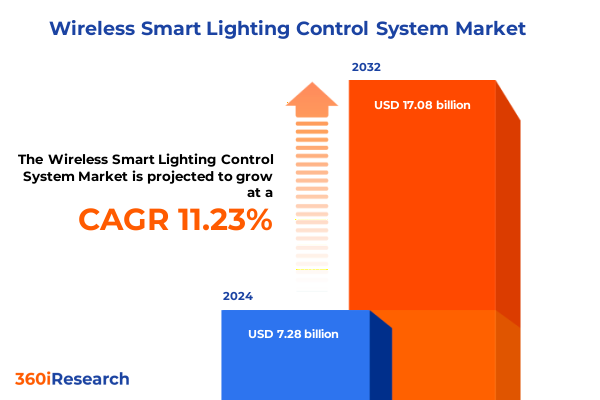
The Wireless Smart Lighting Control System Market size was estimated at USD 8.08 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 8.97 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 11.28% to reach USD 17.08 billion by 2032.
Executive overview of wireless smart lighting control systems as a strategic lever for intelligent, efficient, and resilient built environments
Wireless smart lighting control systems sit at the intersection of energy management, digital infrastructure, and occupant experience. By combining networked luminaires, sensors, controllers, and cloud-based management platforms, these systems enable granular control of lighting based on occupancy, daylight levels, time schedules, and space usage patterns. The result is a move away from static, manually operated installations toward adaptive environments that respond dynamically to how people actually use buildings and urban spaces.
This transition is unfolding against a backdrop of intensifying pressure to reduce energy consumption, decarbonize building operations, and comply with more stringent codes and standards. At the same time, organizations are rethinking their real estate portfolios in light of hybrid work, evolving safety expectations, and the growing value of real-time data about space utilization. Wireless architectures are particularly well suited to this moment: they offer deployment flexibility, lower disruption during retrofits, and faster commissioning compared with traditional wired control networks.
As a result, wireless smart lighting control systems are no longer viewed purely as a means of dimming lights or meeting minimum regulatory requirements. They are increasingly recognized as foundational infrastructure for smart buildings and smart cities, providing sensing and connectivity that can support a wide range of applications beyond illumination, from environmental monitoring to indoor navigation and asset tracking. This executive summary synthesizes the most important technology, policy, and competitive developments shaping the current landscape, and highlights how segmentation by offering, communication technology, installation type, lighting application, end-use sector, and region influences strategic choices for market participants.
Transformative technology, regulatory, and user-experience shifts reshaping the wireless smart lighting control system competitive landscape
The landscape for wireless smart lighting control is undergoing a series of transformative shifts that reach far beyond incremental product upgrades. One major change is the migration from isolated, room-level controls to fully networked, software-defined systems. In place of simple wall switches and stand-alone sensors, modern deployments emphasize addressable luminaires, intelligent drivers, and edge controllers linked to management platforms that run advanced scheduling, analytics, and optimization routines. This architectural evolution allows lighting to operate as a responsive digital service rather than a fixed electrical asset.
Simultaneously, the rise of data-driven building operations is reshaping expectations about what lighting controls should deliver. Occupancy and ambient light sensors, when combined with wireless communication technologies and cloud analytics, provide continuous streams of information about how spaces are used throughout the day. Facility teams increasingly expect to extract space-utilization insights, safety alerts, and predictive maintenance signals from the same infrastructure that controls illumination. This convergence of control and insight is driving greater emphasis on scalable software platforms, open application programming interfaces, and integration with building management systems, access control, and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning.
Another powerful shift involves the growing importance of interoperability and cybersecurity. As buildings add more connected devices, owners are wary of vendor lock-in and fragmented systems that are expensive to maintain. In response, leading providers are prioritizing support for widely adopted wireless communication technologies, alignment with emerging interoperability frameworks, and robust security-by-design practices. At the same time, business models are evolving from one-time equipment sales toward recurring revenue offerings built around software subscriptions, remote monitoring, and performance-based service contracts. Together, these technology and commercial changes are redefining success factors in the market and rewarding companies that can combine reliable hardware with secure, interoperable, and analytically rich software ecosystems.
Cumulative impact of evolving 2025 United States tariff policies on wireless smart lighting hardware, electronics, supply chains, and margins
The cumulative impact of the United States tariff environment in 2025 is reshaping supply chains, cost structures, and sourcing strategies for wireless smart lighting control systems. A universal baseline tariff on most imported goods, layered with additional country- and product-specific measures, has altered the economics of controllers, drivers, gateways, sensors, and communication modules that rely heavily on global electronics manufacturing. Tariff exposure now spans key components such as microcontrollers, wireless chipsets, power electronics, and copper-intensive electrical parts, making bill-of-materials planning and supplier selection strategic rather than purely tactical decisions.
