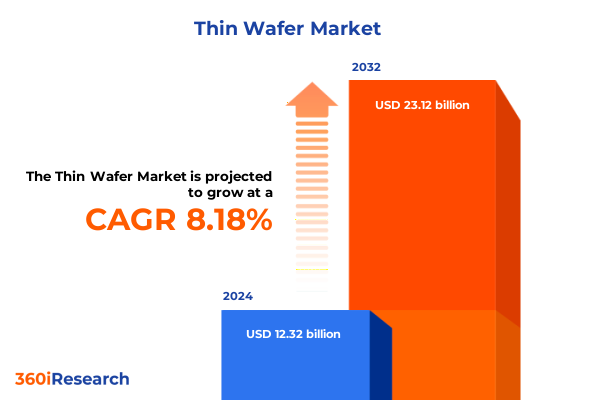
The Thin Wafer Market size was estimated at USD 13.05 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 13.83 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 8.50% to reach USD 23.12 billion by 2032.
Unveiling the Forces Driving Thin Wafer Innovation and Market Evolution in a Rapidly Transforming Semiconductor Landscape
The thin wafer segment stands at the heart of modern semiconductor innovation, enabling a new generation of high-performance and space-efficient devices. Recent advances have driven wafer thicknesses down to as little as 30 micrometers, supporting sophisticated 3D stacking, interposers, and flexible electronics applications. Ultra-thin substrates not only reduce overall device weight but also enhance thermal management and electrical performance, meeting the exacting requirements of AI accelerators, mobile processors, and advanced sensor platforms. As a foundational technology, thin wafers bridge front-end fabrication with back-end packaging, underpinning the evolution of multi-chip module designs and heterogeneous integration strategies that define next-generation systems
Navigating the Major Technological, Supply Chain, and Regulatory Shifts Shaping the Thin Wafer Market Trajectory in 2025
Technological breakthroughs in advanced packaging are reshaping wafer processing and creating new pathways for device integration. Industry-leading techniques such as 2.5D CoWoS (Chip on Wafer on Substrate) and 3D Foveros stacking have moved from research prototypes to production lines, driving demand for wafers capable of withstanding through-silicon via formation and high-precision bonding. Concurrently, the development of gate-all-around transistor architectures at the 2nm node requires substrates with exceptional flatness and structural integrity to facilitate extreme ultraviolet lithography and ultrathin device layers.
Shifts in global supply chains have also accelerated as manufacturers respond to geopolitical pressures and tariff impacts. In the United States, the CHIPS and Science Act has spurred domestic wafer fabrication investments, while alternative hubs in India, Southeast Asia, and Eastern Europe are gaining traction to diversify dependencies. Companies are realigning logistics networks to mitigate exposure, strengthening regional ecosystems for raw materials, and optimizing lead times to sustain throughput under evolving trade policies.
At the same time, competitive dynamics are intensifying as China’s leading suppliers expand mature node capacity, particularly in the 200mm and 300mm segments. This structural shift is driving downward pricing pressures outside China, challenging legacy producers to innovate in process automation, yield optimization, and cost efficiencies to protect margin through a cyclical downturn and subsequent recovery phases.
Assessing the Broad Economic and Operational Consequences of United States Tariffs on Thin Wafer Production and Trade
The imposition of a 25% tariff on semiconductor imports by the United States has introduced significant cost headwinds for thin wafer production and downstream device assembly. Manufacturers sourcing high-purity silicon substrates and specialty materials from established East Asian suppliers now face higher landed costs, translating into elevated capital expenditure requirements for fab expansions and process upgrades. In response, many wafer fabs have begun insourcing precision slicing and thinning steps or relocating sensitive operations to domestic facilities to reduce tariff burdens and maintain production continuity.
Economic analyses indicate that these trade measures will have a cumulative impact extending beyond immediate input price hikes. Over a ten-year horizon, the U.S. economy could experience up to $1.4 trillion in lost GDP due to reduced manufacturing competitiveness and supply chain inefficiencies. The ripple effects include deferred capital investments, constrained R&D spending on next-generation substrates, and the potential reshoring of downstream assembly work into regions with lower or suspended tariff rates.
Operationally, the uncertainty surrounding tariff renewal and scope extensions has prompted strategic supply chain diversification. Leading wafer producers are establishing secondary procurement channels in regions with preferential trade agreements or tariff exemptions. Simultaneously, collaboration with equipment vendors to localize high-precision etching, grinding, and polishing machinery is gaining momentum, reducing dependency on imported toolsets subject to trade restrictions.
Analyzing Material, Size, Process, Application, and End-Use Dimensions to Reveal Critical Thin Wafer Market Dynamics
Material choice exerts a profound influence on both wafer performance and fabrication economics. Gallium arsenide substrates deliver superior electron mobility for RF and photonic devices, while silicon remains the cornerstone for mainstream logic, power, and MEMS applications. Decision-makers evaluate trade-offs between raw material cost, defect density, and compatibility with existing process flows to optimize overall throughput and device yield.
