mount technology is characterized by a blend of global equipment manufacturers, specialized niche providers, and increasingly software‑driven solution vendors. Leading placement equipment suppliers have broadened their portfolios to encompass not only high‑speed chip shooters and flexible mounters, but also integrated line software, feeder logistics solutions, and service offerings that extend throughout the equipment lifecycle. Their differentiation increasingly rests on the ability to support rapid new product introduction, handle a wide range of component sizes and packages, and provide robust data interfaces to factory systems.
In the screen printing and soldering domains, key companies are investing in process consistency and thermal precision as primary value propositions. Modern printers are designed to maintain tight control over paste volume and deposition quality across high‑mix product sets, while reflow and selective soldering systems emphasize profile repeatability, low voiding, and compatibility with lead‑free and high‑reliability alloys. Vendors that can demonstrate strong support for complex packages and double‑sided assemblies, as well as strong global service coverage, are particularly well positioned in automotive, industrial, and telecom segments.
Inspection and test specialists have carved out a critical role by pushing the boundaries of defect detection, metrology, and analytics. Providers of automated optical and X‑ray inspection platforms differentiate through imaging quality, algorithm sophistication, and the ability to flag process deviations before they translate into defects. Many are augmenting their systems with machine learning modules, remote diagnostics, and cloud‑connected dashboards that integrate inspection data with broader manufacturing analytics. Cleaning and rework equipment suppliers, while often smaller in scale, are benefiting from growing emphasis on reliability, sustainability, and repairability, especially in high‑value applications where extending product life has both economic and environmental benefits.
Across these categories, a common strategic trend is the movement toward platform‑based offerings that combine hardware, software, and services into cohesive ecosystems. Major vendors are introducing subscription or outcome‑oriented service models, remote performance monitoring, and advanced training solutions to help customers extract more value from installed equipment. Partnerships with materials suppliers, software firms, and contract manufacturers are becoming more prominent as companies seek to demonstrate validated process windows rather than isolated machine specifications. For buyers, evaluating vendors increasingly involves assessing long‑term roadmaps, integration capabilities, and support infrastructures, alongside the conventional metrics of speed, accuracy, and uptime.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Surface Mount Technology market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- AEMtec GmbH
- Aimtron Corporation
- American Products, Inc.
- ASMPT GmbH & Co. KG
- Assel Sp.z .o.o.
- Cirexx International, Inc.
- Electronic Manufacturing Services Group, Inc.
- ELIM Electronics Corp.
- EMS Solutions
- FUJI Corporation
- Heller Industries, Inc.
- Indium Corporation
- Juki Corporation
- Kasdon Electronics Ltd
- Kurtz Holding GmbH & Co. Beteiligungs KG
- KUS Americas, INC.
- Mycronic AB
- Nordson Corporation
- Panasonic Corporation
- PCBCART
- Seika Corporation
- Solid Semecs B.V. by Sero GmbH
- Star Engineering, Inc.
- Techpoint Group Ltd
- Weidmuller Inc.
- Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd.
- Zhejiang NeoDen Technology Co., Ltd.
Actionable recommendations for industry leaders to align surface mount investments with data, supply resilience, modularity, workforce, and sustainability goals
In the current environment, leadership teams responsible for surface mount strategy should first prioritize data‑centric manufacturing as a foundation for competitive advantage. This means treating equipment not just as capital assets but as sensors and data generators, ensuring that placement, printing, soldering, and inspection platforms all feed standardized, high‑quality data into central systems. With this infrastructure in place, organizations can apply analytics and machine learning to uncover yield patterns, optimize changeover planning, and simulate the impact of process adjustments before making physical changes on the line.
Another actionable priority is the deliberate diversification and qualification of supply chains in light of evolving tariffs and regional policy shifts. Executives should collaborate closely with procurement, engineering, and logistics teams to map current dependencies on particular countries or components, then systematically qualify alternative suppliers and manufacturing locations. This does not necessarily mean abandoning existing hubs, but rather building optionality into sourcing strategies so that board designs, bills of materials, and line configurations can be adjusted with manageable lead times.
Investment decisions for new lines or major upgrades should be framed within modular and scalable architectures. Choosing equipment platforms that share common feeders, software environments, and maintenance strategies reduces complexity over time and facilitates factory rebalancing across sites. In parallel, leaders should ensure that workforce development keeps pace with technology adoption by investing in training programs, digital work instructions, and remote support tools that help operators and engineers master increasingly sophisticated systems.
Sustainability and regulatory compliance should be woven into surface mount strategy from the outset rather than treated as afterthoughts. This involves evaluating the energy profile of ovens, the environmental characteristics of cleaning chemistries, and the recyclability of consumables when selecting equipment and process materials. Finally, leaders should establish governance mechanisms that regularly review trade policy developments, regional incentives, and regulatory changes, ensuring that surface mount investments remain aligned with both current conditions and plausible future scenarios.