One of the most significant developments is the stepped increase in tariffs on semiconductors and certain electrical components sourced from abroad, particularly from China. United States policy has raised the tariff rate on semiconductors from earlier levels to around 50 percent by 2025, explicitly targeting legacy chip capacity used in a wide variety of electronics. In parallel, electrical components and equipment imported from China have been subject to an evolving mix of Section 301 and emergency measures, which initially pushed combined tariff rates sharply higher before a mid-2025 trade understanding temporarily eased them to roughly 30 percent for many items. These measures come on top of a universal “reciprocal” baseline tariff of around 10 percent on most imports, as well as elevated duties on several countries with which the United States has significant trade imbalances. More recently, separate actions have imposed higher tariffs on copper-intensive products and semi-finished copper components, directly affecting cables, busbars, and other electrical infrastructure needed in lighting projects.
For wireless smart lighting control vendors, these policies translate into higher and more volatile input costs, particularly for radio modules, semiconductor-based drivers, and control gear that were previously sourced almost exclusively from Chinese and other Asian suppliers. Some relief comes from exemptions or exclusions in certain electronics categories, but these are narrow and often temporary, complicating long-term planning. As a result, manufacturers are accelerating diversification of their supplier base across multiple Asian countries, exploring greater use of contract manufacturing in the Americas and Europe, and considering partial reshoring of final assembly for high-value control products.
Downstream, integrators and end customers experience these tariff dynamics as increased price pressure and uncertainty in project budgeting. Larger building owners are responding by negotiating multi-year framework agreements, bundling lighting controls with broader smart-building investments, and placing greater emphasis on solutions that deliver verifiable energy and maintenance savings capable of offsetting higher upfront hardware costs. In parallel, vendors are redesigning products to reduce single-country dependence, standardizing platforms around more modular components that can be sourced from different regions, and emphasizing wireless retrofit solutions that minimize labour-intensive wiring changes. Collectively, the 2025 tariff environment is acting as both a headwind, through elevated costs, and a catalyst, by prompting the sector to build more resilient and regionally balanced supply chains for critical lighting control electronics.
Key segmentation insights revealing how offerings, communication technologies, installations, lighting types, and end uses shape adoption pathways
Understanding the structure of the wireless smart lighting control market requires a close look at how offerings are organized and where value is created. At the core are hardware elements that include controllers, drivers, gateways, and sensors. Controllers and drivers embedded in luminaires execute dimming, color tuning, and switching based on commands from higher-level systems. Gateways act as bridges between local wireless networks and enterprise applications or cloud platforms, ensuring that lighting devices can be managed, updated, and monitored at scale. Sensors for occupancy, ambient light, and sometimes environmental parameters provide the data that allows systems to operate intelligently. Around this hardware backbone, services such as consulting and integration, installation and commissioning, and ongoing maintenance and support are becoming increasingly important as customers demand turnkey solutions rather than individual products. Complementing both layers are software analytics and management platforms that provide dashboards, rule engines, alarm management, and integration interfaces, turning raw data into actionable insights about energy use, comfort, and space utilization.
Communication technologies further differentiate solution approaches. Bluetooth is often used for room-level or small-area control, especially in retrofit scenarios where ease of installation and familiarity to installers are paramount. ZigBee and other radio-frequency approaches play a prominent role in large-scale, mesh-based networks where robust routing and low-power operation are critical. Wi-Fi can provide convenient connectivity for gateways and certain luminaires in environments where existing wireless infrastructure is already strong, enabling quick integration with cloud services and remote management tools. The choice of communication technology is rarely purely technical; it reflects trade-offs among range, latency, security, commissioning complexity, and compatibility with existing building systems.
Installation type is another axis along which the market organizes itself. New construction projects allow for holistic design that tightly integrates luminaires, controls, and building management systems from the outset. Here, wireless solutions compete with or complement wired controls, with the decision often hinging on project scale, architectural constraints, and owner preferences. Retrofit installations, by contrast, must contend with existing wiring, tenant occupancy, and budget constraints. Wireless smart lighting control offers a compelling proposition in these cases, enabling upgrades with minimal disruption to ceilings and walls, shorter installation windows, and opportunities to stage investments across different zones or floors.