Wafer dimensions have evolved in concert with process node requirements and equipment capabilities. Early adoption of 125 mm wafers enabled niche RF applications, but the industry rapidly transitioned to 200 mm for analog, MEMS, and specialty devices before converging on 300 mm as the standard for high-volume digital and power substrates. Each form factor presents unique handling challenges in grinding, etching, and polishing, necessitating scalable process modules that can adapt across multiple wafer sizes without compromising surface finish or planarity.
Advanced thinning sequences integrate multiple unit operations. Dry etching techniques deliver sub-micron uniformity, while wet etching offers cost-effective bulk removal prior to final mechanical thinning. Grinding operations balance coarse stock removal with fine refinement stages, including specialized TAIKO workflows, to achieve target thicknesses below 50 µm. Temporary bonding and debonding solutions support wafer-on-wafer stacking for 2.5D and 3D packaging, enabling heterogeneous integration of compute, memory, and sensor dies.
Application requirements further segment the market. Flexible electronics demand ultra-thin, bend-resistant substrates, whereas photonic and power device manufacturers emphasize high-resistivity and low-thermal-expansion materials. End-use industries from automotive safety systems to telecommunications infrastructure prioritize wafer reliability and cleanroom compatibility to meet stringent quality standards.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Thin Wafer market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Material Type
- Wafer Size
- Manufacturing Process
- Application
- End-Use Industry
Dissecting Regional Drivers and Regulatory Influences Across Americas, EMEA, and Asia-Pacific Thin Wafer Markets
In the Americas, aggressive federal incentives under the CHIPS and Science Act have catalyzed expansion of domestic wafer fabrication capacity. States such as Arizona, Texas, and New York now host new facilities equipped for advanced thinning, etching, and bonding operations, aiming to reduce reliance on imported substrates. This policy-driven investment is complemented by significant private capital earmarked for end-to-end semiconductor ecosystems, supporting OEMs, foundries, and advanced packaging firms in proximity to wafer suppliers. As a result, North America has emerged as one of the fastest-growing regions for thin wafer demand, particularly in high-performance computing and defense applications.
Across Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, a diverse set of drivers shape wafer consumption patterns. Germany, France, and the United Kingdom lead industrial automation and automotive electronics programs that require specialized thin wafers for microcontrollers and power modules. Concurrently, regional sustainability mandates are accelerating the adoption of low-defect, energy-efficient processes, driving up demand for wafers manufactured with closed-loop etching systems and solvent reclamation technologies. Local wafer producers are forging partnerships with device manufacturers to embed environmental compliance at the substrate level.
Asia-Pacific continues to dominate volume, supported by scale advantages in China, Taiwan, South Korea, and Japan. China’s “Made in China 2025” initiative has amplified investments in mature node capacity, adding significant 200 mm and 300 mm throughput. Taiwan and South Korea remain at the forefront of research on next-generation wafer architectures and high-yield thinning techniques, while Japan focuses on material specialization and equipment innovation. Together, these dynamics position the region as the primary growth engine for thin wafer production globally.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Thin Wafer market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Profiling Leading Thin Wafer Manufacturers to Highlight Competitive Strategies and Technological Leadership
Samsung Electronics has established itself as a leader in ultra-thin wafer production, leveraging proprietary laser dicing and stress-relief techniques to achieve consistent yields at thicknesses down to 30 µm. Its vertical integration across design, fabrication, and packaging lines enables rapid iteration of process recipes and deployment of cutting-edge 2.5D and 3D IC solutions for AI accelerators and mobile SoCs.
SK Siltron, GlobalWafers, Shin-Etsu Chemical, and SUMCO Corporation collectively control the lion’s share of global thin wafer capacity. These suppliers differentiate through material purity, wafer flatness, and volume scalability. SK Siltron emphasizes advanced polishing chemistries for defect minimization, while GlobalWafers focuses on integrated supply chains to reduce lead times. Shin-Etsu and SUMCO invest heavily in R&D partnerships with foundries to co-develop next-generation substrates tailored for extreme ultraviolet lithography and advanced packaging.
Simultaneously, domestic champions in China and emerging players in Southeast Asia are gaining momentum by leveraging government subsidies and local market access. These companies compete aggressively on pricing and regional logistics, pushing established producers to enhance automation, yield analytics, and service offerings to preserve market share outside their home territories.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Thin Wafer market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- 3M Company
- Aixtron SE
- Atecom Technology Co., Ltd.
- Brewer Science, Inc.
- Chipmetrics Oy
- DISCO Corporation
- EV Group
- Globalwafers Co., Ltd.
- Hangzhou Semiconductor Wafer Co., Ltd .
- Hemlock Semiconductor Corporation
- KYOCERA AVX Components Corporation
- LDK Solar High-Tech Co., Ltd.
- LINTEC Corporation
- MEMC Electronic Materials, Inc.