Research methodology integrating primary insights, policy analysis, and technical review to build a robust view of the surface mount landscape
The insights presented in this executive summary are grounded in a structured research methodology designed to balance breadth of coverage with depth of technical and strategic detail. The analytical process begins with a clear definition of the surface mount technology scope, including equipment categories, component groupings, assembly types, mounting processes, and application domains. This framework ensures that terminology is applied consistently and that comparisons across segments are meaningful.
Primary research plays a central role, incorporating interviews and discussions with equipment manufacturers, contract electronics manufacturers, in‑house assembly operations, materials suppliers, and subject matter experts. These engagements provide nuanced perspectives on process challenges, technology roadmaps, adoption barriers, and emerging use cases. Insights from practitioners are especially valuable in understanding the practical implications of tariffs, regional policy shifts, and new technology introductions on day‑to‑day operations.
Secondary research complements these inputs through the systematic review of industry publications, trade statistics, regulatory announcements, and company disclosures. Particular attention is given to policy documents, such as tariff notices and industrial incentive schemes, that directly influence investment and sourcing decisions. Technical literature and standards documents inform the discussion of process capabilities and reliability requirements, especially in demanding sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and medical electronics.
Analytical synthesis involves cross‑checking qualitative findings against available quantitative indicators and reconciling perspectives across different stakeholder groups. Scenario analysis is used to explore how surface mount strategies may evolve under alternative assumptions about trade policy, technology progression, and regional capacity development. Throughout this process, care is taken to avoid overstating precision where uncertainty remains and to highlight structural drivers and constraints rather than short‑term fluctuations. The result is a coherent narrative that supports strategic decision‑making while remaining transparent about underlying assumptions and data provenance.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Surface Mount Technology market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Surface Mount Technology Market, by Product
- Surface Mount Technology Market, by Component
- Surface Mount Technology Market, by Assembly Type
- Surface Mount Technology Market, by Mounting Process
- Surface Mount Technology Market, by Application
- Surface Mount Technology Market, by Region
- Surface Mount Technology Market, by Group
- Surface Mount Technology Market, by Country
- United States Surface Mount Technology Market
- China Surface Mount Technology Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 17]
- List of Tables [Total: 2226 ]
Conclusion synthesizing technology, segmentation, regional dynamics, and trade policy to clarify the strategic path for surface mount stakeholders
Surface mount technology stands at the intersection of several powerful forces: escalating functional density in electronics, rising expectations for reliability and sustainability, and a reconfiguration of global trade and industrial policy. The interplay of these factors is redefining what successful manufacturing looks like. No longer is it sufficient to operate fast, high‑utilization lines; manufacturers must operate adaptive, insight‑driven systems that can absorb design changes, component disruptions, and regulatory shifts without compromising quality or profitability.
The segmentation of the market by equipment type, component characteristics, assembly mode, mounting process, and application domain reveals a rich tapestry of distinct needs and opportunities. High‑volume consumer electronics lines will continue to drive demand for state‑of‑the‑art automated solutions, while specialized industrial, medical, and aerospace applications sustain a strong role for flexible, often semi‑automated configurations with enhanced traceability and reliability. Regional dynamics, particularly the evolving roles of the Americas, EMEA, and Asia‑Pacific, further influence where capacity is added and how supply chains are configured.
In parallel, developments in United States tariff policy and related trade measures are reshaping cost structures and prompting a more deliberate approach to sourcing and network design. Organizations that integrate these policy considerations into their technology and capacity planning, rather than treating them as external shocks, will be better positioned to maintain continuity and capture emerging opportunities. Ultimately, the winners in this environment will be those who combine technical excellence in surface mount processes with strategic agility, data‑driven decision‑making, and proactive engagement with the broader policy and ecosystem context.
Secure a strategic edge in surface mount technology by engaging with Ketan Rohom to unlock the full depth of this specialized market report
In a landscape where surface mount technology is reshaping how every major electronic system is conceived, built, and deployed, access to deep, structured insight is no longer optional. It is a prerequisite for de‑risking capital expenditure, negotiating resilient supply contracts, and aligning product roadmaps with the realities of tariffs, technology shifts, and regional policy. Executives who act on robust evidence now will be the ones who define the benchmarks for productivity, quality, and responsiveness in the decade ahead.
To translate the themes outlined in this executive summary into concrete strategic guidance, stakeholders are encouraged to engage directly with Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing. Through a focused consultation, he can walk decision‑makers through the complete surface mount technology market report, highlight the sections most relevant to their portfolio, and outline optional enhancements such as custom segmentation cuts, scenario deep dives, or competitive landscaping tailored to specific product lines.
By securing the full report, leadership teams gain a structured foundation for investment cases, board presentations, and cross‑functional planning. The deliverable goes beyond narrative to provide traceable assumptions, clearly defined segment boundaries, and an auditable methodology that can withstand internal scrutiny. Engaging with Ketan ensures that the report is not just purchased but effectively embedded into strategic processes, enabling organizations to convert market intelligence into measurable operational advantage.

- How big is the Surface Mount Technology Market?
- What is the Surface Mount Technology Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