Lighting type and application context significantly shape requirements. Indoor lighting spans ambient, task, and accent applications in offices, retail spaces, schools, hospitals, and homes, each with distinct needs around comfort, visual acuity, and aesthetics. Outdoor lighting encompasses street and roadway illumination, area and site lighting, and parking and garage environments, where durability, wide-area networking, and integration with traffic or public-safety systems are paramount. Industrial and hazardous lighting applications impose stringent demands for reliability, robustness, and compliance with safety regulations. Architectural and landscape lighting emphasizes precise control, color quality, and coordination across complex scenes, while emergency and security lighting must ensure code-compliant performance under fault conditions and integrate with life-safety systems.
End-use sectors and sales channels complete the segmentation picture. Commercial applications in offices, retail, hospitality, healthcare, and education typically require sophisticated control strategies, integration with multiple building systems, and centralized management across large portfolios. Industrial use in logistics, manufacturing, oil and gas, and pharmaceuticals prioritizes uptime, process integration, and ruggedized equipment. Infrastructure projects, such as transportation hubs and public spaces, demand scalability, long life cycles, and often public-sector procurement expertise, while residential settings focus more on ease of use, integration with consumer smart-home ecosystems, and appealing user interfaces. Offline sales through distributors, wholesalers, and system integrators remain vital for complex projects that rely on engineering support and local relationships. At the same time, online sales via company websites and third-party e-commerce platforms are gaining traction for standardized components, retrofit kits, and smaller installations, enabling faster specification and purchase cycles for both professionals and advanced do-it-yourself customers.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Wireless Smart Lighting Control System market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Offering
- Communication Technology
- Installation
- Lighting Type
- End Use
- Sales Channel
Regional dynamics across the Americas, Europe, Middle East, Africa, and Asia-Pacific defining diverse trajectories for wireless lighting control
Regional dynamics add another layer of nuance to the wireless smart lighting control landscape. In the Americas, the United States remains a focal point due to stringent energy codes, aggressive corporate sustainability targets, and strong adoption of cloud-based building management. Wireless controls are frequently deployed as part of broader modernization programs that address heating, cooling, access control, and security, reflecting a holistic view of the smart building. Canada shares many of these drivers, with additional emphasis on green building certifications and high-performance envelopes that benefit from advanced daylight and occupancy-based control. Across Latin America, economic conditions and infrastructure variability can slow large-scale adoption, yet urban redevelopment, hospitality, and premium residential projects are increasingly turning to wireless lighting control to deliver modern experiences with lower installation disruption.
In Europe, policy frameworks related to building performance, ecodesign, and carbon reduction are powerful catalysts for advanced lighting controls. Building owners often face mandatory upgrades when renovating or changing a space’s use, which encourages the adoption of sophisticated control strategies and integrated management platforms. Wireless systems play a growing role in historic buildings and dense urban environments where running new cables is difficult or expensive. The Middle East combines ambitious new-build mega-projects with harsh environmental conditions, leading to demand for robust, highly integrated lighting solutions that can tolerate heat and dust while delivering striking visual effects in hospitality, retail, and public spaces. In Africa, market development is more uneven, yet there is strong potential for leapfrogging to wireless controls in commercial and institutional facilities where intermittent power supply and limited wiring infrastructure make flexible solutions attractive.
Asia-Pacific brings together some of the world’s most advanced smart city initiatives and the largest volume of new construction. Markets such as China, Japan, and South Korea continue to push the boundaries of dense, connected urban environments, where lighting networks share infrastructure with surveillance, environmental sensing, and mobility services. At the same time, China’s role as a major manufacturing base for drivers, luminaires, sensors, and communication modules means that developments in its industrial policy and its trade relationship with the United States have global repercussions for component pricing and availability. Elsewhere in the region, India and Southeast Asian countries are prioritizing efficient street and roadway lighting upgrades, commercial building retrofits, and modern industrial parks, often with public funding or public-private partnerships. Across the region, wireless smart lighting control is well aligned with rapid urbanization, technology-savvy building developers, and governments seeking to curb electricity demand without compromising economic growth.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Wireless Smart Lighting Control System market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Strategic directions of leading wireless smart lighting control system providers as they compete on platforms, services, and innovation
The competitive landscape for wireless smart lighting control systems is shaped by a mix of established electrical and building technology companies and more specialized control and software providers. Large multinational lighting manufacturers have expanded their portfolios beyond luminaires to include integrated drivers, sensors, gateways, and cloud-based management platforms, positioning themselves as end-to-end solution partners for building owners and cities. In parallel, major building automation and electrical distribution firms are embedding lighting control more deeply into their energy management, safety, and power distribution offerings, emphasizing interoperability with heating and cooling, access control, and microgrid systems.