- Okmetic Oy
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Siltronic AG
- Siltronix Silicon Technologies
- SK Siltron Co., Ltd.
- Soitec
- SPTS Technologies Ltd.
- Sumco Corporation
- SÜSS MicroTec SE
- UniversityWafer, Inc.
- Virginia Semiconductor Inc.
- Wafer World Inc.
Strategic Imperatives for Industry Leaders to Capitalize on Opportunities and Mitigate Risks in Thin Wafer Manufacturing
To secure a competitive edge, industry leaders should prioritize investment in advanced packaging research, particularly in 3D stacking and through-silicon via technologies. By co-innovating with equipment suppliers and materials partners, wafer producers can develop process toolsets optimized for extreme thinness and functional integration, unlocking new application segments in high-bandwidth memory and AI inference accelerators.
Supply chain resilience must be enhanced through geographic diversification and strategic partnerships. Establishing backup sourcing arrangements in tariff-friendly jurisdictions and building regional micro-ledgers for material provenance can mitigate the operational risks of sudden trade policy changes. Collaborating with logistics providers to implement real-time tracking and dynamic routing will further reinforce continuity and cost efficiency.
Finally, leveraging government programs and sustainability frameworks can unlock both financial incentives and market differentiation. Aligning process upgrades with environmental certifications, circular economy initiatives, and workforce development grants will not only reduce long-term operational costs but also strengthen corporate reputations among OEMs prioritizing green supply chains and ethical sourcing practices.
Detailing the Rigorous Research Approach Employed to Ensure Robust and Reliable Thin Wafer Market Intelligence
The research methodology underpinning this analysis combined extensive secondary research with targeted primary interviews to ensure depth and accuracy. Proprietary databases and peer-reviewed journals provided foundational insights into material properties, wafer dimensions, and process innovations, while public financial disclosures and equipment vendor roadmaps informed capital investment trends.
Primary data was collected through structured interviews with wafer fab operations managers, packaging engineers, and supply chain executives. These conversations yielded real-world perspectives on tool deployment, yield challenges, and the operational impact of trade policies. Responses were anonymized and aggregated to preserve confidentiality while enabling robust cross-validation of qualitative observations.
Quantitative data underwent a rigorous triangulation process, reconciling shipment volumes, capacity utilization figures, and pricing movements. The segmentation framework was validated through iterative feedback loops with industry subject-matter experts, ensuring that material type, wafer size, manufacturing process stage, application, and end-use categories accurately reflect market realities. All data points were subjected to quality checks to minimize bias and uphold research integrity.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Thin Wafer market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Thin Wafer Market, by Material Type
- Thin Wafer Market, by Wafer Size
- Thin Wafer Market, by Manufacturing Process
- Thin Wafer Market, by Application
- Thin Wafer Market, by End-Use Industry
- Thin Wafer Market, by Region
- Thin Wafer Market, by Group
- Thin Wafer Market, by Country
- United States Thin Wafer Market
- China Thin Wafer Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 17]
- List of Tables [Total: 1272 ]
Summarizing Core Findings to Illuminate Future Directions and Strategic Priorities in the Thin Wafer Market
This report has illuminated the multifaceted dynamics of the thin wafer market, from the technical breakthroughs enabling sub-50 µm substrates to the seismic supply chain shifts driven by geopolitical tensions and tariff policies. By examining material and dimensional segmentation, as well as processing workflows spanning etching, grinding, and bonding, the analysis highlights the critical interplay between fab capabilities and advanced packaging requirements.
Regional insights underscore the emergence of the Americas as a revitalized hub of domestic wafer production, the steady advance of EMEA in specialized automotive and industrial applications, and Asia-Pacific’s sustained dominance through scale and state-backed capacity expansions. Company profiles reveal how established suppliers maintain leadership through vertical integration and R&D partnerships, even as new entrants leverage policy support to gain market share.
In this environment of rapid technological and regulatory change, industry stakeholders must remain agile, investing in innovation while fortifying supply chain resilience. The strategic imperatives and recommendations outlined herein provide a clear roadmap for decision-makers seeking to navigate risks, capture emerging opportunities, and position their organizations for sustainable growth in the evolving thin wafer landscape.
Engage with Ketan Rohom to Secure Comprehensive Thin Wafer Market Analysis for Strategic Decision-Making and Growth
To explore how these insights can inform your strategic initiatives and gain immediate access to this in-depth Thin Wafer market research report, please reach out to Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing at 360iResearch. Ketan specializes in guiding stakeholders through the data, helping you align investment decisions with emerging trends in wafer innovation and supply chain dynamics. By engaging directly with Ketan, you can secure tailored consulting sessions, review detailed appendices on regional and technology analyses, and receive customized pricing options. Don’t miss this opportunity to leverage cutting-edge intelligence and position your organization at the forefront of the thin wafer market’s next phase of growth. Contact Ketan today to begin transforming insights into action.

- How big is the Thin Wafer Market?
- What is the Thin Wafer Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