Specialist players focused on wireless control and advanced software are influencing the market by pushing innovation in user experience, analytics, and integration frameworks. These companies often concentrate on highly scalable platforms that can manage hundreds of thousands of nodes, support multiple wireless communication technologies, and expose open programming interfaces for third-party application developers. Their solutions may be designed to be hardware-agnostic, enabling them to work with luminaires and drivers from a variety of manufacturers and thereby appeal to customers who want to avoid vendor lock-in.
Across the competitive spectrum, several strategic themes stand out. One is the shift toward platform-centric business models in which hardware provides the installed base, but long-term value is captured through software subscriptions, remote monitoring services, and data-enabled applications. Another is the emphasis on verticalized offerings tailored to specific sectors such as healthcare, logistics, or hospitality, which require domain knowledge about workflows, regulations, and user expectations. Cybersecurity and privacy are also emerging as points of differentiation, with customers increasingly seeking evidence of secure development practices, regular firmware updates, and compliance with relevant standards. Finally, partnerships and ecosystems are becoming essential: lighting companies are aligning with cloud providers, property technology platforms, and energy service firms to create integrated solutions that can be specified and deployed at scale across global building portfolios.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Wireless Smart Lighting Control System market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- Signify N.V.
- Lutron Electronics Co., Inc.
- ams-OSRAM AG
- Delta Electronics, Inc.
- Legrand S.A.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Johnson Controls International plc
- Infineon Technologies AG
- Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
- GE Lighting (A Savant Company)
- Panasonic Holdings Corporation
- Eaton Corporation plc
- AMO Smart Lighting
- Green Ideas Technology
- LITE-ON Technology Corporation
- Gainwise Technology Co., Ltd.
- LinkCom Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
- Wentai Technology Corp.
- Siemens AG
- Glamox AS
- Yeelight MY
- TJ2 Lighting
- CACKLE Collection Co., Ltd.
- Casambi Technologies Oy / Inc.
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Itron, Inc.
- K-Source Technology Ltd.
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- Schneider Electric SE
- Texas Instruments Incorporated
Actionable recommendations enabling manufacturers, technology partners, and end users to navigate disruption and unlock new lighting control value
In light of both structural technology shifts and the 2025 tariff environment, industry leaders need to pursue strategies that strengthen resilience while unlocking new sources of value. A first priority is to deepen supply chain diversification for critical components such as drivers, controllers, wireless modules, and sensors. Sourcing from multiple regions, qualifying alternative component designs, and building modular hardware platforms that can accommodate different chipsets or radio technologies help reduce exposure to abrupt policy changes. At the same time, companies should invest in detailed bill-of-materials mapping to understand which parts of their portfolios carry the highest tariff and logistics risk and to inform targeted redesign efforts.
Equally important is a renewed focus on software and services as primary value drivers. By enhancing management platforms with advanced analytics, intuitive interfaces, and robust integration capabilities, vendors can justify premium pricing and build recurring revenue streams that are less sensitive to hardware cost volatility. Delivering high-quality consulting, integration, installation, and maintenance services further differentiates offerings, especially for complex commercial, industrial, and infrastructure projects. Industry leaders should also prioritize cybersecurity and interoperability certifications, as these factors increasingly influence procurement decisions among sophisticated owners and facility managers.
On the market-development side, stakeholders can accelerate adoption by tailoring go-to-market strategies to the realities of each segment. For new construction, aligning closely with architects, engineers, and developers early in the design process can position wireless controls as standard infrastructure rather than optional add-ons. For retrofits, simplified upgrade paths, pre-configured kits, and financing models that link payments to energy and maintenance savings can help overcome budget and disruption concerns. Collaborating with utilities, energy service companies, and government programs to align with incentive structures and regulatory requirements can further expand opportunities. Ultimately, leaders who combine technical excellence with thoughtful risk management and customer-centric business models will be best positioned to navigate uncertainty and capture emerging demand.
Robust research methodology integrating primary insights, policy analysis, and technology assessment to deliver decision-ready lighting intelligence
The insights synthesized in this executive summary are grounded in a research approach that combines multiple complementary streams of evidence. At its foundation is extensive secondary analysis of policy documents, technical standards, tariff schedules, building codes, and public information from manufacturers, technology providers, utilities, and government agencies. This material provides critical context on regulatory drivers, technology roadmaps, and trade conditions that shape the environment in which wireless smart lighting control systems are specified and deployed.
Building on this foundation, the research incorporates structured interviews and discussions with stakeholders across the value chain, including component suppliers, luminaire manufacturers, system integrators, software platform providers, consultants, facility managers, and building owners. These conversations illuminate practical challenges encountered during design, installation, commissioning, and operation, as well as emerging best practices for integrating lighting controls with other building systems. They also provide real-world perspectives on how tariffs, supply constraints, and evolving procurement models are influencing project timelines, vendor selection, and solution architecture.
The research process further employs systematic analysis of case studies, pilot projects, and documented deployments in commercial, industrial, infrastructure, and residential settings across the Americas, Europe, the Middle East, Africa, and Asia-Pacific. Examining both successful and challenging implementations helps identify patterns related to communication technology choices, installation types, and application-specific requirements. Throughout, the methodology emphasizes triangulation, cross-checking insights from different sources to ensure consistency and reduce bias. The result is a coherent, decision-oriented view of the market that connects high-level policy and technology trends with on-the-ground realities faced by organizations implementing wireless smart lighting control systems today.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Wireless Smart Lighting Control System market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Wireless Smart Lighting Control System Market, by Offering
- Wireless Smart Lighting Control System Market, by Communication Technology
- Wireless Smart Lighting Control System Market, by Installation
- Wireless Smart Lighting Control System Market, by Lighting Type
- Wireless Smart Lighting Control System Market, by End Use
- Wireless Smart Lighting Control System Market, by Sales Channel
- Wireless Smart Lighting Control System Market, by Region
- Wireless Smart Lighting Control System Market, by Group
- Wireless Smart Lighting Control System Market, by Country
- United States Wireless Smart Lighting Control System Market
- China Wireless Smart Lighting Control System Market
- Taiwan Wireless Smart Lighting Control System Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 19]
- List of Tables [Total: 2415 ]
Integrated conclusion on the strategic role of wireless smart lighting control systems in future-ready, efficient, and human-centric environments
As buildings and cities accelerate their transition toward digital, data-rich, and decarbonized operations, wireless smart lighting control systems are emerging as a foundational layer of infrastructure. They transform luminaires from static endpoints into intelligent nodes that sense occupancy, daylight, and environmental conditions, enabling more efficient use of energy and better experiences for occupants. By eliminating much of the complexity and disruption associated with traditional wired control networks, wireless architectures open compelling pathways for retrofitting the vast existing building stock, where most energy and carbon savings potential resides.
The broader operating environment, however, is increasingly complex. Rapid innovation in communication technologies, software platforms, and integration frameworks requires careful architectural choices to avoid fragmentation and lock-in. Evolving tariff regimes and geopolitical tensions introduce additional uncertainty around component costs and availability, prompting the industry to rethink long-standing sourcing and manufacturing assumptions. At the same time, end users are seeking not just compliance with codes and standards, but robust, secure systems that provide actionable insights about space utilization, safety, and asset performance.
Against this backdrop, success in the wireless smart lighting control market will favor organizations that view lighting not simply as a commodity, but as a strategic digital asset. Vendors that can combine resilient supply chains, interoperable hardware, sophisticated analytics, and high-quality services will be well positioned to support the next generation of smart buildings and urban spaces. For decision-makers on the buy side, understanding how offerings, communication technologies, installation types, lighting applications, and regional conditions intersect is essential to crafting roadmaps that deliver reliable performance, financial returns, and long-term flexibility. The decisions made today about wireless lighting controls will shape the character and capabilities of built environments for years to come.
Call to action for engaging with Ketan Rohom to access in-depth wireless smart lighting control system market intelligence and guidance
Wireless smart lighting control is no longer a niche upgrade; it is becoming an operational necessity for organizations seeking resilience, efficiency, and better user experiences. However, the complexity of technologies, shifting tariff regimes, and rapidly evolving standards make it difficult to decide where and how to invest. To move from curiosity to confident action, decision-makers benefit from a structured, vendor-neutral view of the ecosystem, grounded in current policy conditions and real-world deployment practices.
For leaders who want to go deeper than this executive summary, the full market intelligence report offers a detailed breakdown of offerings, communication technologies, installation scenarios, lighting types, end-use sectors, and regional dynamics. It also examines tariff exposure across the hardware bill of materials, evaluates strategic moves by key providers, and provides scenario-based guidance to help organizations stress-test their investment roadmaps.
Engaging directly with Ketan Rohom, Associate Director, Sales & Marketing, allows stakeholders to align the report with their specific objectives, whether they are evaluating product strategy, planning large-scale retrofits, or benchmarking competitive positioning. By discussing your priorities with him through corporate contact channels, you can determine the most suitable license type, explore options for analyst briefings or workshops, and ensure your teams have the insight required to translate market complexity into practical, revenue-generating decisions.

- How big is the Wireless Smart Lighting Control System Market?
- What is the Wireless Smart Lighting Control System Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




